| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6480864 | 1428772 | 2017 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
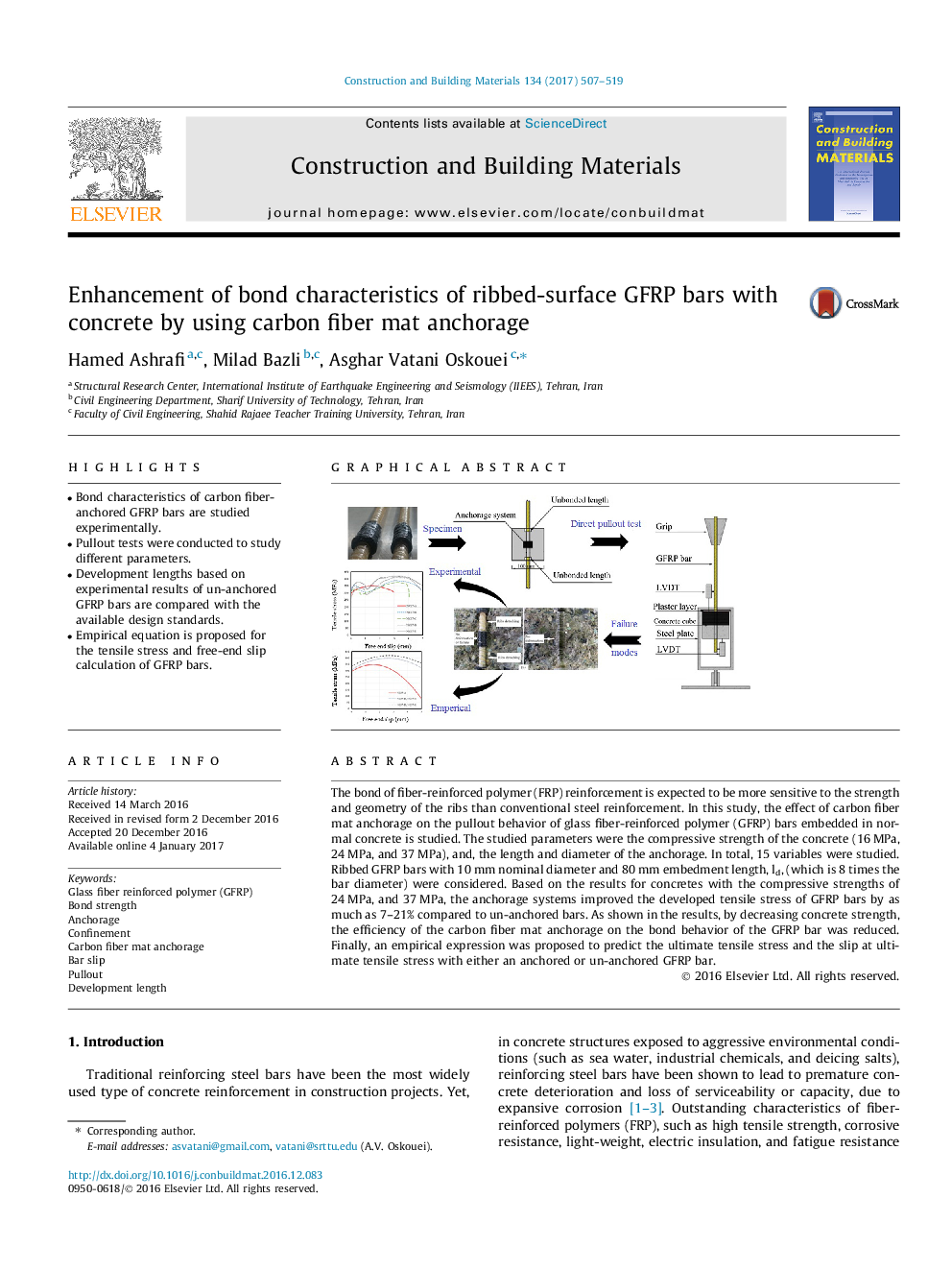
- Bond characteristics of carbon fiber-anchored GFRP bars are studied experimentally.
- Pullout tests were conducted to study different parameters.
- Development lengths based on experimental results of un-anchored GFRP bars are compared with the available design standards.
- Empirical equation is proposed for the tensile stress and free-end slip calculation of GFRP bars.
The bond of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement is expected to be more sensitive to the strength and geometry of the ribs than conventional steel reinforcement. In this study, the effect of carbon fiber mat anchorage on the pullout behavior of glass fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP) bars embedded in normal concrete is studied. The studied parameters were the compressive strength of the concrete (16Â MPa, 24Â MPa, and 37Â MPa), and, the length and diameter of the anchorage. In total, 15 variables were studied. Ribbed GFRP bars with 10Â mm nominal diameter and 80Â mm embedment length, ld, (which is 8 times the bar diameter) were considered. Based on the results for concretes with the compressive strengths of 24Â MPa, and 37Â MPa, the anchorage systems improved the developed tensile stress of GFRP bars by as much as 7-21% compared to un-anchored bars. As shown in the results, by decreasing concrete strength, the efficiency of the carbon fiber mat anchorage on the bond behavior of the GFRP bar was reduced. Finally, an empirical expression was proposed to predict the ultimate tensile stress and the slip at ultimate tensile stress with either an anchored or un-anchored GFRP bar.
169
Journal: Construction and Building Materials - Volume 134, 1 March 2017, Pages 507-519