| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9942504 | 1573257 | 2005 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
عنوان انگلیسی مقاله ISI
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia Due to Insulin Antibodies against Therapeutic Human Insulin: Treatment with Double Filtration Plasmapheresis and Prednisolone
دانلود مقاله + سفارش ترجمه
دانلود مقاله ISI انگلیسی
رایگان برای ایرانیان
کلمات کلیدی
موضوعات مرتبط
علوم پزشکی و سلامت
پزشکی و دندانپزشکی
کاردیولوژی و پزشکی قلب و عروق
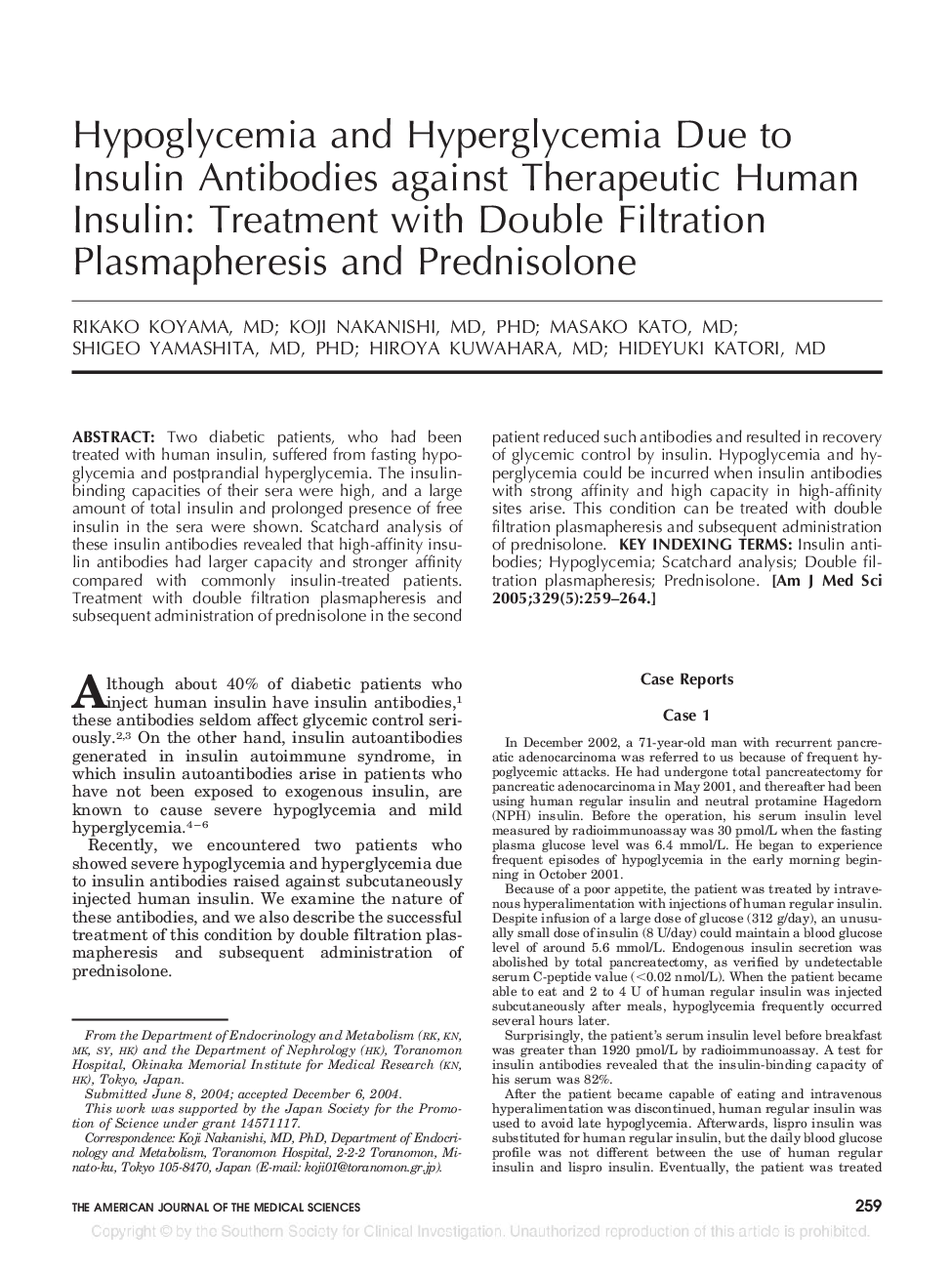
پیش نمایش صفحه اول مقاله
چکیده انگلیسی
Two diabetic patients, who had been treated with human insulin, suffered from fasting hypoglycemia and postprandial hyperglycemia. The insulin-binding capacities of their sera were high, and a large amount of total insulin and prolonged presence of free insulin in the sera were shown. Scatchard analysis of these insulin antibodies revealed that high-affinity insulin antibodies had larger capacity and stronger affinity compared with commonly insulin-treated patients. Treatment with double filtration plasmapheresis and subsequent administration of prednisolone in the second patient reduced such antibodies and resulted in recovery of glycemic control by insulin. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia could be incurred when insulin antibodies with strong affinity and high capacity in high-affinity sites arise. This condition can be treated with double filtration plasmapheresis and subsequent administration of prednisolone.
ناشر
Database: Elsevier - ScienceDirect (ساینس دایرکت)
Journal: The American Journal of the Medical Sciences - Volume 329, Issue 5, May 2005, Pages 259-264
Journal: The American Journal of the Medical Sciences - Volume 329, Issue 5, May 2005, Pages 259-264
نویسندگان
Rikako MD, Masako MD, Shigeo MD, PHD, Koji MD, PHD, Hiroya MD, Hideyuki MD,