| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229405 | 1495229 | 2015 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
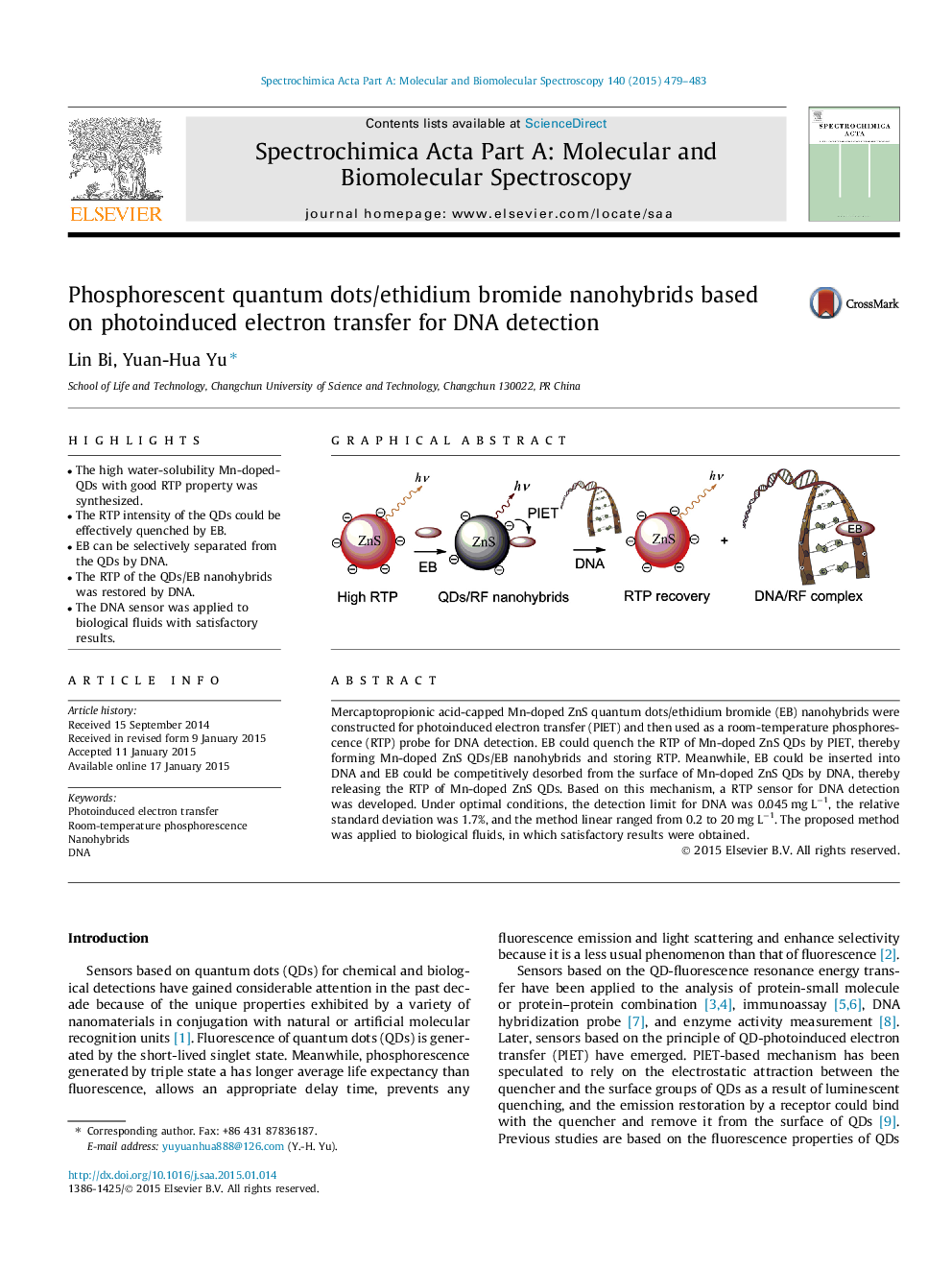
• The high water-solubility Mn-doped-QDs with good RTP property was synthesized.
• The RTP intensity of the QDs could be effectively quenched by EB.
• EB can be selectively separated from the QDs by DNA.
• The RTP of the QDs/EB nanohybrids was restored by DNA.
• The DNA sensor was applied to biological fluids with satisfactory results.
Mercaptopropionic acid-capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots/ethidium bromide (EB) nanohybrids were constructed for photoinduced electron transfer (PIET) and then used as a room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) probe for DNA detection. EB could quench the RTP of Mn-doped ZnS QDs by PIET, thereby forming Mn-doped ZnS QDs/EB nanohybrids and storing RTP. Meanwhile, EB could be inserted into DNA and EB could be competitively desorbed from the surface of Mn-doped ZnS QDs by DNA, thereby releasing the RTP of Mn-doped ZnS QDs. Based on this mechanism, a RTP sensor for DNA detection was developed. Under optimal conditions, the detection limit for DNA was 0.045 mg L−1, the relative standard deviation was 1.7%, and the method linear ranged from 0.2 to 20 mg L−1. The proposed method was applied to biological fluids, in which satisfactory results were obtained.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 140, 5 April 2015, Pages 479–483