| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230759 | 1495256 | 2013 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• The structures of aniline and phenylenediamines were optimized at the DFT and MP2 levels.
• The vibrational wavenumbers of the molecules were calculated at the DFT level.
• Vibrational assignments were provided by combining experimental and theoretical data.
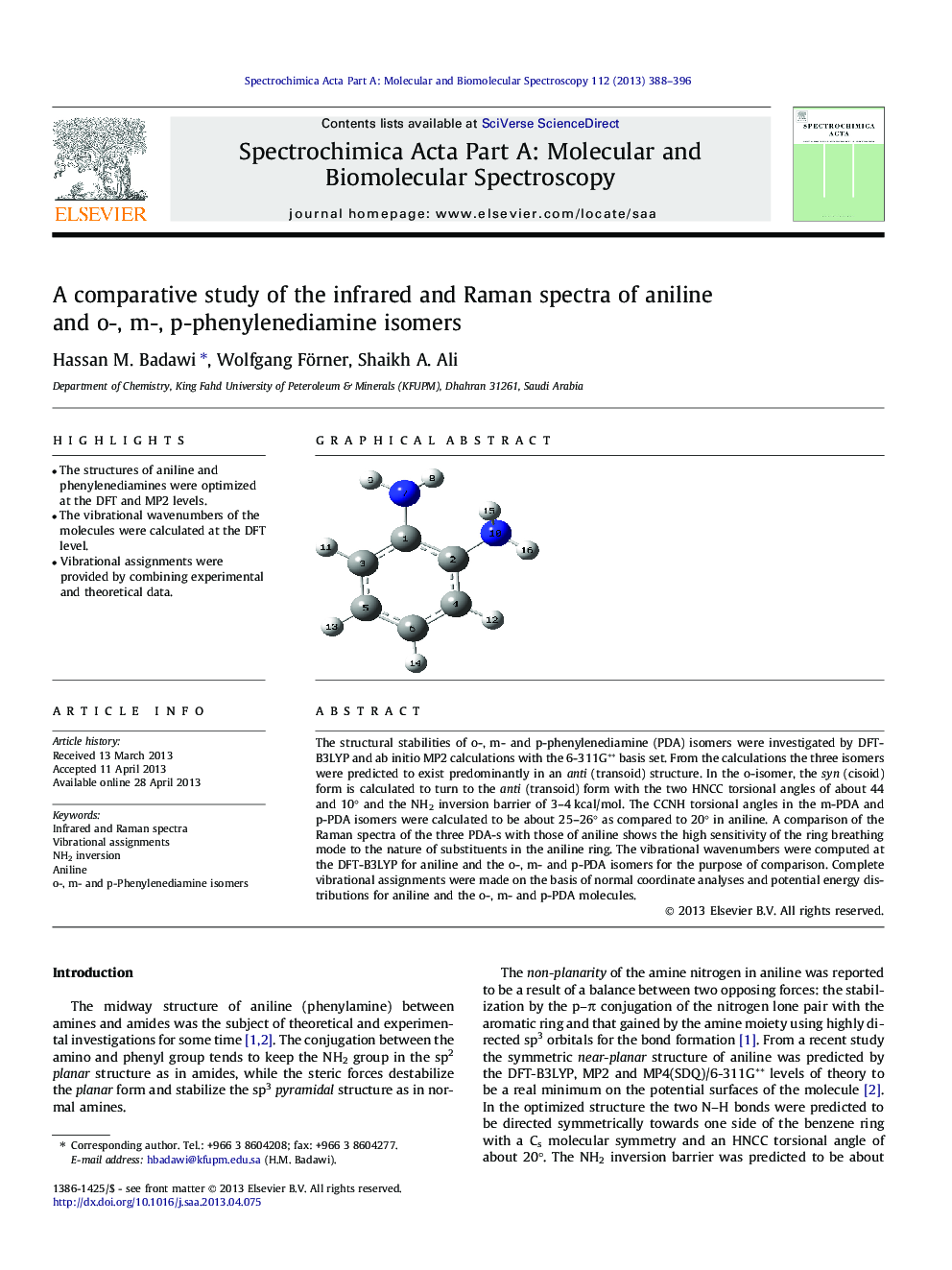
The structural stabilities of o-, m- and p-phenylenediamine (PDA) isomers were investigated by DFT-B3LYP and ab initio MP2 calculations with the 6-311G** basis set. From the calculations the three isomers were predicted to exist predominantly in an anti (transoid) structure. In the o-isomer, the syn (cisoid) form is calculated to turn to the anti (transoid) form with the two HNCC torsional angles of about 44 and 10° and the NH2 inversion barrier of 3–4 kcal/mol. The CCNH torsional angles in the m-PDA and p-PDA isomers were calculated to be about 25–26° as compared to 20° in aniline. A comparison of the Raman spectra of the three PDA-s with those of aniline shows the high sensitivity of the ring breathing mode to the nature of substituents in the aniline ring. The vibrational wavenumbers were computed at the DFT-B3LYP for aniline and the o-, m- and p-PDA isomers for the purpose of comparison. Complete vibrational assignments were made on the basis of normal coordinate analyses and potential energy distributions for aniline and the o-, m- and p-PDA molecules.
The optimized anti structure of o-phenylenediamine.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 112, August 2013, Pages 388–396