| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232322 | 1495271 | 2012 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
This paper investigates the interactions between human serum albumin (HSA) and CdTe quantum dots (QDs) with nearly identical hydrodynamic size, but capped with four different ligands (MPA, NAC, and GSH are negatively charged; CA is positively charged) under physiological conditions. The investigation was carried out using fluorescence spectroscopy, circular dichroism (CD) spectra, UV–vis spectroscopy, and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The results of fluorescence quenching and UV–vis absorption spectra experiments indicated the formation of the complex of HSA and negatively charged QDs (MPA-CdTe, NAC-CdTe, and GSH-CdTe), which was also reconfirmed by the increasing of the hydrodynamic radius of QDs. The Ka values of the three negatively charged QDs are of the same order of magnitude, indicating that the interactions are related to the nanoparticle itself rather than the ligands. ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0 implied that the electrostatic interactions play predominant roles in the adsorption process. Furthermore, it was also proven that QDs can induce the conformational changes of HSA from the CD spectra and the three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of HSA. However, our results demonstrate that the interaction mechanism between the positively charged QDs (CA-CdTe) and HSA is significantly different from negatively charged QDs. For CA-CdTe QDs, both the static and dynamic quenching occur within the investigated range of concentrations. According to the DLS results, some large-size agglomeration also emerged.
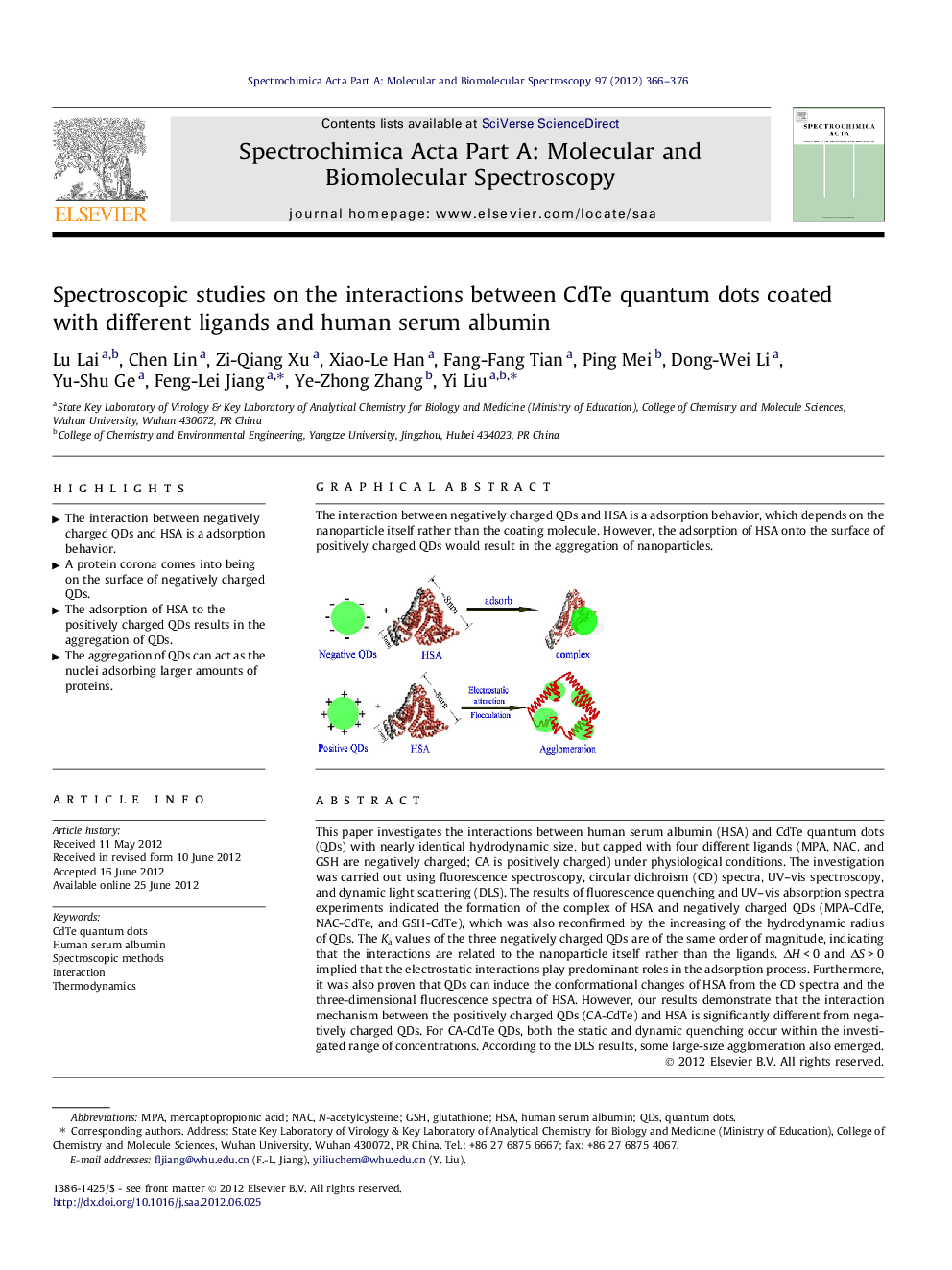
The interaction between negatively charged QDs and HSA is a adsorption behavior, which depends on the nanoparticle itself rather than the coating molecule. However, the adsorption of HSA onto the surface of positively charged QDs would result in the aggregation of nanoparticles.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► The interaction between negatively charged QDs and HSA is a adsorption behavior.
► A protein corona comes into being on the surface of negatively charged QDs.
► The adsorption of HSA to the positively charged QDs results in the aggregation of QDs.
► The aggregation of QDs can act as the nuclei adsorbing larger amounts of proteins.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 97, November 2012, Pages 366–376