| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232844 | 1495245 | 2014 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• New mono- and binuclear CuII complexes of a sulfamethazine Schiff-base were prepared.
• Correlation between the experimental and theoretical work was performed.
• Mononuclear complex is less toxic than free ligand, while the binuclear one is inactive.
• ELUMO, ΔE, dipole moment and polarizability correlate well with experimental LC50.
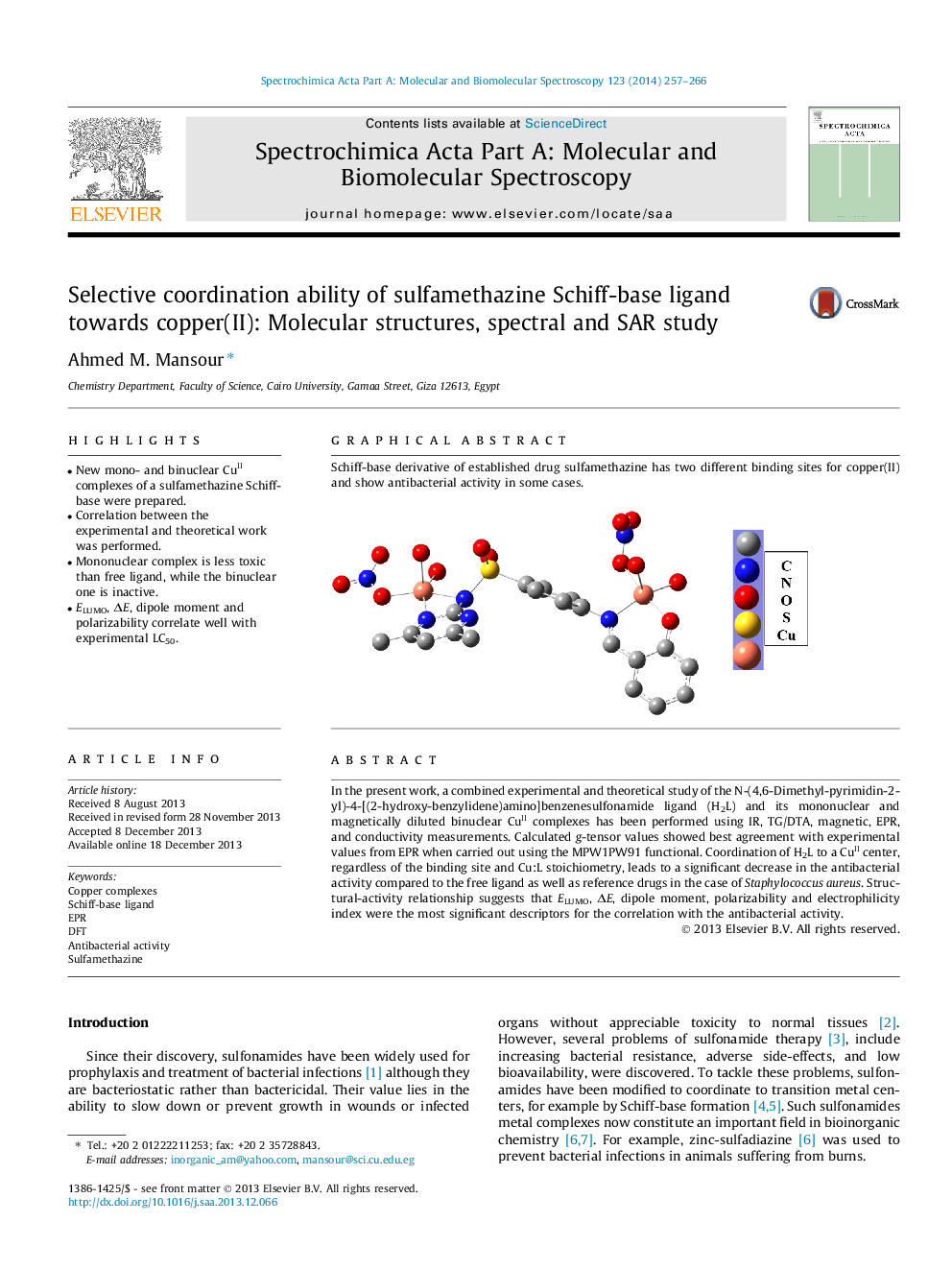
In the present work, a combined experimental and theoretical study of the N-(4,6-Dimethyl-pyrimidin-2-yl)-4-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]benzenesulfonamide ligand (H2L) and its mononuclear and magnetically diluted binuclear CuII complexes has been performed using IR, TG/DTA, magnetic, EPR, and conductivity measurements. Calculated g-tensor values showed best agreement with experimental values from EPR when carried out using the MPW1PW91 functional. Coordination of H2L to a CuII center, regardless of the binding site and Cu:L stoichiometry, leads to a significant decrease in the antibacterial activity compared to the free ligand as well as reference drugs in the case of Staphylococcus aureus. Structural-activity relationship suggests that ELUMO, ΔE, dipole moment, polarizability and electrophilicity index were the most significant descriptors for the correlation with the antibacterial activity.
Schiff-base derivative of established drug sulfamethazine has two different binding sites for copper(II) and show antibacterial activity in some cases.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 123, 5 April 2014, Pages 257–266