| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234469 | 1495272 | 2012 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
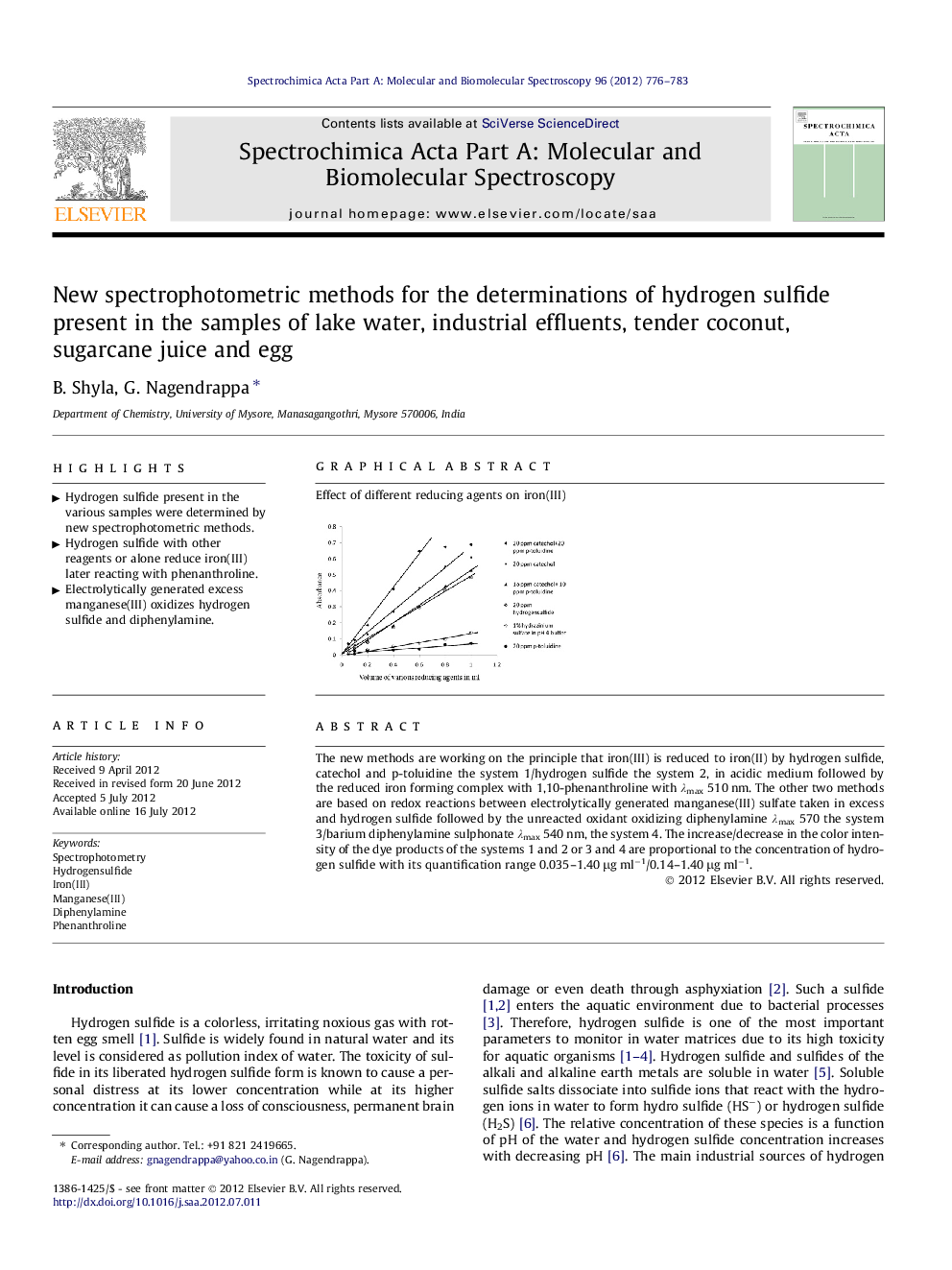
The new methods are working on the principle that iron(III) is reduced to iron(II) by hydrogen sulfide, catechol and p-toluidine the system 1/hydrogen sulfide the system 2, in acidic medium followed by the reduced iron forming complex with 1,10-phenanthroline with λmax 510 nm. The other two methods are based on redox reactions between electrolytically generated manganese(III) sulfate taken in excess and hydrogen sulfide followed by the unreacted oxidant oxidizing diphenylamine λmax 570 the system 3/barium diphenylamine sulphonate λmax 540 nm, the system 4. The increase/decrease in the color intensity of the dye products of the systems 1 and 2 or 3 and 4 are proportional to the concentration of hydrogen sulfide with its quantification range 0.035–1.40 μg ml−1/0.14–1.40 μg ml−1.
Effect of different reducing agents on iron(III).Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Hydrogen sulfide present in the various samples were determined by new spectrophotometric methods.
► Hydrogen sulfide with other reagents or alone reduce iron(III) later reacting with phenanthroline.
► Electrolytically generated excess manganese(III) oxidizes hydrogen sulfide and diphenylamine.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 96, October 2012, Pages 776–783