| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234749 | 1495260 | 2013 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
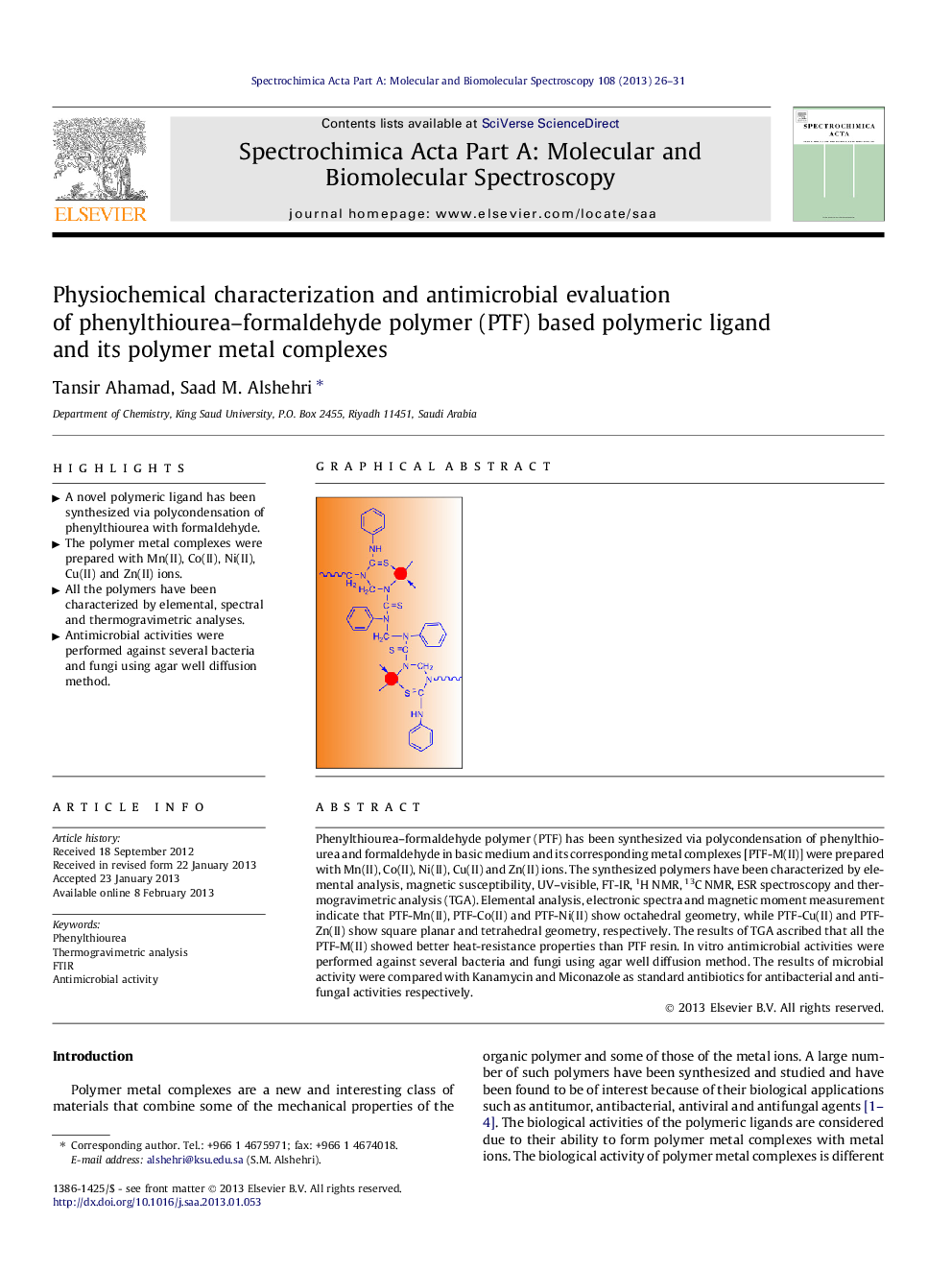
Phenylthiourea–formaldehyde polymer (PTF) has been synthesized via polycondensation of phenylthiourea and formaldehyde in basic medium and its corresponding metal complexes [PTF-M(II)] were prepared with Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions. The synthesized polymers have been characterized by elemental analysis, magnetic susceptibility, UV–visible, FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESR spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Elemental analysis, electronic spectra and magnetic moment measurement indicate that PTF-Mn(II), PTF-Co(II) and PTF-Ni(II) show octahedral geometry, while PTF-Cu(II) and PTF-Zn(II) show square planar and tetrahedral geometry, respectively. The results of TGA ascribed that all the PTF-M(II) showed better heat-resistance properties than PTF resin. In vitro antimicrobial activities were performed against several bacteria and fungi using agar well diffusion method. The results of microbial activity were compared with Kanamycin and Miconazole as standard antibiotics for antibacterial and antifungal activities respectively.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► A novel polymeric ligand has been synthesized via polycondensation of phenylthiourea with formaldehyde.
► The polymer metal complexes were prepared with Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions.
► All the polymers have been characterized by elemental, spectral and thermogravimetric analyses.
► Antimicrobial activities were performed against several bacteria and fungi using agar well diffusion method.
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 108, May 2013, Pages 26–31