| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1284200 | 1497977 | 2014 | 5 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
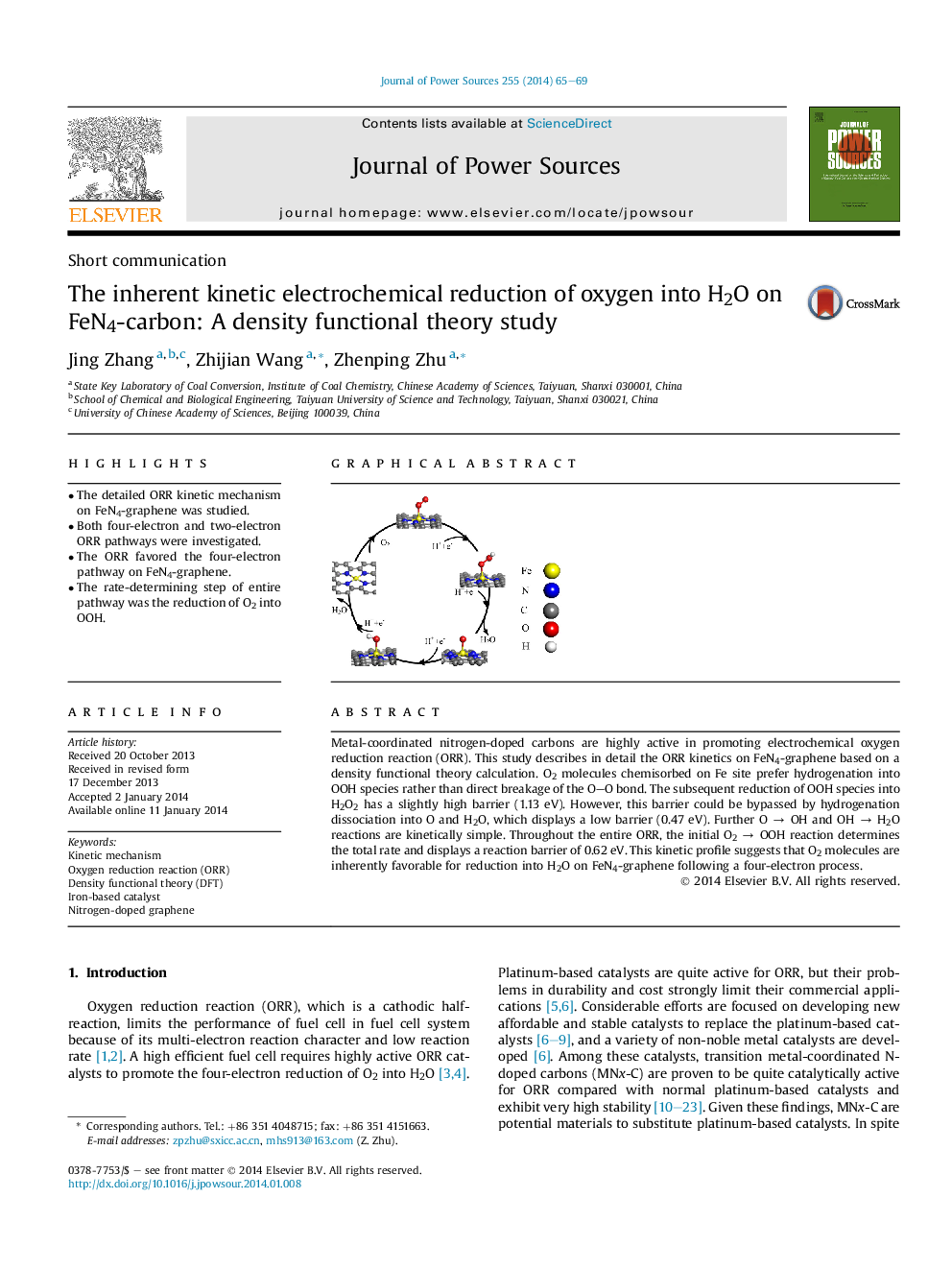
• The detailed ORR kinetic mechanism on FeN4-graphene was studied.
• Both four-electron and two-electron ORR pathways were investigated.
• The ORR favored the four-electron pathway on FeN4-graphene.
• The rate-determining step of entire pathway was the reduction of O2 into OOH.
Metal-coordinated nitrogen-doped carbons are highly active in promoting electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). This study describes in detail the ORR kinetics on FeN4-graphene based on a density functional theory calculation. O2 molecules chemisorbed on Fe site prefer hydrogenation into OOH species rather than direct breakage of the O–O bond. The subsequent reduction of OOH species into H2O2 has a slightly high barrier (1.13 eV). However, this barrier could be bypassed by hydrogenation dissociation into O and H2O, which displays a low barrier (0.47 eV). Further O → OH and OH → H2O reactions are kinetically simple. Throughout the entire ORR, the initial O2 → OOH reaction determines the total rate and displays a reaction barrier of 0.62 eV. This kinetic profile suggests that O2 molecules are inherently favorable for reduction into H2O on FeN4-graphene following a four-electron process.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Power Sources - Volume 255, 1 June 2014, Pages 65–69