| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1284373 | 1497994 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
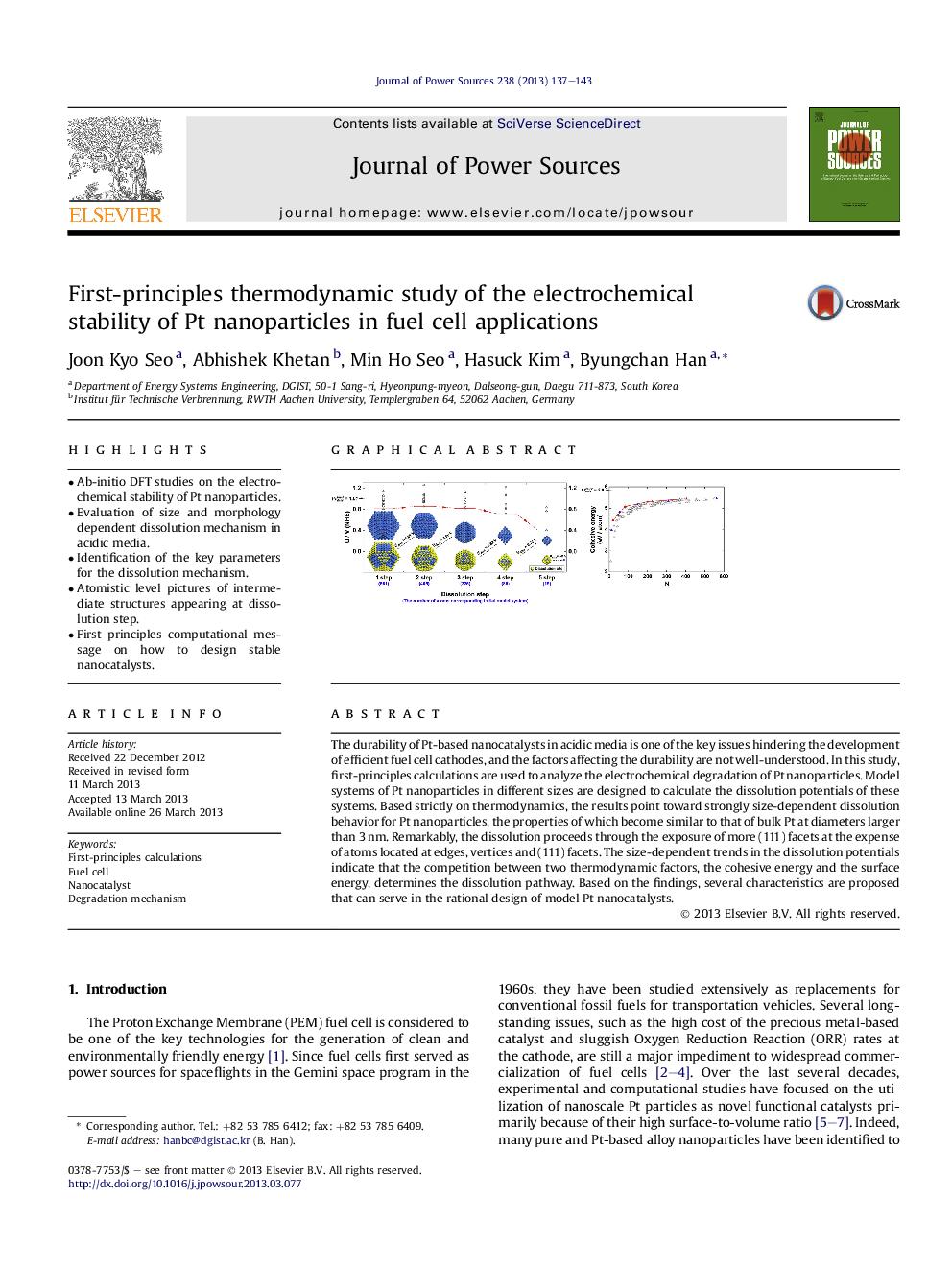
• Ab-initio DFT studies on the electrochemical stability of Pt nanoparticles.
• Evaluation of size and morphology dependent dissolution mechanism in acidic media.
• Identification of the key parameters for the dissolution mechanism.
• Atomistic level pictures of intermediate structures appearing at dissolution step.
• First principles computational message on how to design stable nanocatalysts.
The durability of Pt-based nanocatalysts in acidic media is one of the key issues hindering the development of efficient fuel cell cathodes, and the factors affecting the durability are not well-understood. In this study, first-principles calculations are used to analyze the electrochemical degradation of Pt nanoparticles. Model systems of Pt nanoparticles in different sizes are designed to calculate the dissolution potentials of these systems. Based strictly on thermodynamics, the results point toward strongly size-dependent dissolution behavior for Pt nanoparticles, the properties of which become similar to that of bulk Pt at diameters larger than 3 nm. Remarkably, the dissolution proceeds through the exposure of more (111) facets at the expense of atoms located at edges, vertices and (111) facets. The size-dependent trends in the dissolution potentials indicate that the competition between two thermodynamic factors, the cohesive energy and the surface energy, determines the dissolution pathway. Based on the findings, several characteristics are proposed that can serve in the rational design of model Pt nanocatalysts.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Power Sources - Volume 238, 15 September 2013, Pages 137–143