| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1286753 | 1497966 | 2014 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Osmium tetroxide (OsO4) staining greatly improves material contrast in LIB electrodes.
• Detection and study of distribution of lithium dendrites on graphitic anodes possible.
• Coordinated reaction of OsO4 with components of the SEI is shown.
• Electrochemically removed lithium dendrites can be located by their stained SEI shells.
• Applicable for cross sectional study of Li dendrite distribution and SEI layer evolution.
Osmium tetroxide (OsO4) staining, commonly used to enhance scattering contrast in electron microscopy of biologic tissue and polymer blends, has been adopted for studies of graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. OsO4 shows a coordinated reaction with components of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and lithium dendrites, thereby increasing material contrast for scanning electron microscopy investigations. Utilizing the high affinity of lithium metal to react with osmium tetroxide it was possible to localize even small lithium deposits on graphite electrodes. In spite of their reaction with the OsO4 fume, the lithium dendrite morphology remains almost untouched by the staining procedure, offering information on the dendrite growth process. Correlating the quantity of osmium detected with the amount of residual (“dead”) lithium of a discharged electrode, it was possible to obtain a practical measure for lithium plating and stripping efficiencies. EDX mappings allowed for a localization of electrochemically stripped lithium dendrites by their residual stained SEI shells. Cross sections, prepared by focused ion beam (FIB) of cycled graphite electrodes treated with OsO4, revealed important information about deposition and distribution of metallic lithium and the electrolyte reduction layer across the electrode.
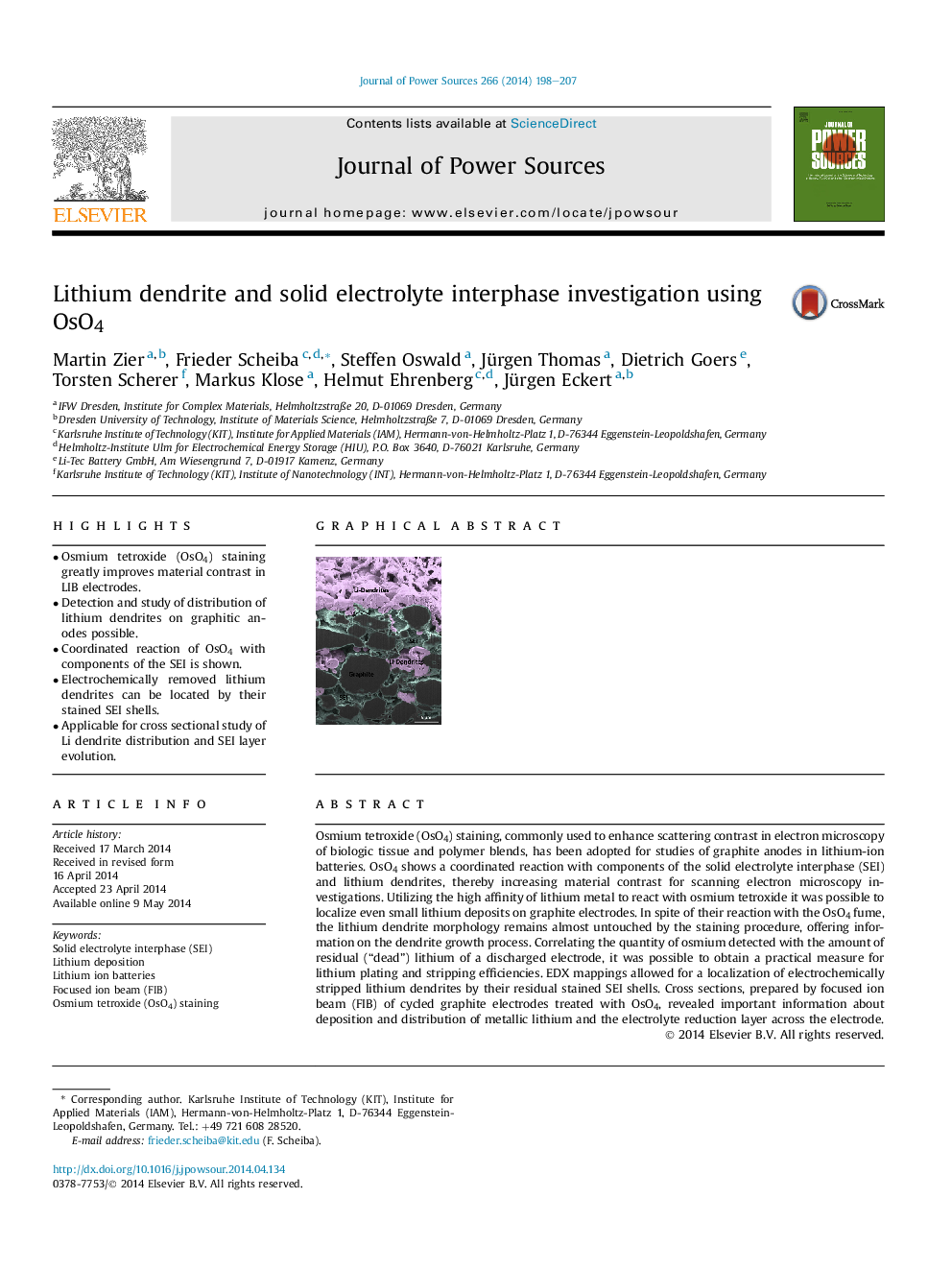
Pseudo color image of the cross section of an aged graphite electrode after osmium tetroxide staining. The increased material contrast due to OsO4-staining enables easy distinction between graphite particles (dark gray) that are covered by a stained SEI (mint) and surrounded by metallic lithium (pink). The electrode surface is located towards the top of the image.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Power Sources - Volume 266, 15 November 2014, Pages 198–207