| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1287705 | 1497995 | 2013 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
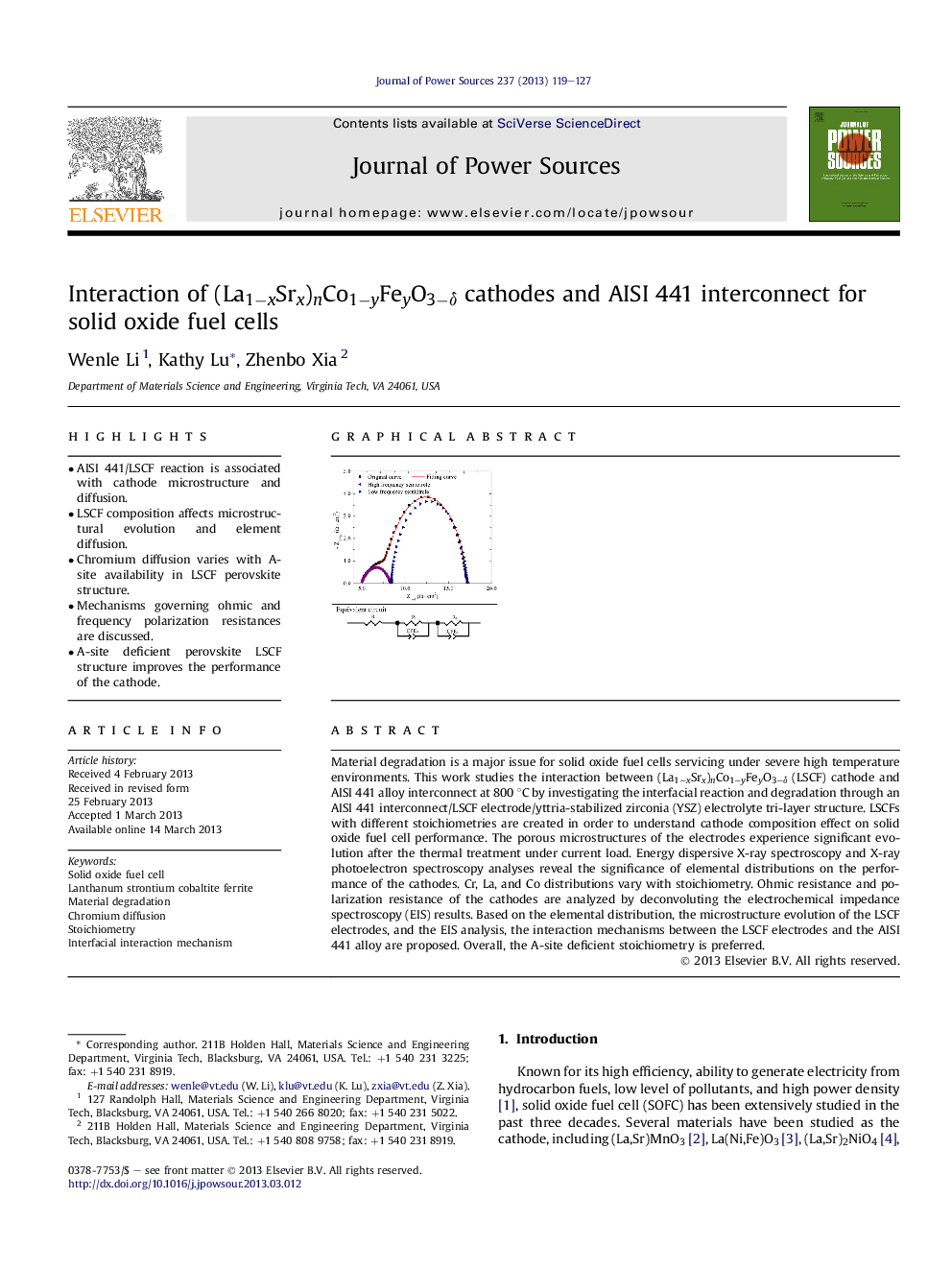
• AISI 441/LSCF reaction is associated with cathode microstructure and diffusion.
• LSCF composition affects microstructural evolution and element diffusion.
• Chromium diffusion varies with A-site availability in LSCF perovskite structure.
• Mechanisms governing ohmic and frequency polarization resistances are discussed.
• A-site deficient perovskite LSCF structure improves the performance of the cathode.
Material degradation is a major issue for solid oxide fuel cells servicing under severe high temperature environments. This work studies the interaction between (La1−xSrx)nCo1−yFeyO3−δ (LSCF) cathode and AISI 441 alloy interconnect at 800 °C by investigating the interfacial reaction and degradation through an AISI 441 interconnect/LSCF electrode/yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte tri-layer structure. LSCFs with different stoichiometries are created in order to understand cathode composition effect on solid oxide fuel cell performance. The porous microstructures of the electrodes experience significant evolution after the thermal treatment under current load. Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses reveal the significance of elemental distributions on the performance of the cathodes. Cr, La, and Co distributions vary with stoichiometry. Ohmic resistance and polarization resistance of the cathodes are analyzed by deconvoluting the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) results. Based on the elemental distribution, the microstructure evolution of the LSCF electrodes, and the EIS analysis, the interaction mechanisms between the LSCF electrodes and the AISI 441 alloy are proposed. Overall, the A-site deficient stoichiometry is preferred.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Power Sources - Volume 237, 1 September 2013, Pages 119–127