| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292417 | 1497926 | 2016 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
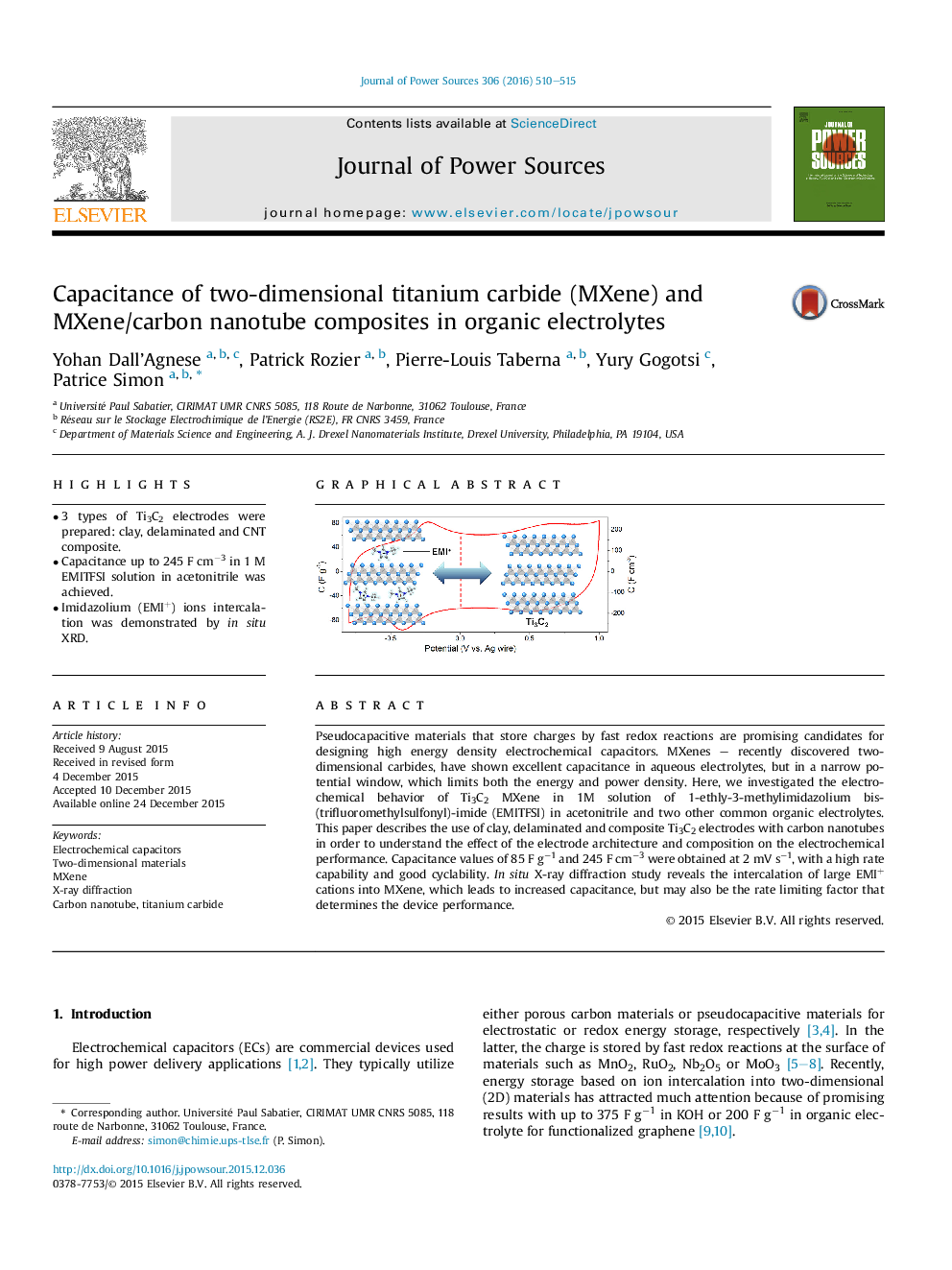
• 3 types of Ti3C2 electrodes were prepared: clay, delaminated and CNT composite.
• Capacitance up to 245 F cm−3 in 1 M EMITFSI solution in acetonitrile was achieved.
• Imidazolium (EMI+) ions intercalation was demonstrated by in situ XRD.
Pseudocapacitive materials that store charges by fast redox reactions are promising candidates for designing high energy density electrochemical capacitors. MXenes – recently discovered two-dimensional carbides, have shown excellent capacitance in aqueous electrolytes, but in a narrow potential window, which limits both the energy and power density. Here, we investigated the electrochemical behavior of Ti3C2 MXene in 1M solution of 1-ethly-3-methylimidazolium bis- (trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide (EMITFSI) in acetonitrile and two other common organic electrolytes. This paper describes the use of clay, delaminated and composite Ti3C2 electrodes with carbon nanotubes in order to understand the effect of the electrode architecture and composition on the electrochemical performance. Capacitance values of 85 F g−1 and 245 F cm−3 were obtained at 2 mV s−1, with a high rate capability and good cyclability. In situ X-ray diffraction study reveals the intercalation of large EMI+ cations into MXene, which leads to increased capacitance, but may also be the rate limiting factor that determines the device performance.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Power Sources - Volume 306, 29 February 2016, Pages 510–515