| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1358987 | 981375 | 2010 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
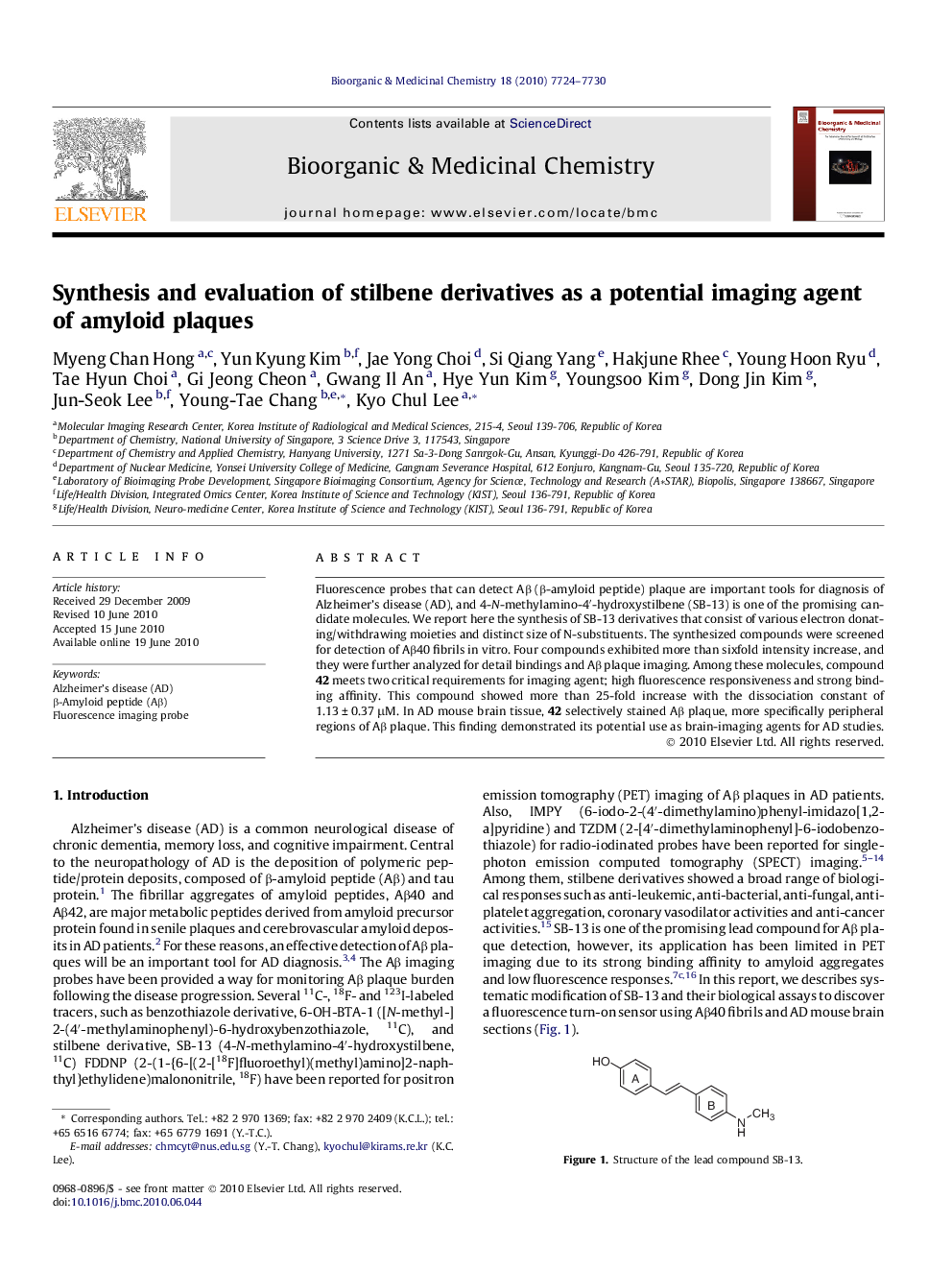
Fluorescence probes that can detect Aβ (β-amyloid peptide) plaque are important tools for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and 4-N-methylamino-4′-hydroxystilbene (SB-13) is one of the promising candidate molecules. We report here the synthesis of SB-13 derivatives that consist of various electron donating/withdrawing moieties and distinct size of N-substituents. The synthesized compounds were screened for detection of Aβ40 fibrils in vitro. Four compounds exhibited more than sixfold intensity increase, and they were further analyzed for detail bindings and Aβ plaque imaging. Among these molecules, compound 42 meets two critical requirements for imaging agent; high fluorescence responsiveness and strong binding affinity. This compound showed more than 25-fold increase with the dissociation constant of 1.13 ± 0.37 μM. In AD mouse brain tissue, 42 selectively stained Aβ plaque, more specifically peripheral regions of Aβ plaque. This finding demonstrated its potential use as brain-imaging agents for AD studies.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry - Volume 18, Issue 22, 15 November 2010, Pages 7724–7730