| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1391309 | 983241 | 2012 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
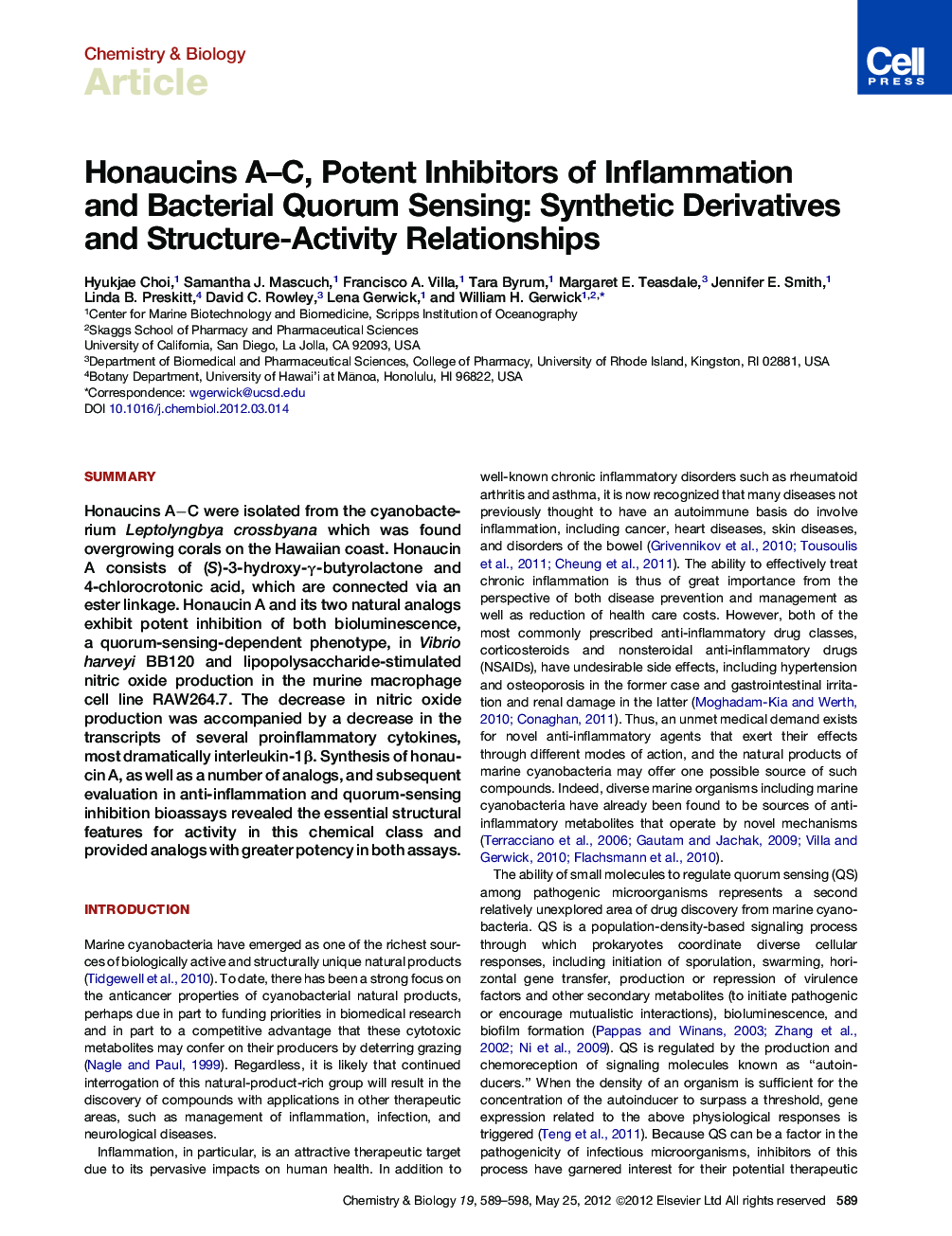
SummaryHonaucins A−C were isolated from the cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya crossbyana which was found overgrowing corals on the Hawaiian coast. Honaucin A consists of (S)-3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone and 4-chlorocrotonic acid, which are connected via an ester linkage. Honaucin A and its two natural analogs exhibit potent inhibition of both bioluminescence, a quorum-sensing-dependent phenotype, in Vibrio harveyi BB120 and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nitric oxide production in the murine macrophage cell line RAW264.7. The decrease in nitric oxide production was accompanied by a decrease in the transcripts of several proinflammatory cytokines, most dramatically interleukin-1β. Synthesis of honaucin A, as well as a number of analogs, and subsequent evaluation in anti-inflammation and quorum-sensing inhibition bioassays revealed the essential structural features for activity in this chemical class and provided analogs with greater potency in both assays.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (420 K)Download as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Honaucins A−C were isolated from the cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya crossbyana
► Honaucins A−C displayed potent anti-inflammatory and QS inhibitory activities
► SAR study revealed crucial structural features for bioactivity of the honaucins
► 4′-Bromohonaucin A is a potent modulator of inflammation and quorum sensing
Journal: - Volume 19, Issue 5, 25 May 2012, Pages 589–598