| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1391971 | 983689 | 2015 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
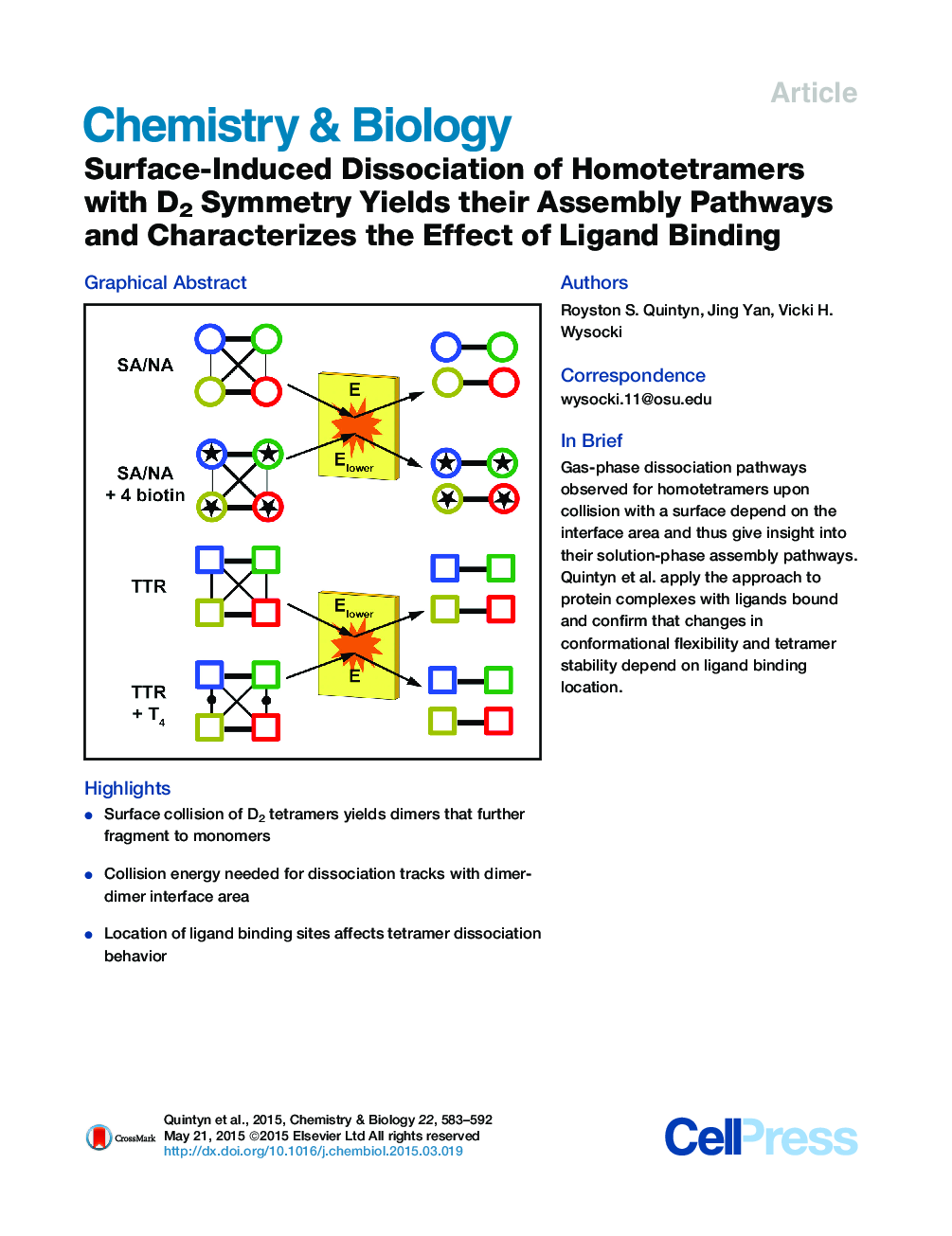
• Surface collision of D2 tetramers yields dimers that further fragment to monomers
• Collision energy needed for dissociation tracks with dimer-dimer interface area
• Location of ligand binding sites affects tetramer dissociation behavior
SummaryUnderstanding of protein complex assembly and the effect of ligand binding on their native topologies is integral to discerning how alterations in their architecture can affect function. Probing the disassembly pathway may offer insight into the mechanisms through which various subunits self-assemble into complexes. Here, a gas-phase dissociation method, surface-induced dissociation (SID) coupled with ion mobility (IM), was utilized to determine whether disassembly pathways are consistent with the assembly of three homotetramers and to probe the effects of ligand binding on conformational flexibility and tetramer stability. The results indicate that the smaller interface in the complex is initially cleaved upon dissociation, conserving the larger interface, and suggest that assembly of a D2 homotetramer from its constituent monomers occurs via a C2 dimer intermediate. In addition, we demonstrate that ligand-mediated changes in tetramer SID dissociation behavior are dependent on where and how the ligand binds.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (155 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 22, Issue 5, 21 May 2015, Pages 583–592