| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145336 | 456338 | 2016 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Membrane made of TiO2 nanowires/Fe2O3 nanoparticles/GO sheets was fabricated.
• Fe2O3 nanoparticles improved adsorption of humic acid onto membrane surface.
• GO sheets improved charge transfer from TiO2 and membrane photocatalytic activity.
• Superb humic acid degradation and membrane antifouling ability under solar radiation.
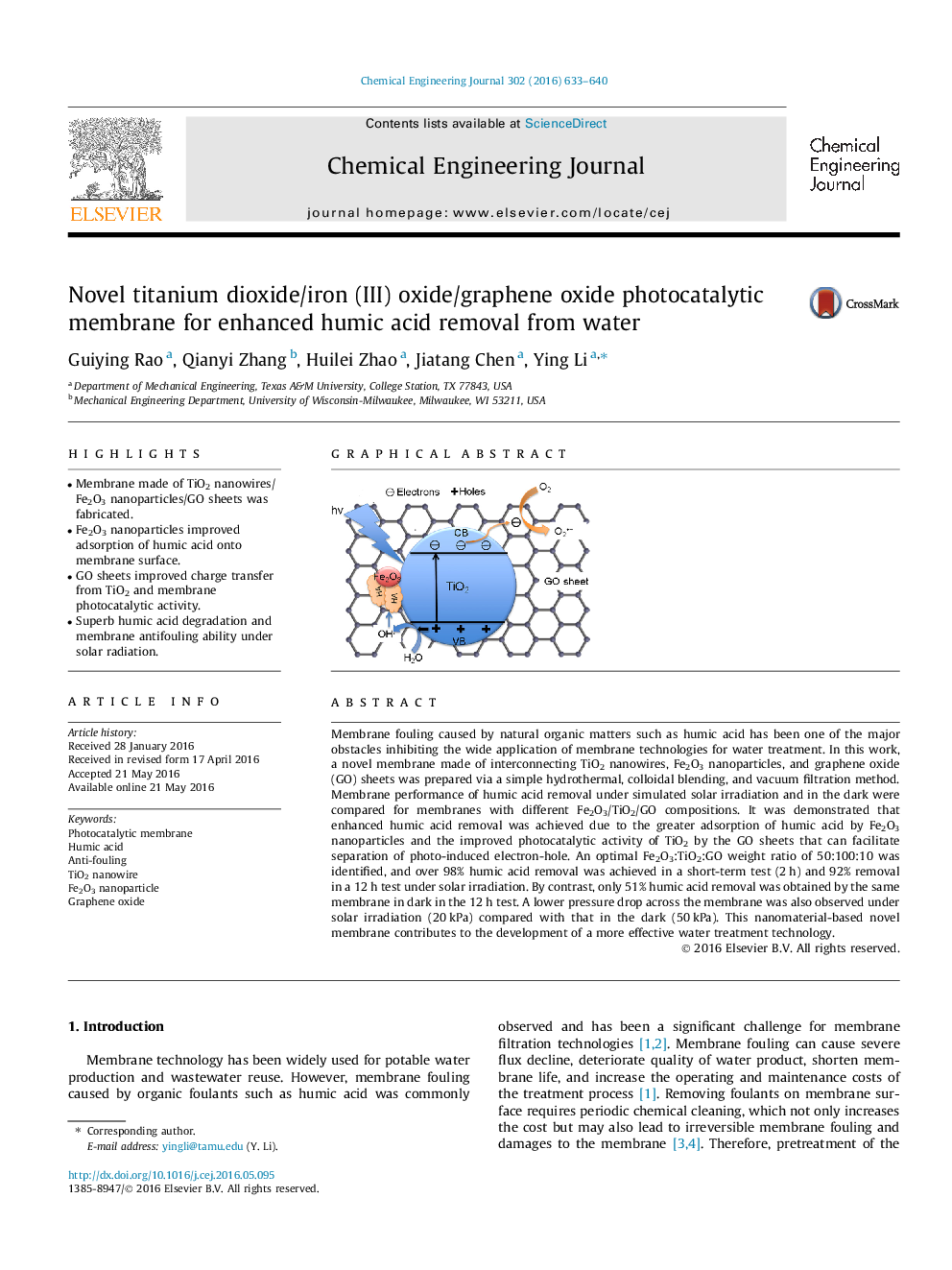
Membrane fouling caused by natural organic matters such as humic acid has been one of the major obstacles inhibiting the wide application of membrane technologies for water treatment. In this work, a novel membrane made of interconnecting TiO2 nanowires, Fe2O3 nanoparticles, and graphene oxide (GO) sheets was prepared via a simple hydrothermal, colloidal blending, and vacuum filtration method. Membrane performance of humic acid removal under simulated solar irradiation and in the dark were compared for membranes with different Fe2O3/TiO2/GO compositions. It was demonstrated that enhanced humic acid removal was achieved due to the greater adsorption of humic acid by Fe2O3 nanoparticles and the improved photocatalytic activity of TiO2 by the GO sheets that can facilitate separation of photo-induced electron-hole. An optimal Fe2O3:TiO2:GO weight ratio of 50:100:10 was identified, and over 98% humic acid removal was achieved in a short-term test (2 h) and 92% removal in a 12 h test under solar irradiation. By contrast, only 51% humic acid removal was obtained by the same membrane in dark in the 12 h test. A lower pressure drop across the membrane was also observed under solar irradiation (20 kPa) compared with that in the dark (50 kPa). This nanomaterial-based novel membrane contributes to the development of a more effective water treatment technology.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 302, 15 October 2016, Pages 633–640