| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145595 | 456345 | 2016 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
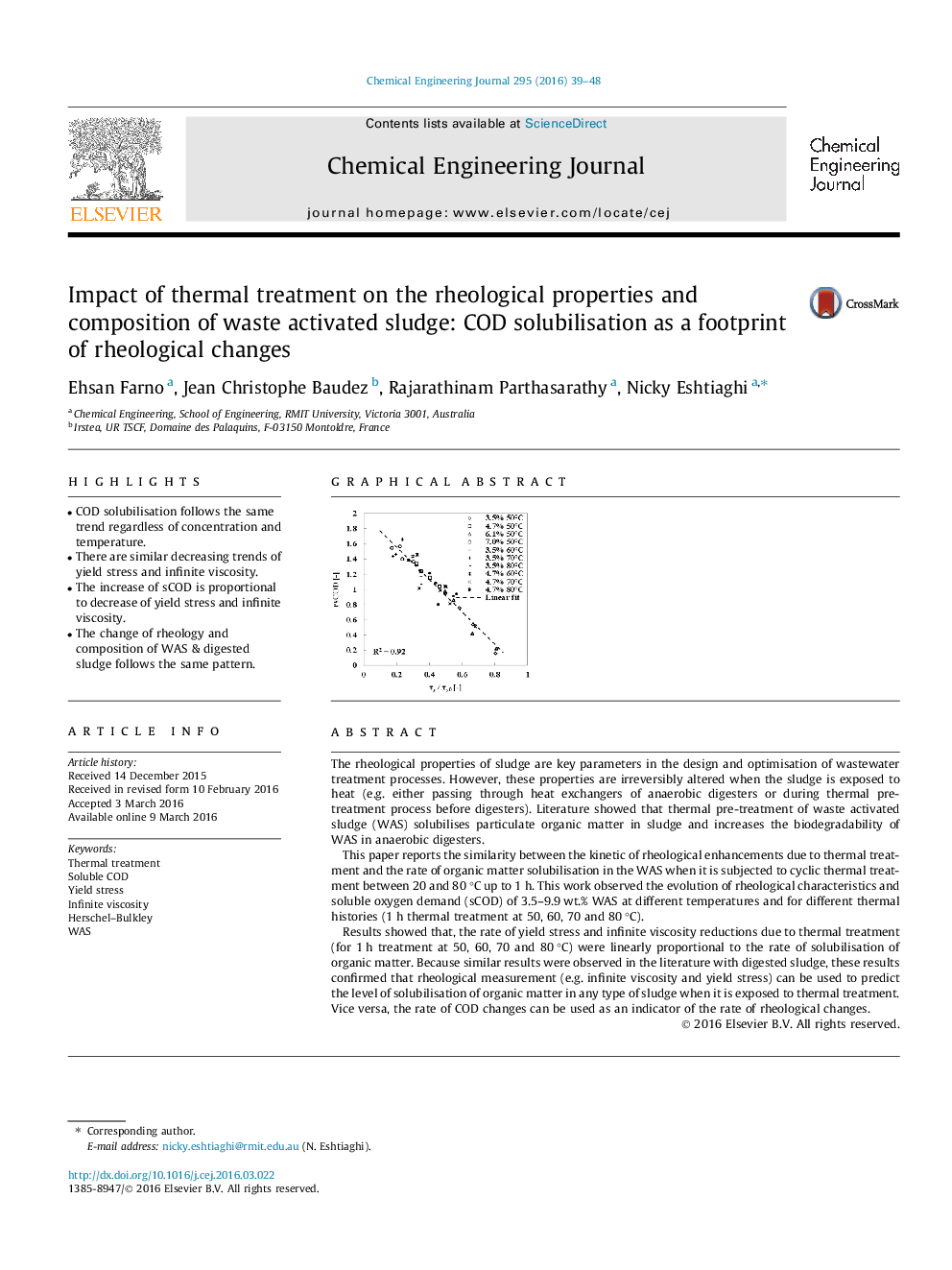
• COD solubilisation follows the same trend regardless of concentration and temperature.
• There are similar decreasing trends of yield stress and infinite viscosity.
• The increase of sCOD is proportional to decrease of yield stress and infinite viscosity.
• The change of rheology and composition of WAS & digested sludge follows the same pattern.
The rheological properties of sludge are key parameters in the design and optimisation of wastewater treatment processes. However, these properties are irreversibly altered when the sludge is exposed to heat (e.g. either passing through heat exchangers of anaerobic digesters or during thermal pre-treatment process before digesters). Literature showed that thermal pre-treatment of waste activated sludge (WAS) solubilises particulate organic matter in sludge and increases the biodegradability of WAS in anaerobic digesters.This paper reports the similarity between the kinetic of rheological enhancements due to thermal treatment and the rate of organic matter solubilisation in the WAS when it is subjected to cyclic thermal treatment between 20 and 80 °C up to 1 h. This work observed the evolution of rheological characteristics and soluble oxygen demand (sCOD) of 3.5–9.9 wt.% WAS at different temperatures and for different thermal histories (1 h thermal treatment at 50, 60, 70 and 80 °C).Results showed that, the rate of yield stress and infinite viscosity reductions due to thermal treatment (for 1 h treatment at 50, 60, 70 and 80 °C) were linearly proportional to the rate of solubilisation of organic matter. Because similar results were observed in the literature with digested sludge, these results confirmed that rheological measurement (e.g. infinite viscosity and yield stress) can be used to predict the level of solubilisation of organic matter in any type of sludge when it is exposed to thermal treatment. Vice versa, the rate of COD changes can be used as an indicator of the rate of rheological changes.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 295, 1 July 2016, Pages 39–48