| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145815 | 456352 | 2016 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
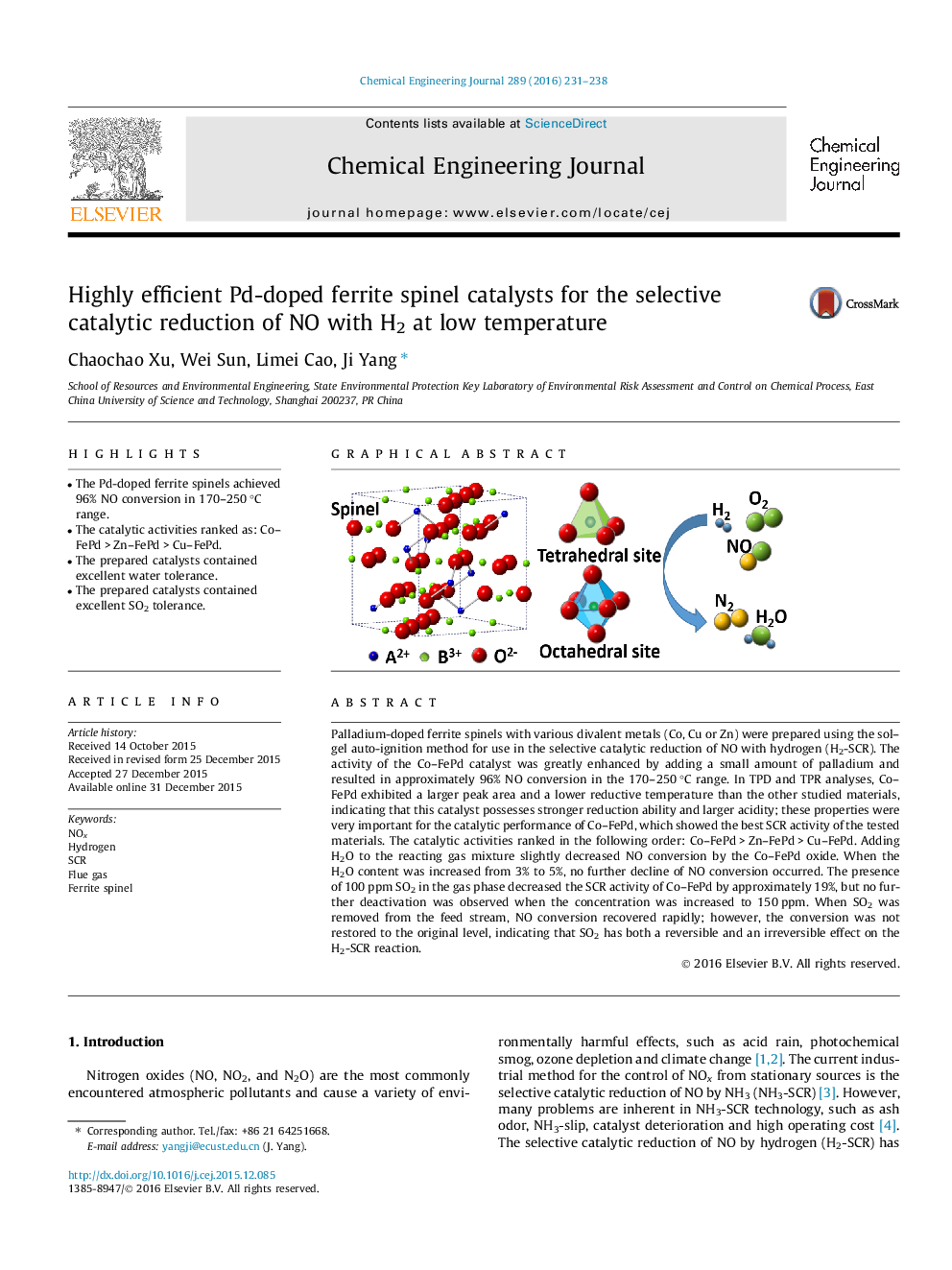
• The Pd-doped ferrite spinels achieved 96% NO conversion in 170–250 °C range.
• The catalytic activities ranked as: Co–FePd > Zn–FePd > Cu–FePd.
• The prepared catalysts contained excellent water tolerance.
• The prepared catalysts contained excellent SO2 tolerance.
Palladium-doped ferrite spinels with various divalent metals (Co, Cu or Zn) were prepared using the sol–gel auto-ignition method for use in the selective catalytic reduction of NO with hydrogen (H2-SCR). The activity of the Co–FePd catalyst was greatly enhanced by adding a small amount of palladium and resulted in approximately 96% NO conversion in the 170–250 °C range. In TPD and TPR analyses, Co–FePd exhibited a larger peak area and a lower reductive temperature than the other studied materials, indicating that this catalyst possesses stronger reduction ability and larger acidity; these properties were very important for the catalytic performance of Co–FePd, which showed the best SCR activity of the tested materials. The catalytic activities ranked in the following order: Co–FePd > Zn–FePd > Cu–FePd. Adding H2O to the reacting gas mixture slightly decreased NO conversion by the Co–FePd oxide. When the H2O content was increased from 3% to 5%, no further decline of NO conversion occurred. The presence of 100 ppm SO2 in the gas phase decreased the SCR activity of Co–FePd by approximately 19%, but no further deactivation was observed when the concentration was increased to 150 ppm. When SO2 was removed from the feed stream, NO conversion recovered rapidly; however, the conversion was not restored to the original level, indicating that SO2 has both a reversible and an irreversible effect on the H2-SCR reaction.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 289, 1 April 2016, Pages 231–238