| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146144 | 456362 | 2015 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
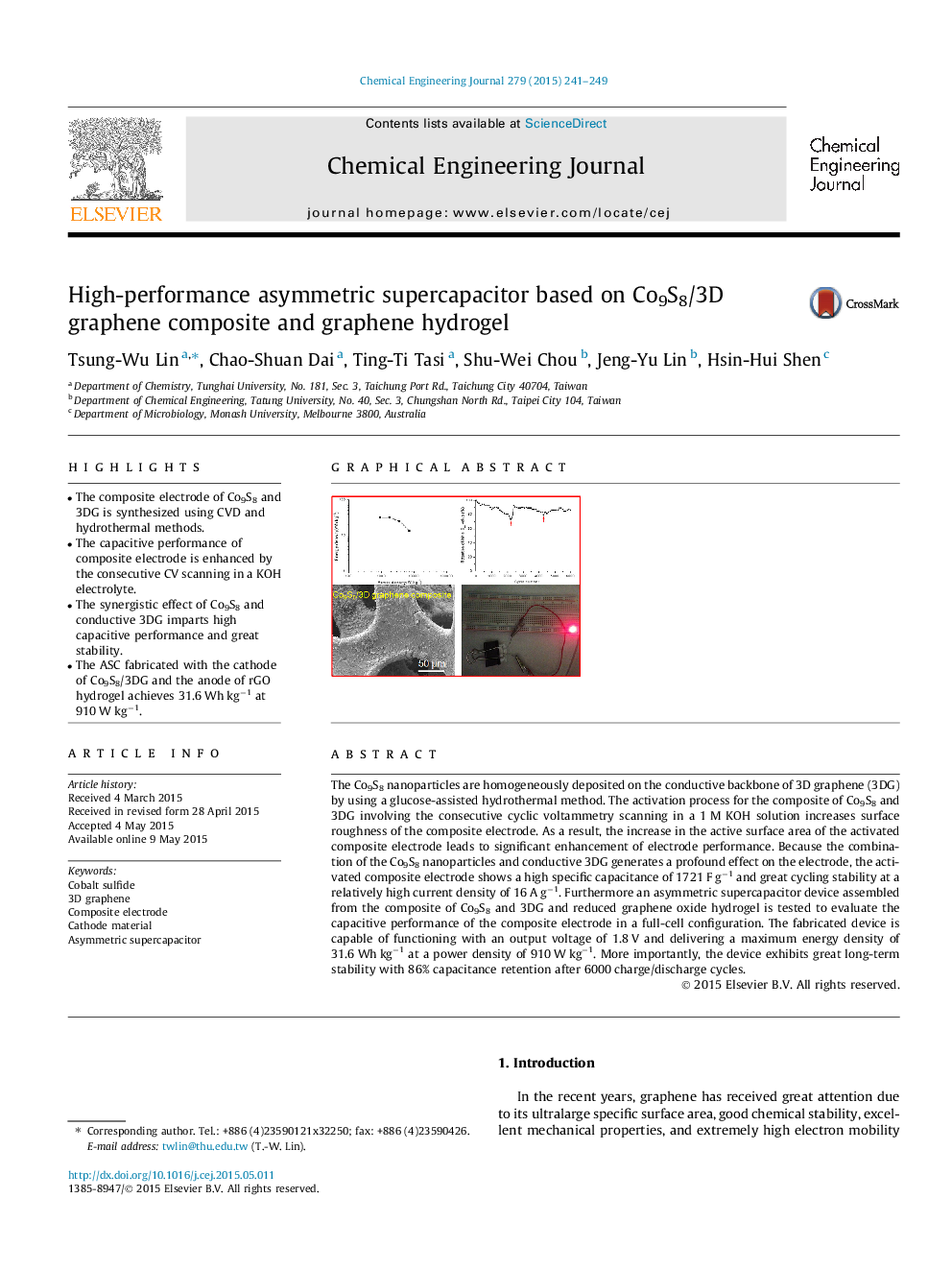
• The composite electrode of Co9S8 and 3DG is synthesized using CVD and hydrothermal methods.
• The capacitive performance of composite electrode is enhanced by the consecutive CV scanning in a KOH electrolyte.
• The synergistic effect of Co9S8 and conductive 3DG imparts high capacitive performance and great stability.
• The ASC fabricated with the cathode of Co9S8/3DG and the anode of rGO hydrogel achieves 31.6 Wh kg−1 at 910 W kg−1.
The Co9S8 nanoparticles are homogeneously deposited on the conductive backbone of 3D graphene (3DG) by using a glucose-assisted hydrothermal method. The activation process for the composite of Co9S8 and 3DG involving the consecutive cyclic voltammetry scanning in a 1 M KOH solution increases surface roughness of the composite electrode. As a result, the increase in the active surface area of the activated composite electrode leads to significant enhancement of electrode performance. Because the combination of the Co9S8 nanoparticles and conductive 3DG generates a profound effect on the electrode, the activated composite electrode shows a high specific capacitance of 1721 F g−1 and great cycling stability at a relatively high current density of 16 A g−1. Furthermore an asymmetric supercapacitor device assembled from the composite of Co9S8 and 3DG and reduced graphene oxide hydrogel is tested to evaluate the capacitive performance of the composite electrode in a full-cell configuration. The fabricated device is capable of functioning with an output voltage of 1.8 V and delivering a maximum energy density of 31.6 Wh kg−1 at a power density of 910 W kg−1. More importantly, the device exhibits great long-term stability with 86% capacitance retention after 6000 charge/discharge cycles.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 279, 1 November 2015, Pages 241–249