| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146864 | 456379 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Six different aluminas were investigated and compared for Sb(V) removal.
• Mesoporous alumina (MA) is superior to aluminum hydroxide and commercial aluminas.
• XPS spectra confirmed Sb(V) chemical bonding to MA without surface precipitation.
• 27Al NMR showed AlO4 and AlO5 in MA was enhanced by Sb(V) adsorption.
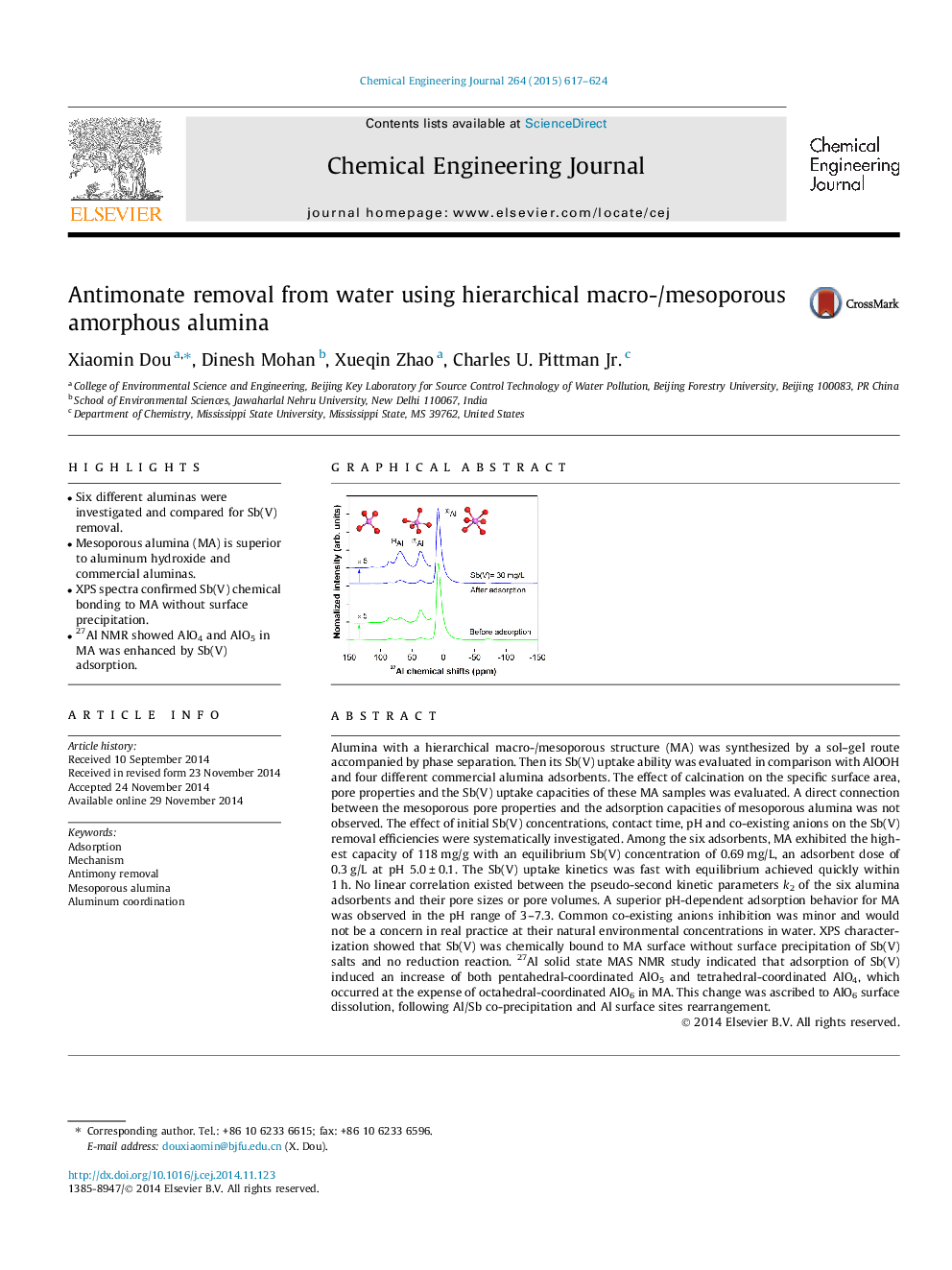
Alumina with a hierarchical macro-/mesoporous structure (MA) was synthesized by a sol–gel route accompanied by phase separation. Then its Sb(V) uptake ability was evaluated in comparison with AlOOH and four different commercial alumina adsorbents. The effect of calcination on the specific surface area, pore properties and the Sb(V) uptake capacities of these MA samples was evaluated. A direct connection between the mesoporous pore properties and the adsorption capacities of mesoporous alumina was not observed. The effect of initial Sb(V) concentrations, contact time, pH and co-existing anions on the Sb(V) removal efficiencies were systematically investigated. Among the six adsorbents, MA exhibited the highest capacity of 118 mg/g with an equilibrium Sb(V) concentration of 0.69 mg/L, an adsorbent dose of 0.3 g/L at pH 5.0 ± 0.1. The Sb(V) uptake kinetics was fast with equilibrium achieved quickly within 1 h. No linear correlation existed between the pseudo-second kinetic parameters k2 of the six alumina adsorbents and their pore sizes or pore volumes. A superior pH-dependent adsorption behavior for MA was observed in the pH range of 3–7.3. Common co-existing anions inhibition was minor and would not be a concern in real practice at their natural environmental concentrations in water. XPS characterization showed that Sb(V) was chemically bound to MA surface without surface precipitation of Sb(V) salts and no reduction reaction. 27Al solid state MAS NMR study indicated that adsorption of Sb(V) induced an increase of both pentahedral-coordinated AlO5 and tetrahedral-coordinated AlO4, which occurred at the expense of octahedral-coordinated AlO6 in MA. This change was ascribed to AlO6 surface dissolution, following Al/Sb co-precipitation and Al surface sites rearrangement.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 264, 15 March 2015, Pages 617–624