| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147326 | 456389 | 2014 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• A Gemini surfactant EBAB was introduced in iron ore flotation.
• EBAB exhibited superior selectivity for quartz against magnetite.
• EBAB displayed superior flotation performances than conventional surfactant DAC.
• EBAB adsorbed on quartz and magnetite surfaces by electrostatic attraction.
• A “four-stage” adsorption model was proposed.
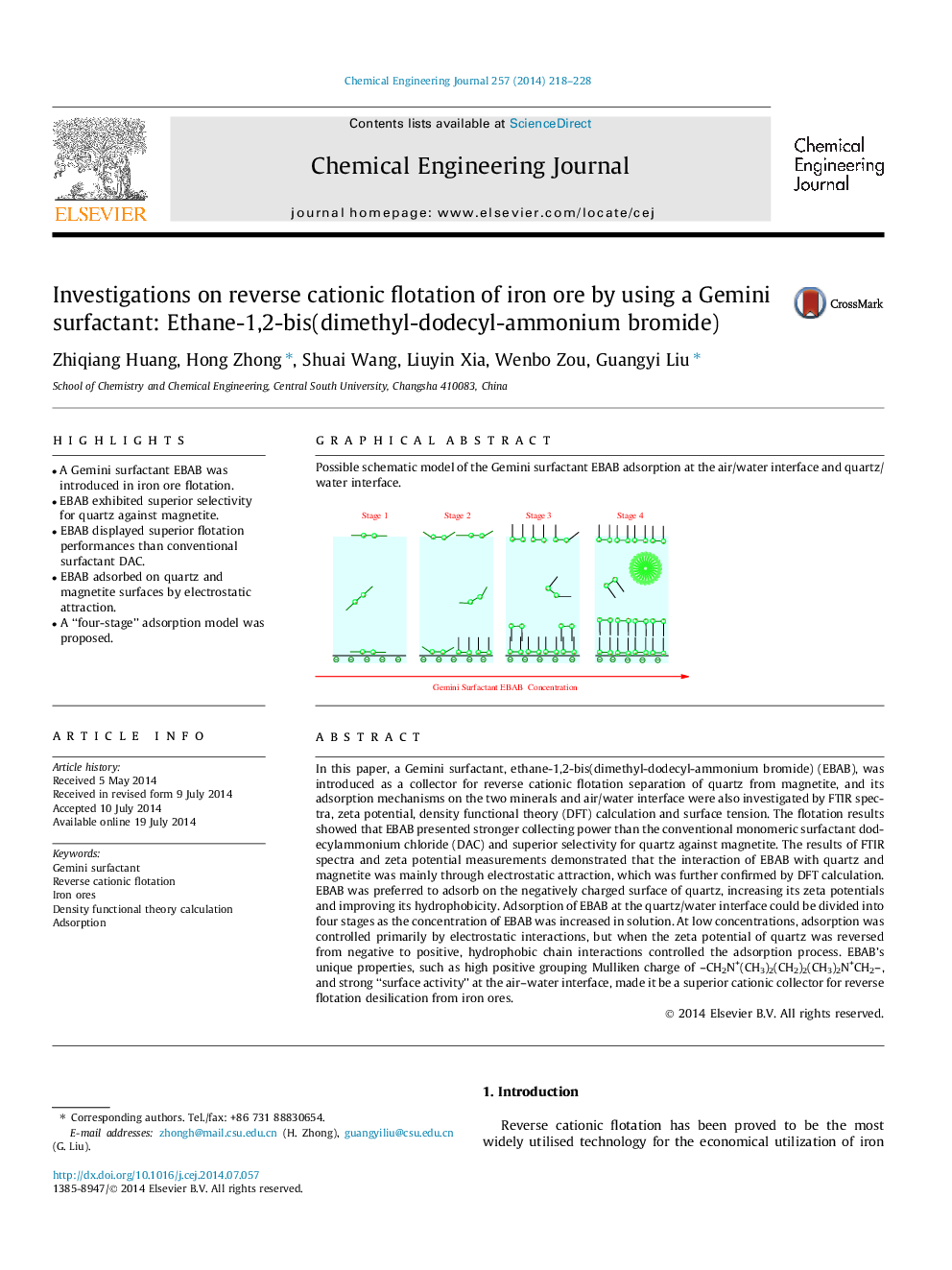
In this paper, a Gemini surfactant, ethane-1,2-bis(dimethyl-dodecyl-ammonium bromide) (EBAB), was introduced as a collector for reverse cationic flotation separation of quartz from magnetite, and its adsorption mechanisms on the two minerals and air/water interface were also investigated by FTIR spectra, zeta potential, density functional theory (DFT) calculation and surface tension. The flotation results showed that EBAB presented stronger collecting power than the conventional monomeric surfactant dodecylammonium chloride (DAC) and superior selectivity for quartz against magnetite. The results of FTIR spectra and zeta potential measurements demonstrated that the interaction of EBAB with quartz and magnetite was mainly through electrostatic attraction, which was further confirmed by DFT calculation. EBAB was preferred to adsorb on the negatively charged surface of quartz, increasing its zeta potentials and improving its hydrophobicity. Adsorption of EBAB at the quartz/water interface could be divided into four stages as the concentration of EBAB was increased in solution. At low concentrations, adsorption was controlled primarily by electrostatic interactions, but when the zeta potential of quartz was reversed from negative to positive, hydrophobic chain interactions controlled the adsorption process. EBAB’s unique properties, such as high positive grouping Mulliken charge of –CH2N+(CH3)2(CH2)2(CH3)2N+CH2–, and strong “surface activity” at the air–water interface, made it be a superior cationic collector for reverse flotation desilication from iron ores.
Possible schematic model of the Gemini surfactant EBAB adsorption at the air/water interface and quartz/water interface.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 257, 1 December 2014, Pages 218–228