| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147828 | 456400 | 2014 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Water-soluble polyacrylamide coated-Fe3O4 magnetic composites were synthesized successfully.
• PAM@Fe3O4 showed high efficient enrichment of U(VI) from wastewater.
• The Qmax of U(VI) on PAM@Fe3O4 reached 220.9 mg/g.
• Amide groups on the surface of PAM@Fe3O4 facilitated U(VI) sorption.
• The used PAM@Fe3O4 could be effectually regenerated.
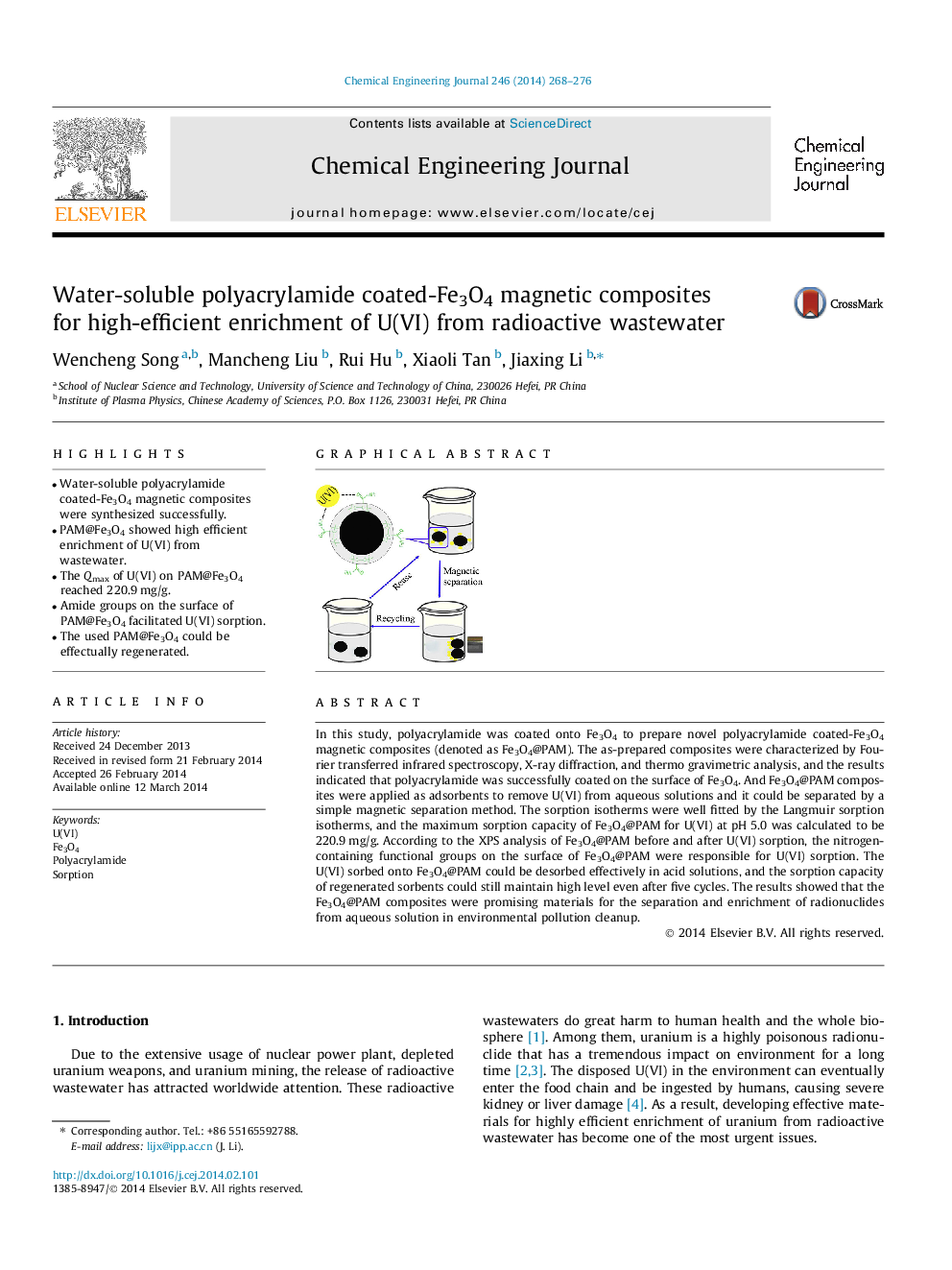
In this study, polyacrylamide was coated onto Fe3O4 to prepare novel polyacrylamide coated-Fe3O4 magnetic composites (denoted as Fe3O4@PAM). The as-prepared composites were characterized by Fourier transferred infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and thermo gravimetric analysis, and the results indicated that polyacrylamide was successfully coated on the surface of Fe3O4. And Fe3O4@PAM composites were applied as adsorbents to remove U(VI) from aqueous solutions and it could be separated by a simple magnetic separation method. The sorption isotherms were well fitted by the Langmuir sorption isotherms, and the maximum sorption capacity of Fe3O4@PAM for U(VI) at pH 5.0 was calculated to be 220.9 mg/g. According to the XPS analysis of Fe3O4@PAM before and after U(VI) sorption, the nitrogen-containing functional groups on the surface of Fe3O4@PAM were responsible for U(VI) sorption. The U(VI) sorbed onto Fe3O4@PAM could be desorbed effectively in acid solutions, and the sorption capacity of regenerated sorbents could still maintain high level even after five cycles. The results showed that the Fe3O4@PAM composites were promising materials for the separation and enrichment of radionuclides from aqueous solution in environmental pollution cleanup.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 246, 15 June 2014, Pages 268–276