| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148313 | 456408 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• In situ encapsulation of a fatty acid ester-based phase change material (PCM).
• Poly(urethane-urea) shell formation with N-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine and TDI.
• Influence of different surfactants on encapsulation and thermal properties reported.
• Leakage-free, thermally stable composites for low temperature thermal applications.
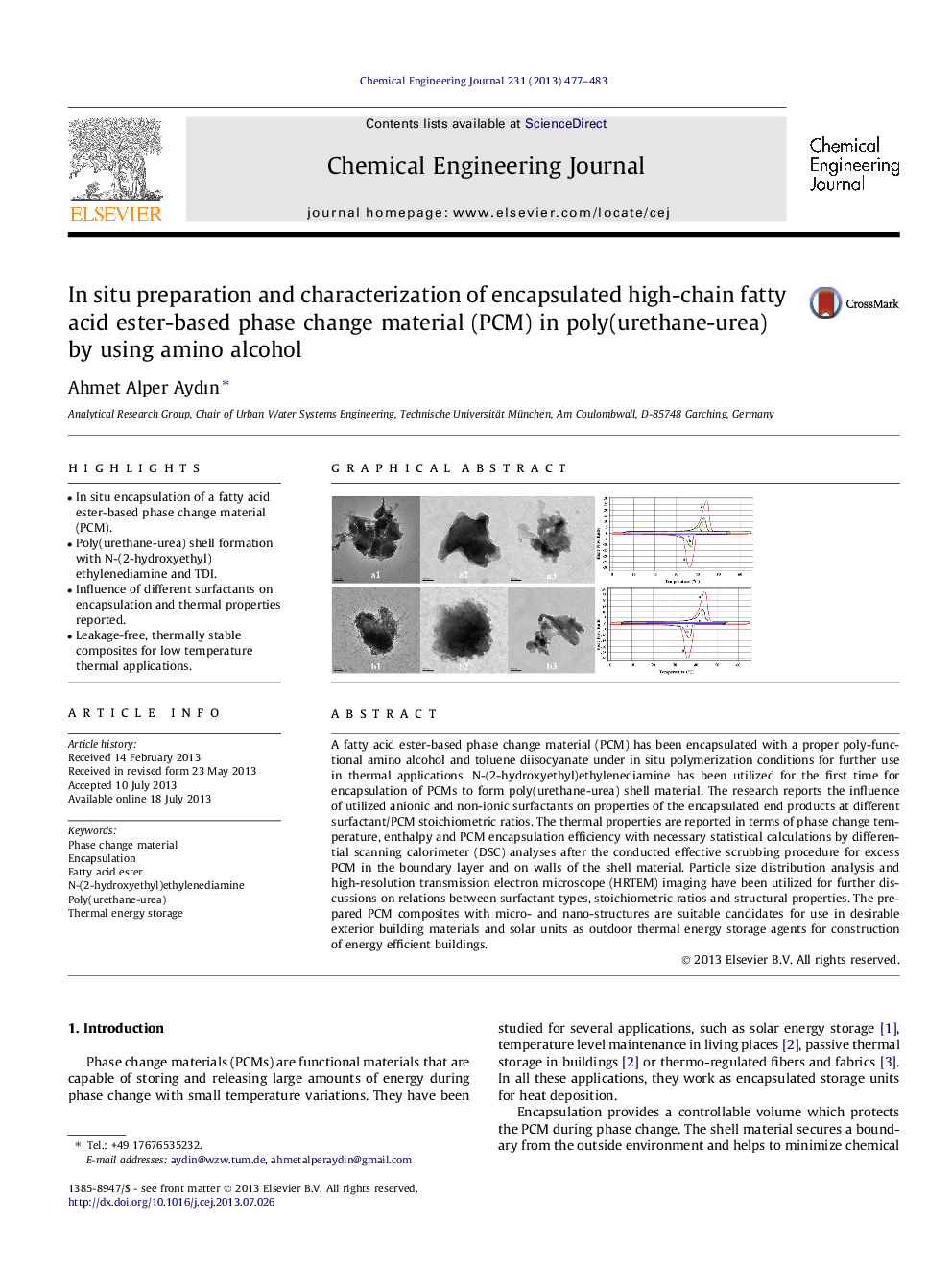
A fatty acid ester-based phase change material (PCM) has been encapsulated with a proper poly-functional amino alcohol and toluene diisocyanate under in situ polymerization conditions for further use in thermal applications. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine has been utilized for the first time for encapsulation of PCMs to form poly(urethane-urea) shell material. The research reports the influence of utilized anionic and non-ionic surfactants on properties of the encapsulated end products at different surfactant/PCM stoichiometric ratios. The thermal properties are reported in terms of phase change temperature, enthalpy and PCM encapsulation efficiency with necessary statistical calculations by differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) analyses after the conducted effective scrubbing procedure for excess PCM in the boundary layer and on walls of the shell material. Particle size distribution analysis and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) imaging have been utilized for further discussions on relations between surfactant types, stoichiometric ratios and structural properties. The prepared PCM composites with micro- and nano-structures are suitable candidates for use in desirable exterior building materials and solar units as outdoor thermal energy storage agents for construction of energy efficient buildings.
Graphical abtractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 231, September 2013, Pages 477–483