| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148717 | 456421 | 2013 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• TiO2 nanotube arrays (TNTs) are fabricated for the photocatalytic reduction of NO.
• Effects of electrolyte composition on the morphology of TNTs are investigated.
• Smooth TNTs are fabricated by suppressing the local ions concentration fluctuations.
• Concentration profile of H+ within TiO2 nanotubes dominates the dimension of TNTs.
• Tubular TiO2 shows higher activity for NO reduction as compared to spherical TiO2.
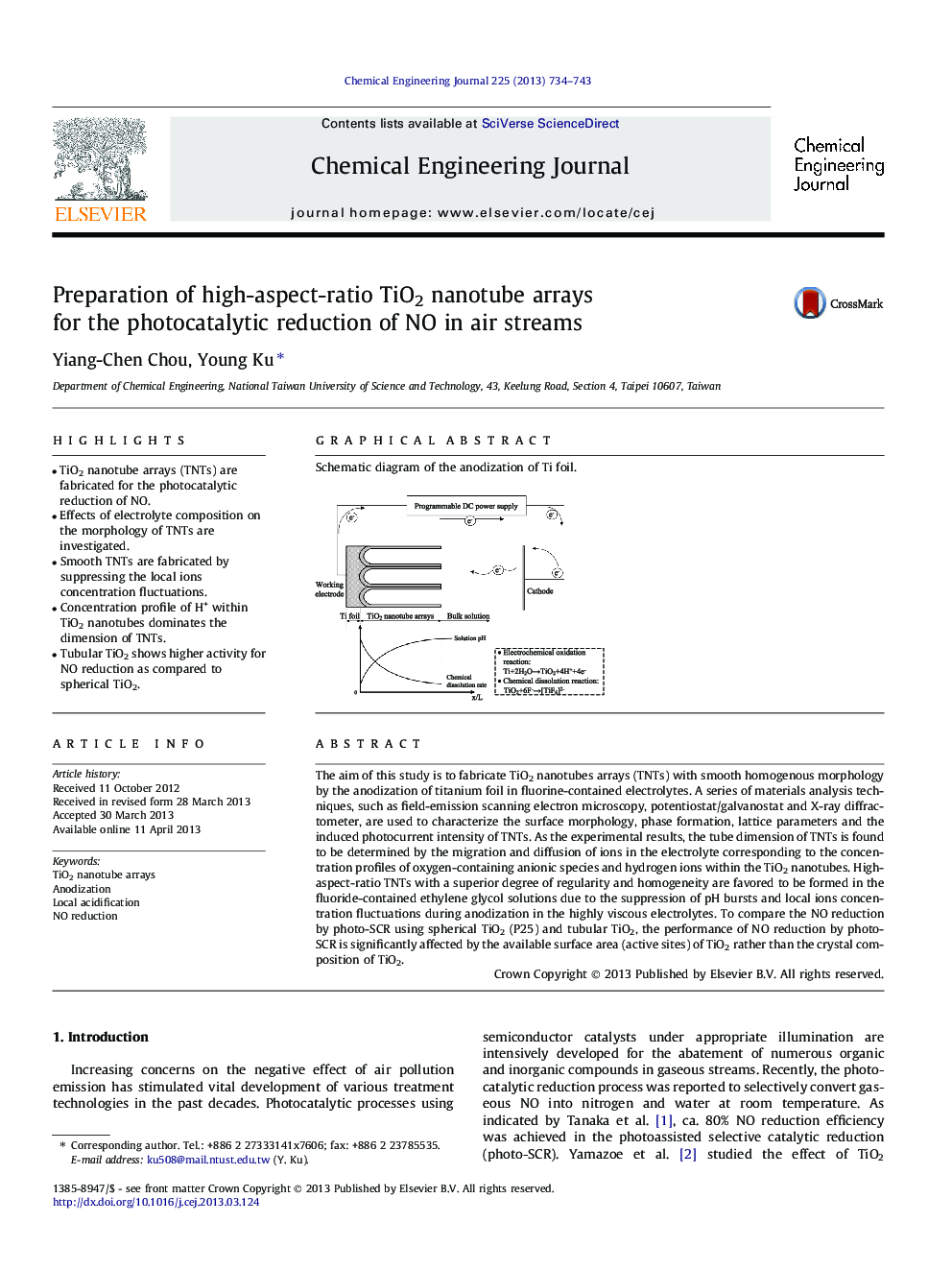
The aim of this study is to fabricate TiO2 nanotubes arrays (TNTs) with smooth homogenous morphology by the anodization of titanium foil in fluorine-contained electrolytes. A series of materials analysis techniques, such as field-emission scanning electron microscopy, potentiostat/galvanostat and X-ray diffractometer, are used to characterize the surface morphology, phase formation, lattice parameters and the induced photocurrent intensity of TNTs. As the experimental results, the tube dimension of TNTs is found to be determined by the migration and diffusion of ions in the electrolyte corresponding to the concentration profiles of oxygen-containing anionic species and hydrogen ions within the TiO2 nanotubes. High-aspect-ratio TNTs with a superior degree of regularity and homogeneity are favored to be formed in the fluoride-contained ethylene glycol solutions due to the suppression of pH bursts and local ions concentration fluctuations during anodization in the highly viscous electrolytes. To compare the NO reduction by photo-SCR using spherical TiO2 (P25) and tubular TiO2, the performance of NO reduction by photo-SCR is significantly affected by the available surface area (active sites) of TiO2 rather than the crystal composition of TiO2.
Schematic diagram of the anodization of Ti foil.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 225, 1 June 2013, Pages 734–743