| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148892 | 456424 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
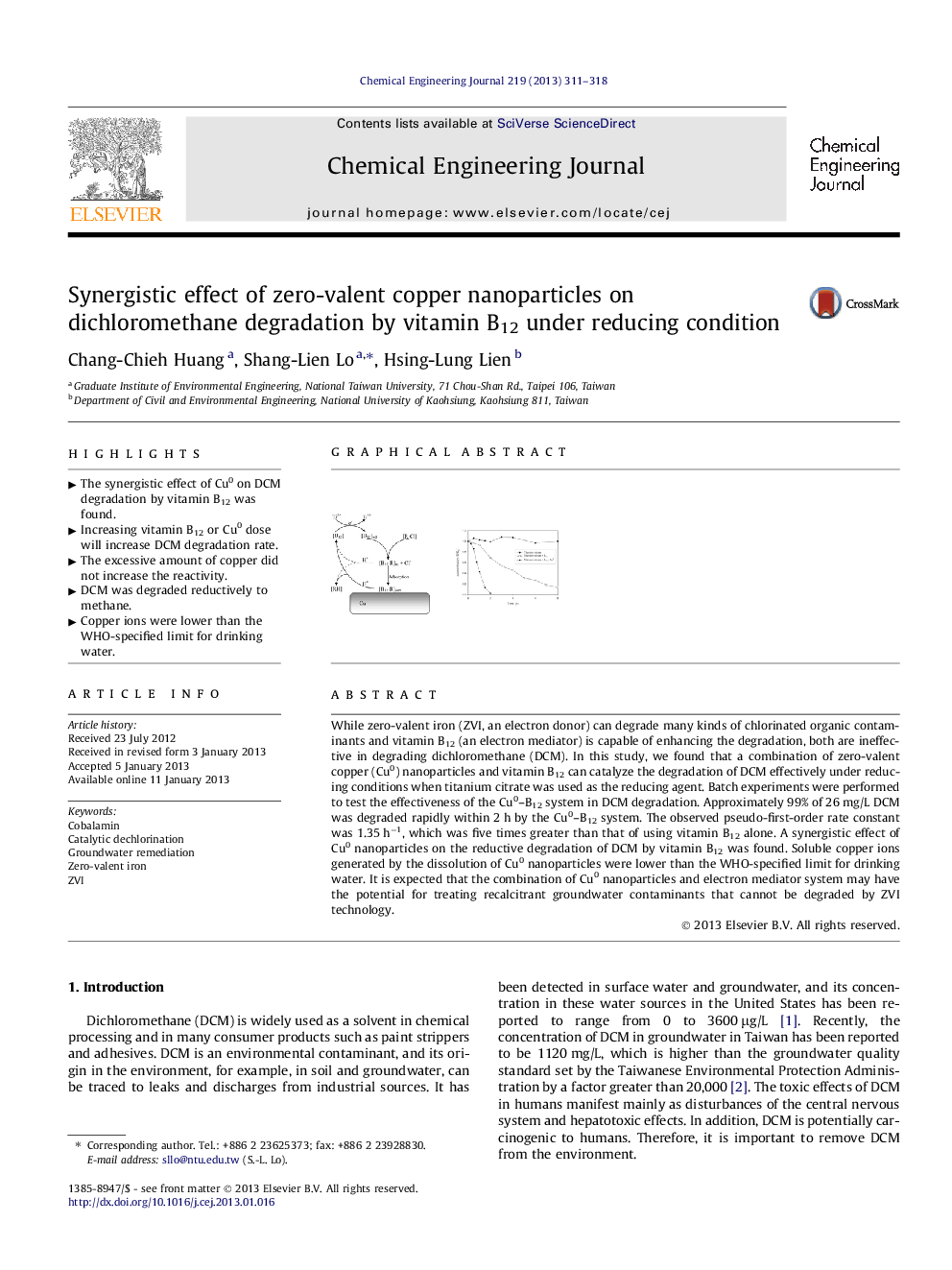
While zero-valent iron (ZVI, an electron donor) can degrade many kinds of chlorinated organic contaminants and vitamin B12 (an electron mediator) is capable of enhancing the degradation, both are ineffective in degrading dichloromethane (DCM). In this study, we found that a combination of zero-valent copper (Cu0) nanoparticles and vitamin B12 can catalyze the degradation of DCM effectively under reducing conditions when titanium citrate was used as the reducing agent. Batch experiments were performed to test the effectiveness of the Cu0–B12 system in DCM degradation. Approximately 99% of 26 mg/L DCM was degraded rapidly within 2 h by the Cu0–B12 system. The observed pseudo-first-order rate constant was 1.35 h−1, which was five times greater than that of using vitamin B12 alone. A synergistic effect of Cu0 nanoparticles on the reductive degradation of DCM by vitamin B12 was found. Soluble copper ions generated by the dissolution of Cu0 nanoparticles were lower than the WHO-specified limit for drinking water. It is expected that the combination of Cu0 nanoparticles and electron mediator system may have the potential for treating recalcitrant groundwater contaminants that cannot be degraded by ZVI technology.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► The synergistic effect of Cu0 on DCM degradation by vitamin B12 was found.
► Increasing vitamin B12 or Cu0 dose will increase DCM degradation rate.
► The excessive amount of copper did not increase the reactivity.
► DCM was degraded reductively to methane.
► Copper ions were lower than the WHO-specified limit for drinking water.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 219, 1 March 2013, Pages 311–318