| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149548 | 456434 | 2012 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
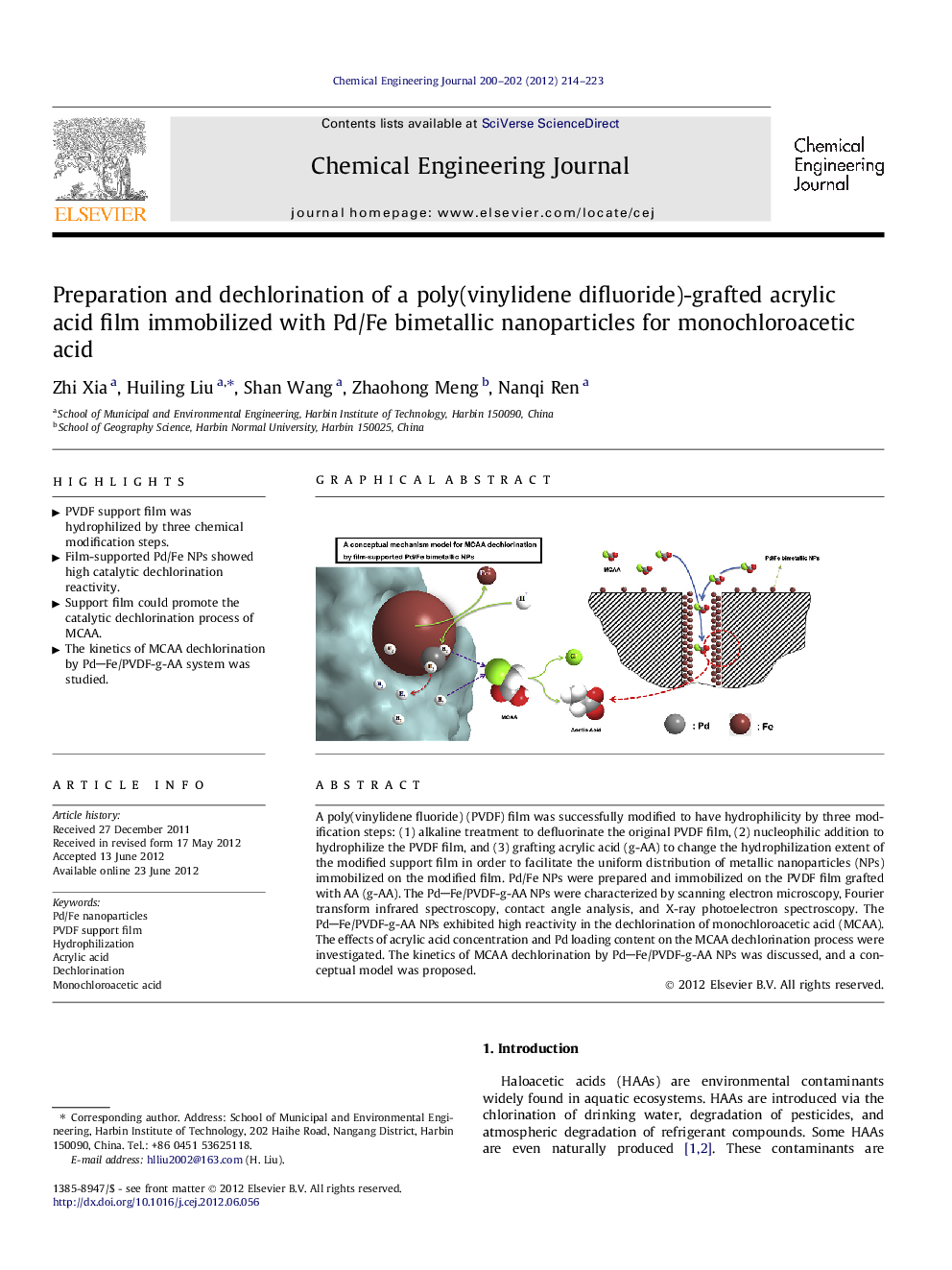
A poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) film was successfully modified to have hydrophilicity by three modification steps: (1) alkaline treatment to defluorinate the original PVDF film, (2) nucleophilic addition to hydrophilize the PVDF film, and (3) grafting acrylic acid (g-AA) to change the hydrophilization extent of the modified support film in order to facilitate the uniform distribution of metallic nanoparticles (NPs) immobilized on the modified film. Pd/Fe NPs were prepared and immobilized on the PVDF film grafted with AA (g-AA). The PdFe/PVDF-g-AA NPs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, contact angle analysis, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The PdFe/PVDF-g-AA NPs exhibited high reactivity in the dechlorination of monochloroacetic acid (MCAA). The effects of acrylic acid concentration and Pd loading content on the MCAA dechlorination process were investigated. The kinetics of MCAA dechlorination by PdFe/PVDF-g-AA NPs was discussed, and a conceptual model was proposed.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► PVDF support film was hydrophilized by three chemical modification steps.
► Film-supported Pd/Fe NPs showed high catalytic dechlorination reactivity.
► Support film could promote the catalytic dechlorination process of MCAA.
► The kinetics of MCAA dechlorination by PdFe/PVDF-g-AA system was studied.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volumes 200–202, 15 August 2012, Pages 214–223