| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981775 | 1539421 | 2013 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
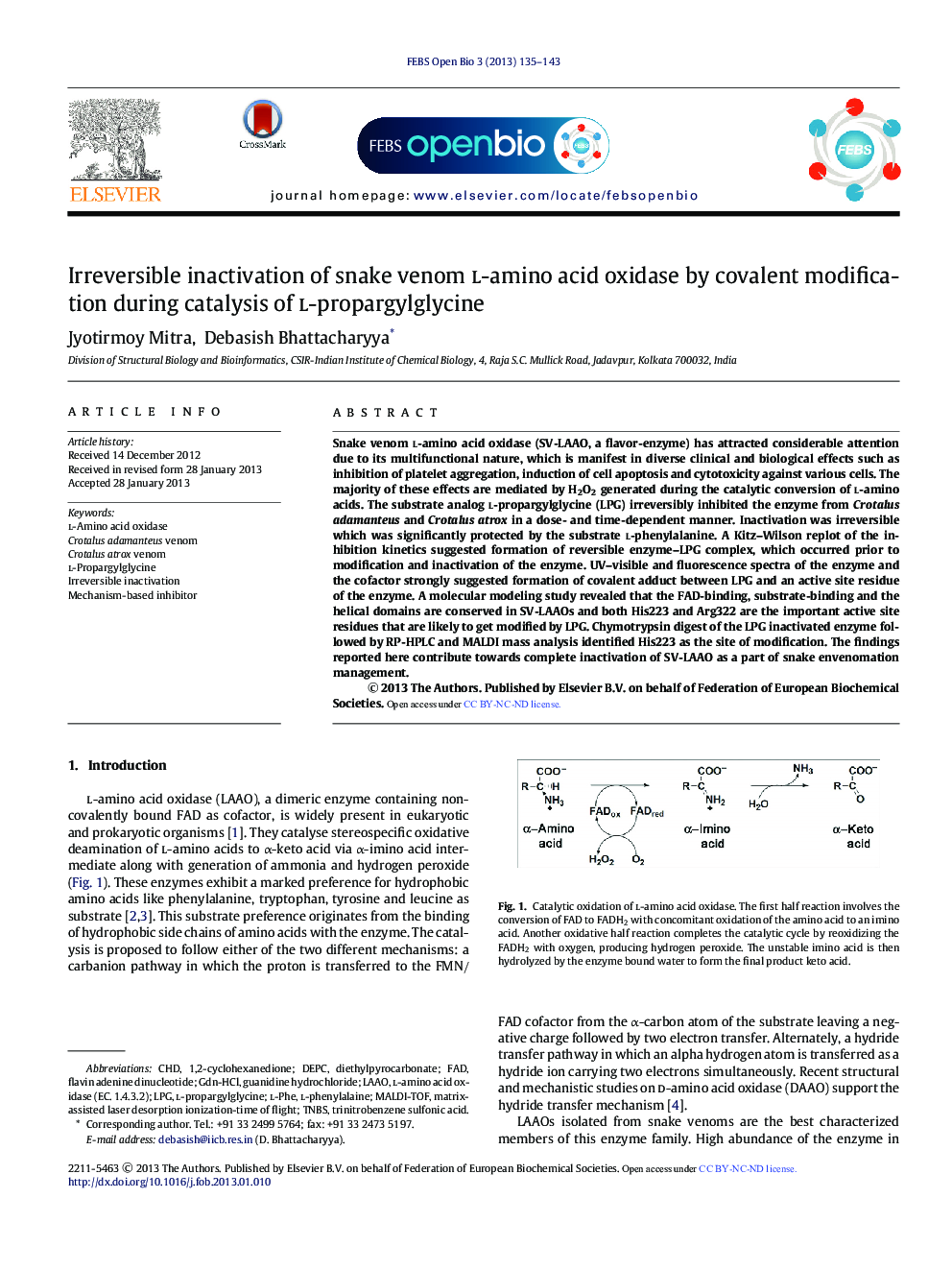
Snake venom l-amino acid oxidase (SV-LAAO, a flavor-enzyme) has attracted considerable attention due to its multifunctional nature, which is manifest in diverse clinical and biological effects such as inhibition of platelet aggregation, induction of cell apoptosis and cytotoxicity against various cells. The majority of these effects are mediated by H2O2 generated during the catalytic conversion of l-amino acids. The substrate analog l-propargylglycine (LPG) irreversibly inhibited the enzyme from Crotalus adamanteus and Crotalus atrox in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Inactivation was irreversible which was significantly protected by the substrate l-phenylalanine. A Kitz–Wilson replot of the inhibition kinetics suggested formation of reversible enzyme–LPG complex, which occurred prior to modification and inactivation of the enzyme. UV–visible and fluorescence spectra of the enzyme and the cofactor strongly suggested formation of covalent adduct between LPG and an active site residue of the enzyme. A molecular modeling study revealed that the FAD-binding, substrate-binding and the helical domains are conserved in SV-LAAOs and both His223 and Arg322 are the important active site residues that are likely to get modified by LPG. Chymotrypsin digest of the LPG inactivated enzyme followed by RP-HPLC and MALDI mass analysis identified His223 as the site of modification. The findings reported here contribute towards complete inactivation of SV-LAAO as a part of snake envenomation management.
▸ We describe the suicide inactivation of l-amino acid oxidase by l-propargylglycine (LPG). ▸ Protection against inactivation by l-Phe indicates modification at the substrate binding site. ▸ LPG modification takes place at active site His239, while FAD remains unaffected.
Journal: FEBS Open Bio - Volume 3, 2013, Pages 135–143