| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 258089 | 503611 | 2013 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
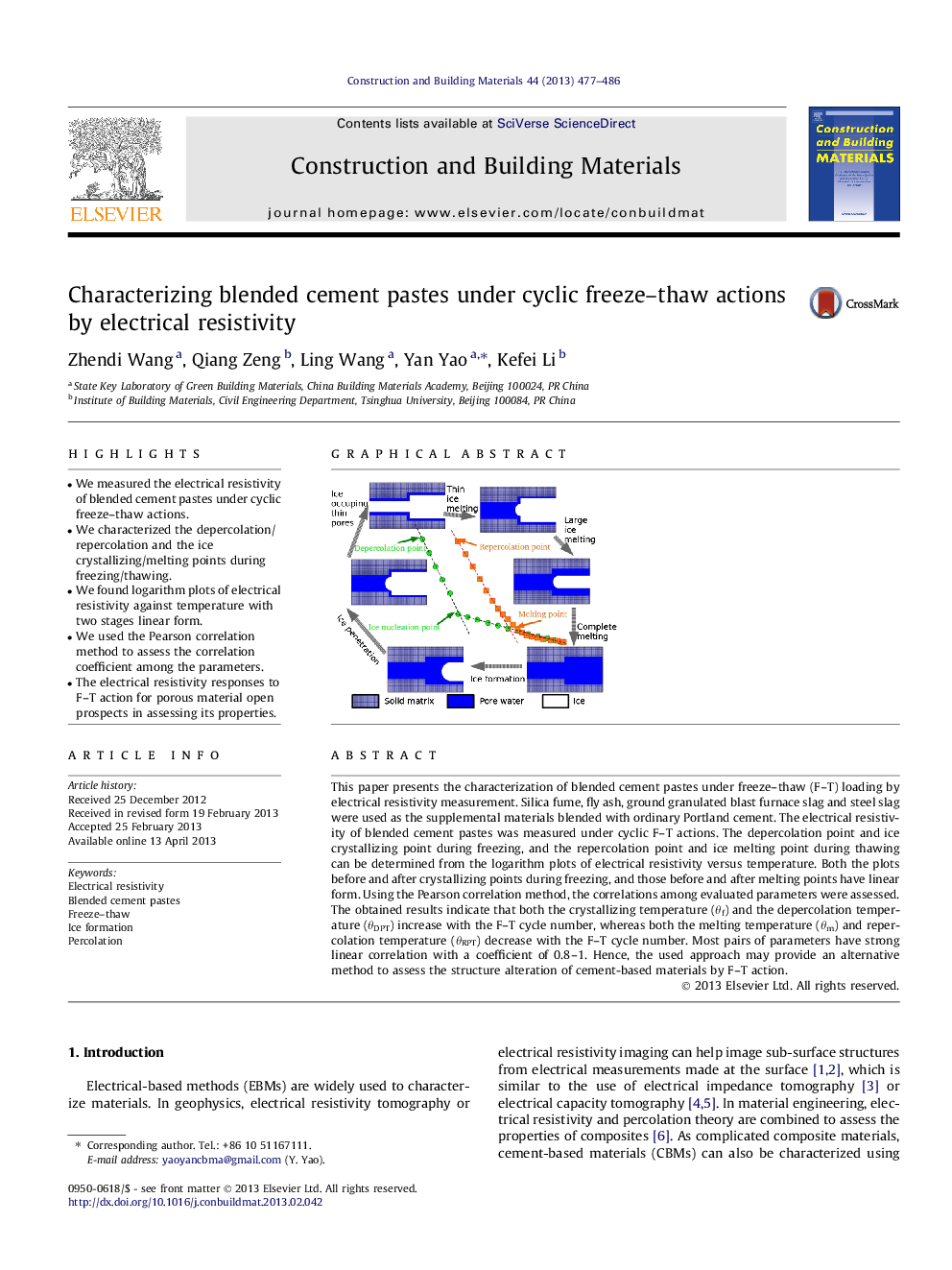
• We measured the electrical resistivity of blended cement pastes under cyclic freeze–thaw actions.
• We characterized the depercolation/repercolation and the ice crystallizing/melting points during freezing/thawing.
• We found logarithm plots of electrical resistivity against temperature with two stages linear form.
• We used the Pearson correlation method to assess the correlation coefficient among the parameters.
• The electrical resistivity responses to F–T action for porous material open prospects in assessing its properties.
This paper presents the characterization of blended cement pastes under freeze–thaw (F–T) loading by electrical resistivity measurement. Silica fume, fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag and steel slag were used as the supplemental materials blended with ordinary Portland cement. The electrical resistivity of blended cement pastes was measured under cyclic F–T actions. The depercolation point and ice crystallizing point during freezing, and the repercolation point and ice melting point during thawing can be determined from the logarithm plots of electrical resistivity versus temperature. Both the plots before and after crystallizing points during freezing, and those before and after melting points have linear form. Using the Pearson correlation method, the correlations among evaluated parameters were assessed. The obtained results indicate that both the crystallizing temperature (θf) and the depercolation temperature (θDPT) increase with the F–T cycle number, whereas both the melting temperature (θm) and repercolation temperature (θRPT) decrease with the F–T cycle number. Most pairs of parameters have strong linear correlation with a coefficient of 0.8–1. Hence, the used approach may provide an alternative method to assess the structure alteration of cement-based materials by F–T action.
We measured electrical resistivity of cement pastes blended with silic fume, fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag and blast steel furnace slag. By means of log-arithm plotting the electrical resistivity against temperature, both the freezing and thawing phases show two-stages curves with σ = 10Aθ+B. Crystallization/liquidlization and depercolation/repercolation account for the stage changes during freezing/thawing.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Construction and Building Materials - Volume 44, July 2013, Pages 477–486