| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792385 | 1155047 | 2015 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
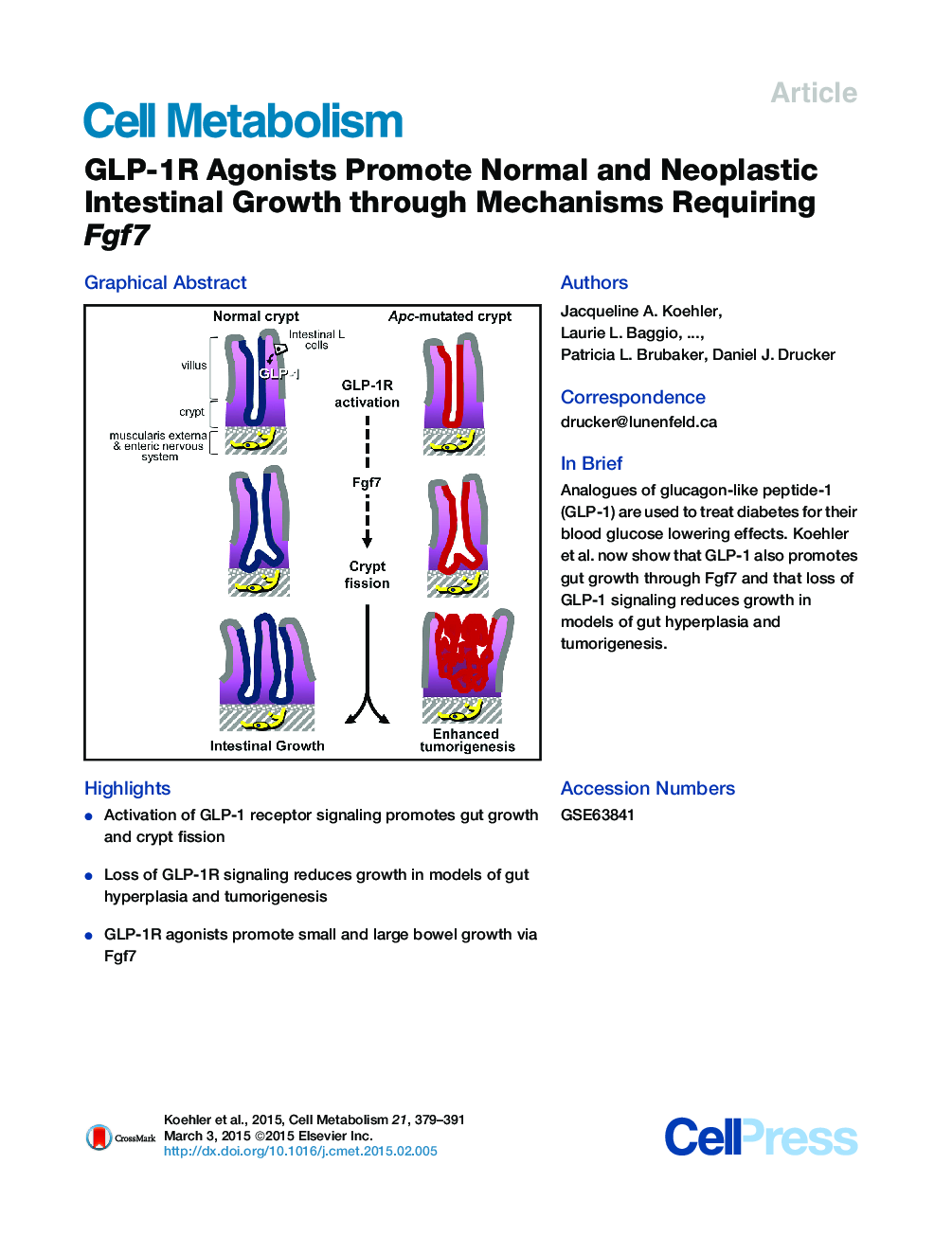
• Activation of GLP-1 receptor signaling promotes gut growth and crypt fission
• Loss of GLP-1R signaling reduces growth in models of gut hyperplasia and tumorigenesis
• GLP-1R agonists promote small and large bowel growth via Fgf7
SummaryGlucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secreted from enteroendocrine L cells promotes nutrient disposal via the incretin effect. However, the majority of L cells are localized to the distal gut, suggesting additional biological roles for GLP-1. Here, we demonstrate that GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) signaling controls mucosal expansion of the small bowel (SB) and colon. These actions did not require the epidermal growth factor (EGF) or intestinal epithelial insulin-like growth factor (IGF1) receptors but were absent in Glp1r−/− mice. Polyp number and size were increased in SB of exendin-4-treated ApcMin/+ mice, whereas polyp number was reduced in SB and colon of Glp1r−/−:ApcMin/+ mice. Exendin-4 increased fibroblast growth factor 7 (Fgf7) expression in colonic polyps of ApcMin/+ mice and failed to increase intestinal growth in mice lacking Fgf7. Exogenous exendin-4 and Fgf7 regulated an overlapping set of genes important for intestinal growth. Thus, gain and loss of GLP-1R signaling regulates gut growth and intestinal tumorigenesis.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (192 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 21, Issue 3, 3 March 2015, Pages 379–391