| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792393 | 1155047 | 2015 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
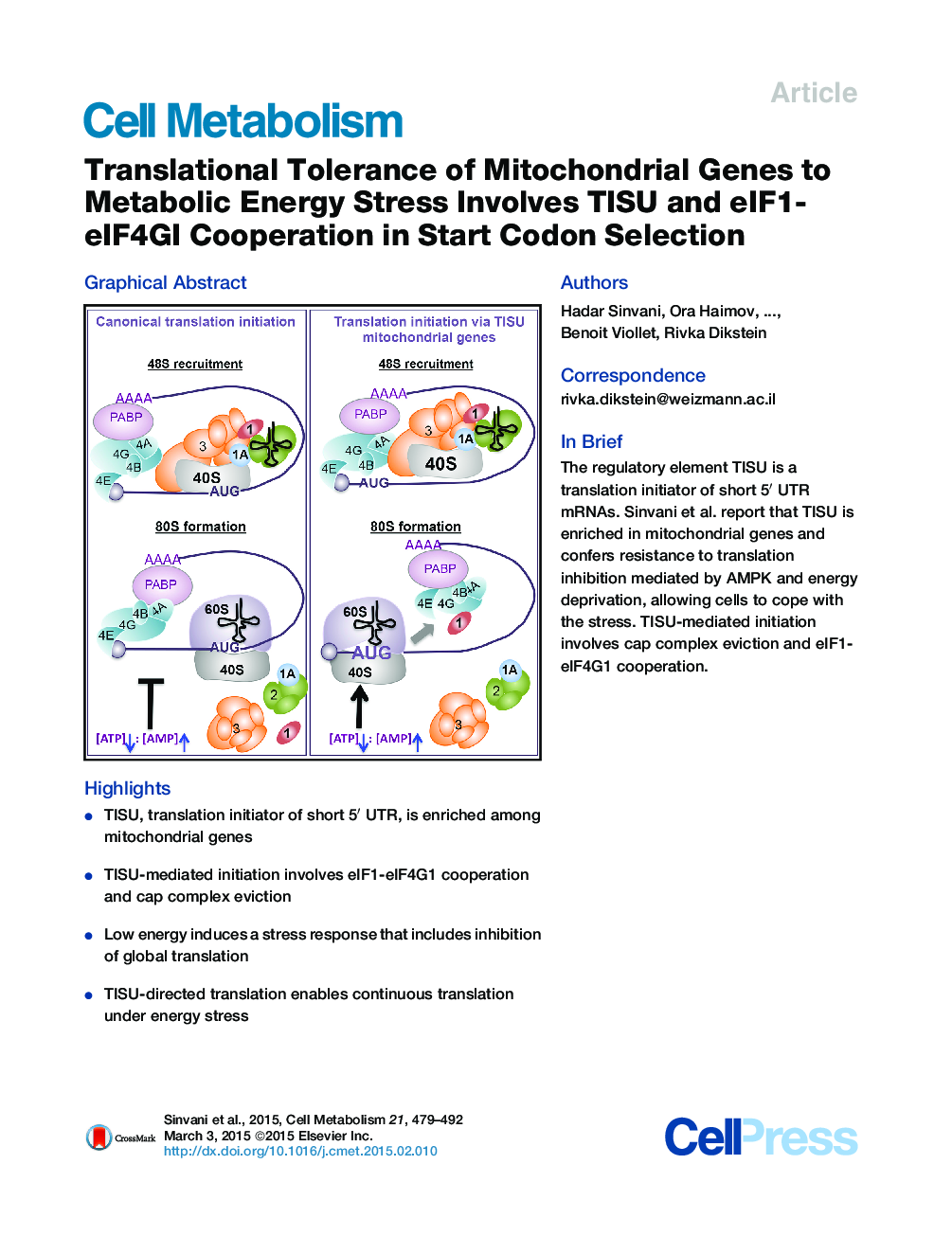
• TISU, translation initiator of short 5′ UTR, is enriched among mitochondrial genes
• TISU-mediated initiation involves eIF1-eIF4G1 cooperation and cap complex eviction
• Low energy induces a stress response that includes inhibition of global translation
• TISU-directed translation enables continuous translation under energy stress
SummaryProtein synthesis is a major energy-consuming process, which is rapidly repressed upon energy stress by AMPK. How energy deficiency affects translation of mRNAs that cope with the stress response is poorly understood. We found that mitochondrial genes remain translationally active upon energy deprivation. Surprisingly, inhibition of translation is partially retained in AMPKα1/AMPKα2 knockout cells. Mitochondrial mRNAs are enriched with TISU, a translation initiator of short 5′ UTR, which confers resistance specifically to energy stress. Purified 48S preinitiation complex is sufficient for initiation via TISU AUG, when preceded by a short 5′ UTR. eIF1 stimulates TISU but inhibits non-TISU-directed initiation. Remarkably, eIF4GI shares this activity and also interacts with eIF1. Furthermore, eIF4F is released upon 48S formation on TISU. These findings describe a specialized translation tolerance mechanism enabling continuous translation of TISU genes under energy stress and reveal that a key step in start codon selection of short 5′ UTR is eIF4F release.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (268 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 21, Issue 3, 3 March 2015, Pages 479–492