| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792410 | 1155048 | 2016 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Nutritional ketone bodies can promote the advantageous aspects to starvation ketosis
• Nutritional ketosis alters the hierarchy of substrate competition for respiration in exercise
• Ketosis increases metabolic flexibility during exercise, reducing glycolysis and increasing muscle fat oxidation
• Improved performance during cycling time trial suggests ketosis during exercise may be beneficial for some athletes
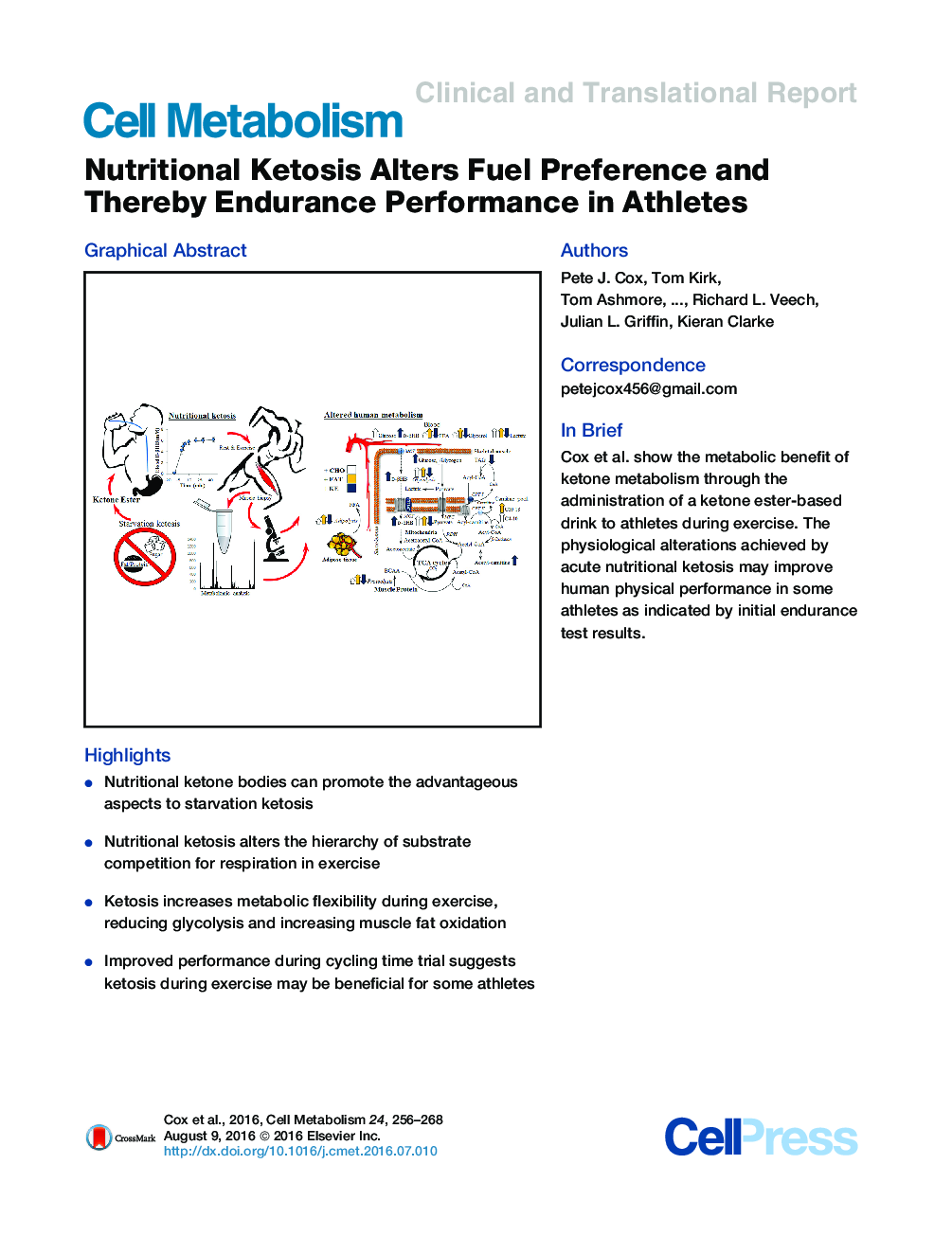
SummaryKetosis, the metabolic response to energy crisis, is a mechanism to sustain life by altering oxidative fuel selection. Often overlooked for its metabolic potential, ketosis is poorly understood outside of starvation or diabetic crisis. Thus, we studied the biochemical advantages of ketosis in humans using a ketone ester-based form of nutrition without the unwanted milieu of endogenous ketone body production by caloric or carbohydrate restriction. In five separate studies of 39 high-performance athletes, we show how this unique metabolic state improves physical endurance by altering fuel competition for oxidative respiration. Ketosis decreased muscle glycolysis and plasma lactate concentrations, while providing an alternative substrate for oxidative phosphorylation. Ketosis increased intramuscular triacylglycerol oxidation during exercise, even in the presence of normal muscle glycogen, co-ingested carbohydrate and elevated insulin. These findings may hold clues to greater human potential and a better understanding of fuel metabolism in health and disease.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (196 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 24, Issue 2, 9 August 2016, Pages 256–268