| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2937539 | 1576542 | 2016 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
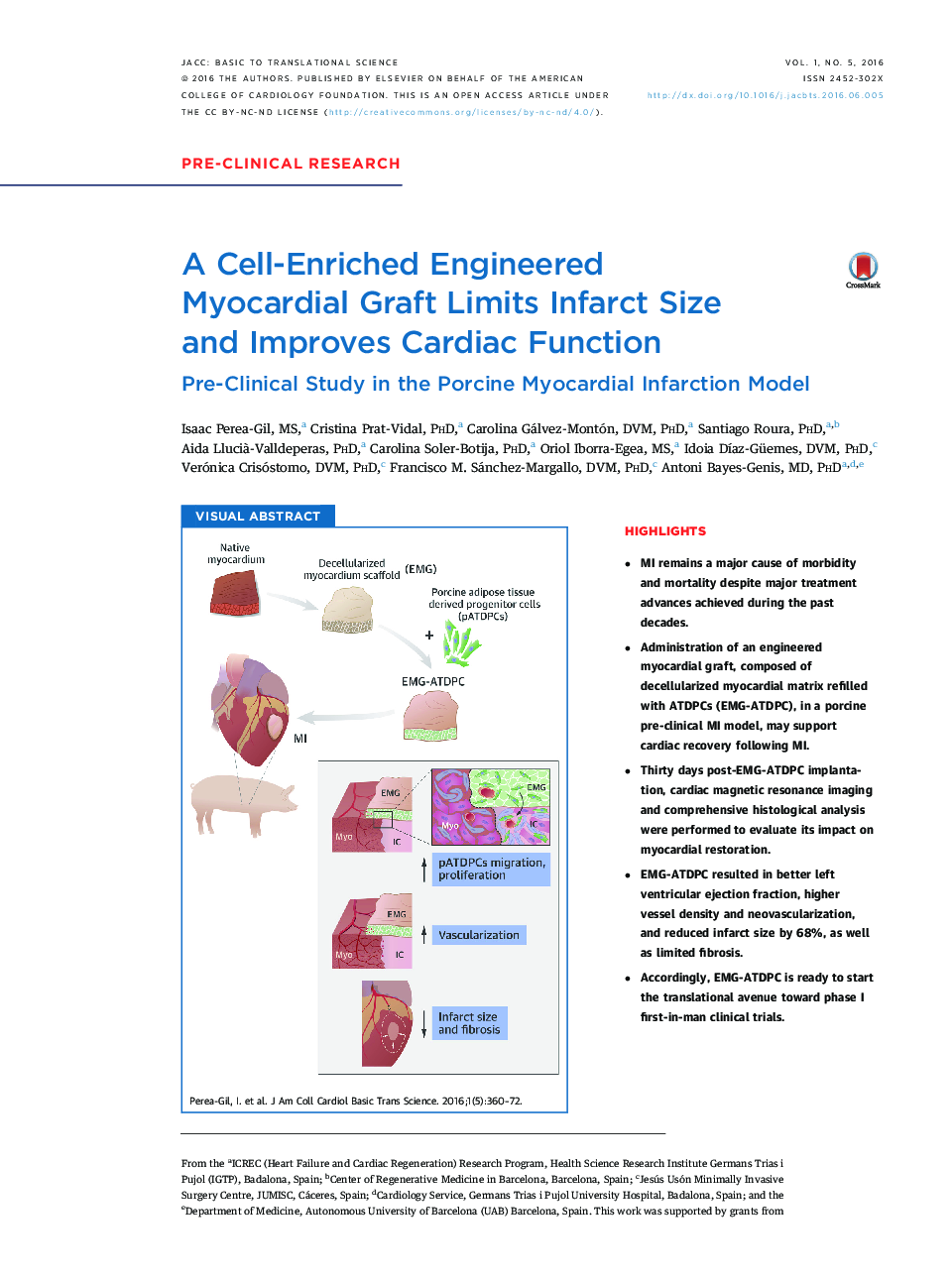
• MI remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality despite major treatment advances achieved during the past decades.
• Administration of an engineered myocardial graft, composed of decellularized myocardial matrix refilled with ATDPCs (EMG-ATDPC), in a porcine pre-clinical MI model, may support cardiac recovery following MI.
• Thirty days post-EMG-ATDPC implantation, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and comprehensive histological analysis were performed to evaluate its impact on myocardial restoration.
• EMG-ATDPC resulted in better left ventricular ejection fraction, higher vessel density and neovascularization, and reduced infarct size by 68%, as well as limited fibrosis.
• Accordingly, EMG-ATDPC is ready to start the translational avenue toward phase I first-in-man clinical trials.
SummaryMyocardial infarction (MI) remains a dreadful disease around the world, causing irreversible sequelae that shorten life expectancy and reduce quality of life despite current treatment. Here, the authors engineered a cell-enriched myocardial graft, composed of a decellularized myocardial matrix refilled with adipose tissue-derived progenitor cells (EMG-ATDPC). Once applied over the infarcted area in the swine MI model, the EMG-ATDPC improved cardiac function, reduced infarct size, attenuated fibrosis progression, and promoted neovascularization of the ischemic myocardium. The beneficial effects exerted by the EMG-ATDPC and the absence of identified adverse side effects should facilitate its clinical translation as a novel MI therapy in humans.
Visual AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (929 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: JACC: Basic to Translational Science - Volume 1, Issue 5, August 2016, Pages 360–372