| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4371069 | 1617016 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
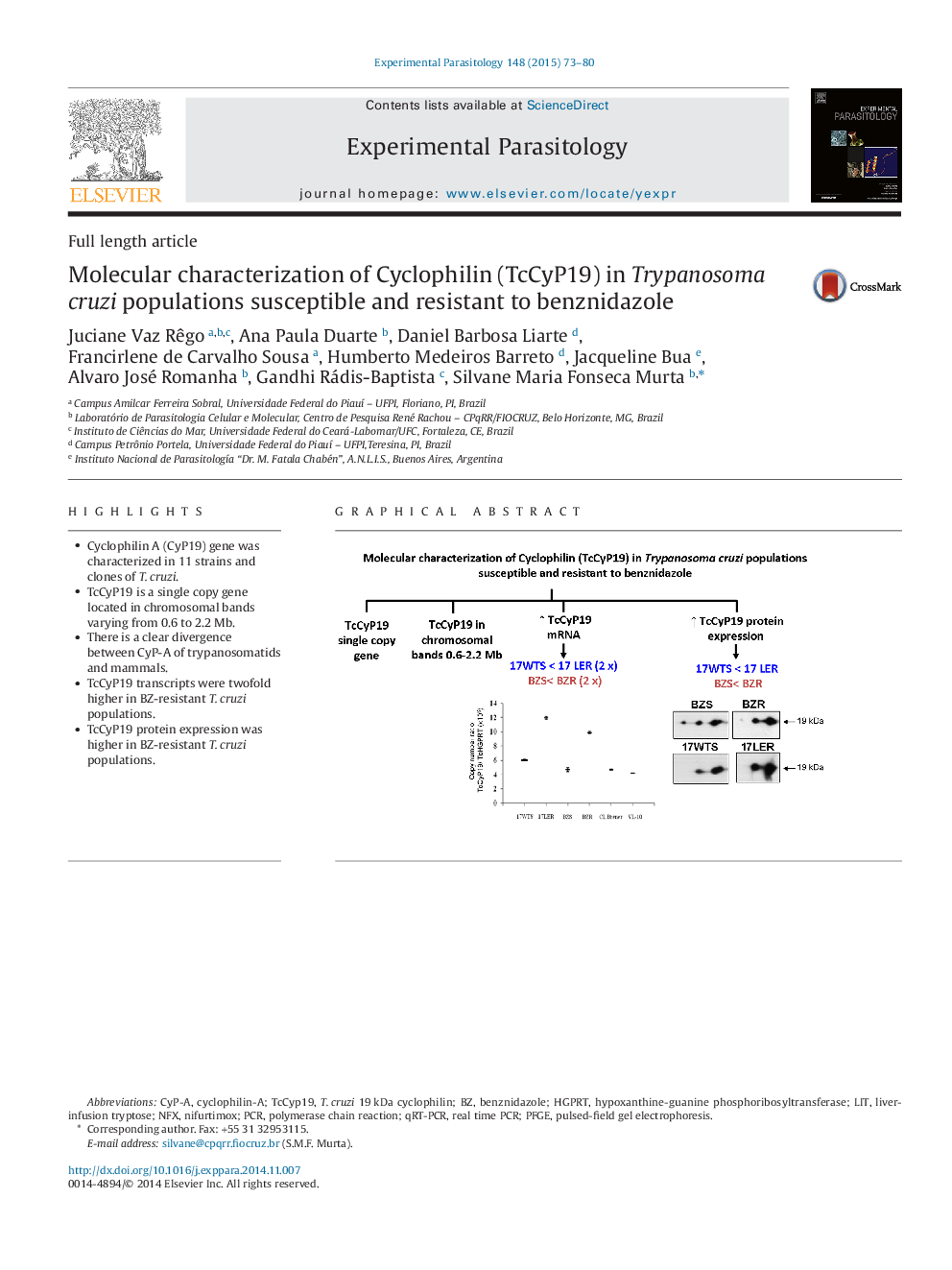
• Cyclophilin A (CyP19) gene was characterized in 11 strains and clones of T. cruzi.
• TcCyP19 is a single copy gene located in chromosomal bands varying from 0.6 to 2.2 Mb.
• There is a clear divergence between CyP-A of trypanosomatids and mammals.
• TcCyP19 transcripts were twofold higher in BZ-resistant T. cruzi populations.
• TcCyP19 protein expression was higher in BZ-resistant T. cruzi populations.
Cyclophilin (CyP), a peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase, is a key molecule with diverse biological functions that include roles in molecular chaperoning, stress response, immune modulation, and signal transduction. In this respect, CyP could serve as a potential drug target in disease-causing parasites. Previous studies employing proteomics techniques have shown that the TcCyP19 isoform was more abundant in a benznidazole (BZ)-resistant Trypanosoma cruzi population than in its susceptible counterpart. In this study, TcCyP19 has been characterized in BZ-susceptible and BZ-resistant T. cruzi populations. Phylogenetic analysis revealed a clear dichotomy between Cyphophilin A (CyPA) sequences from trypanosomatids and mammals. Sequencing analysis revealed that the amino acid sequences of TcCyP19 were identical among the T. cruzi samples analyzed. Southern blot analysis showed that TcCyP19 is a single-copy gene, located in chromosomal bands varying in size from 0.68 to 2.2 Mb, depending on the strain of T. cruzi. Northern blot and qPCR indicated that the levels of TcCyP19 mRNA were twofold higher in drug-resistant T. cruzi populations than in their drug-susceptible counterparts. Similarly, as determined by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis immunoblot, the expression of TcCyP19 protein was increased to the same degree in BZ-resistant T. cruzi populations. No differences in TcCyP19 mRNA and protein expression levels were observed between the susceptible and the naturally resistant T. cruzi strains analyzed. Taken together, these data indicate that cyclophilin TcCyP19 expression is up-regulated at both transcriptional and translational levels in T. cruzi populations that were in vitro-induced and in vivo-selected for resistance to BZ.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Experimental Parasitology - Volume 148, January 2015, Pages 73–80