| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4428408 | 1619758 | 2015 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
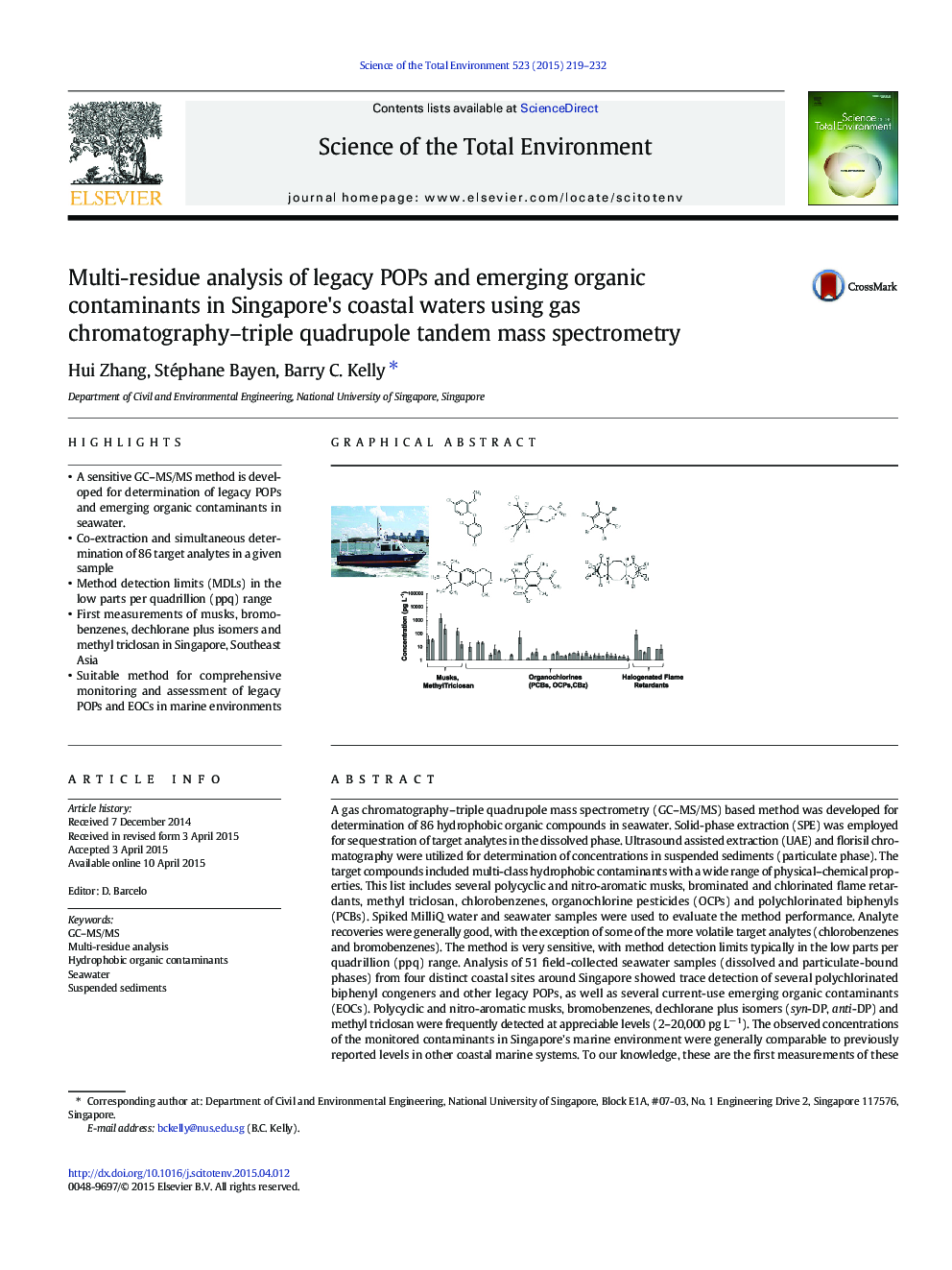
• A sensitive GC–MS/MS method is developed for determination of legacy POPs and emerging organic contaminants in seawater.
• Co-extraction and simultaneous determination of 86 target analytes in a given sample
• Method detection limits (MDLs) in the low parts per quadrillion (ppq) range
• First measurements of musks, bromobenzenes, dechlorane plus isomers and methyl triclosan in Singapore, Southeast Asia
• Suitable method for comprehensive monitoring and assessment of legacy POPs and EOCs in marine environments
A gas chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) based method was developed for determination of 86 hydrophobic organic compounds in seawater. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) was employed for sequestration of target analytes in the dissolved phase. Ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) and florisil chromatography were utilized for determination of concentrations in suspended sediments (particulate phase). The target compounds included multi-class hydrophobic contaminants with a wide range of physical–chemical properties. This list includes several polycyclic and nitro-aromatic musks, brominated and chlorinated flame retardants, methyl triclosan, chlorobenzenes, organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Spiked MilliQ water and seawater samples were used to evaluate the method performance. Analyte recoveries were generally good, with the exception of some of the more volatile target analytes (chlorobenzenes and bromobenzenes). The method is very sensitive, with method detection limits typically in the low parts per quadrillion (ppq) range. Analysis of 51 field-collected seawater samples (dissolved and particulate-bound phases) from four distinct coastal sites around Singapore showed trace detection of several polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and other legacy POPs, as well as several current-use emerging organic contaminants (EOCs). Polycyclic and nitro-aromatic musks, bromobenzenes, dechlorane plus isomers (syn-DP, anti-DP) and methyl triclosan were frequently detected at appreciable levels (2–20,000 pg L− 1). The observed concentrations of the monitored contaminants in Singapore's marine environment were generally comparable to previously reported levels in other coastal marine systems. To our knowledge, these are the first measurements of these emerging contaminants of concern in Singapore or Southeast Asia. The developed method may prove beneficial for future environmental monitoring of hydrophobic organic contaminants in marine environments. Further, the study provides novel information regarding several potentially hazardous contaminants of concern in Singapore's marine environment, which will aid future risk assessment initiatives.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Science of The Total Environment - Volume 523, 1 August 2015, Pages 219–232