| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4438102 | 1310931 | 2015 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
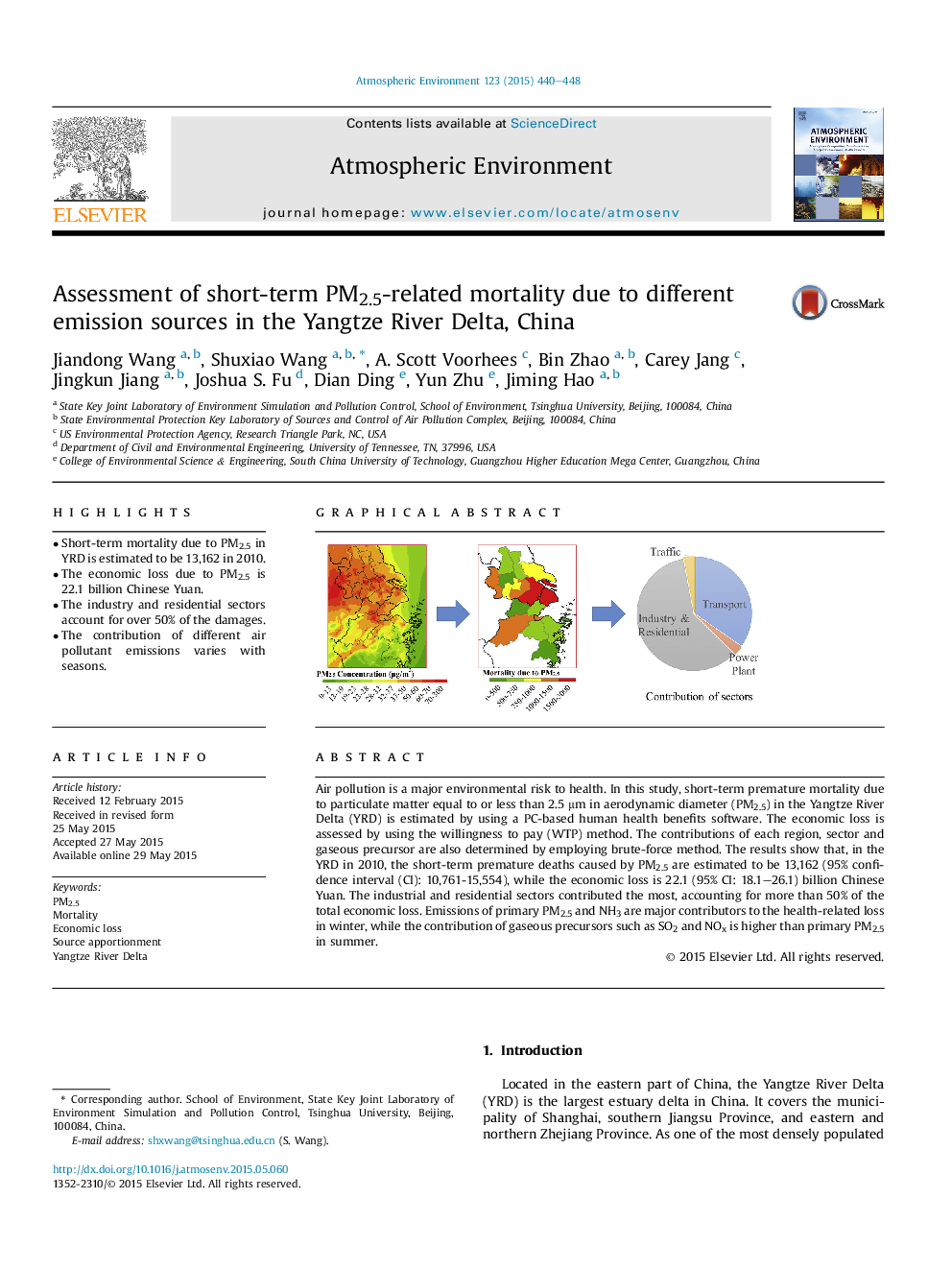
• Short-term mortality due to PM2.5 in YRD is estimated to be 13,162 in 2010.
• The economic loss due to PM2.5 is 22.1 billion Chinese Yuan.
• The industry and residential sectors account for over 50% of the damages.
• The contribution of different air pollutant emissions varies with seasons.
Air pollution is a major environmental risk to health. In this study, short-term premature mortality due to particulate matter equal to or less than 2.5 μm in aerodynamic diameter (PM2.5) in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) is estimated by using a PC-based human health benefits software. The economic loss is assessed by using the willingness to pay (WTP) method. The contributions of each region, sector and gaseous precursor are also determined by employing brute-force method. The results show that, in the YRD in 2010, the short-term premature deaths caused by PM2.5 are estimated to be 13,162 (95% confidence interval (CI): 10,761-15,554), while the economic loss is 22.1 (95% CI: 18.1–26.1) billion Chinese Yuan. The industrial and residential sectors contributed the most, accounting for more than 50% of the total economic loss. Emissions of primary PM2.5 and NH3 are major contributors to the health-related loss in winter, while the contribution of gaseous precursors such as SO2 and NOx is higher than primary PM2.5 in summer.
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (356 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Atmospheric Environment - Volume 123, Part B, December 2015, Pages 440–448