| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4998016 | 1459921 | 2016 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
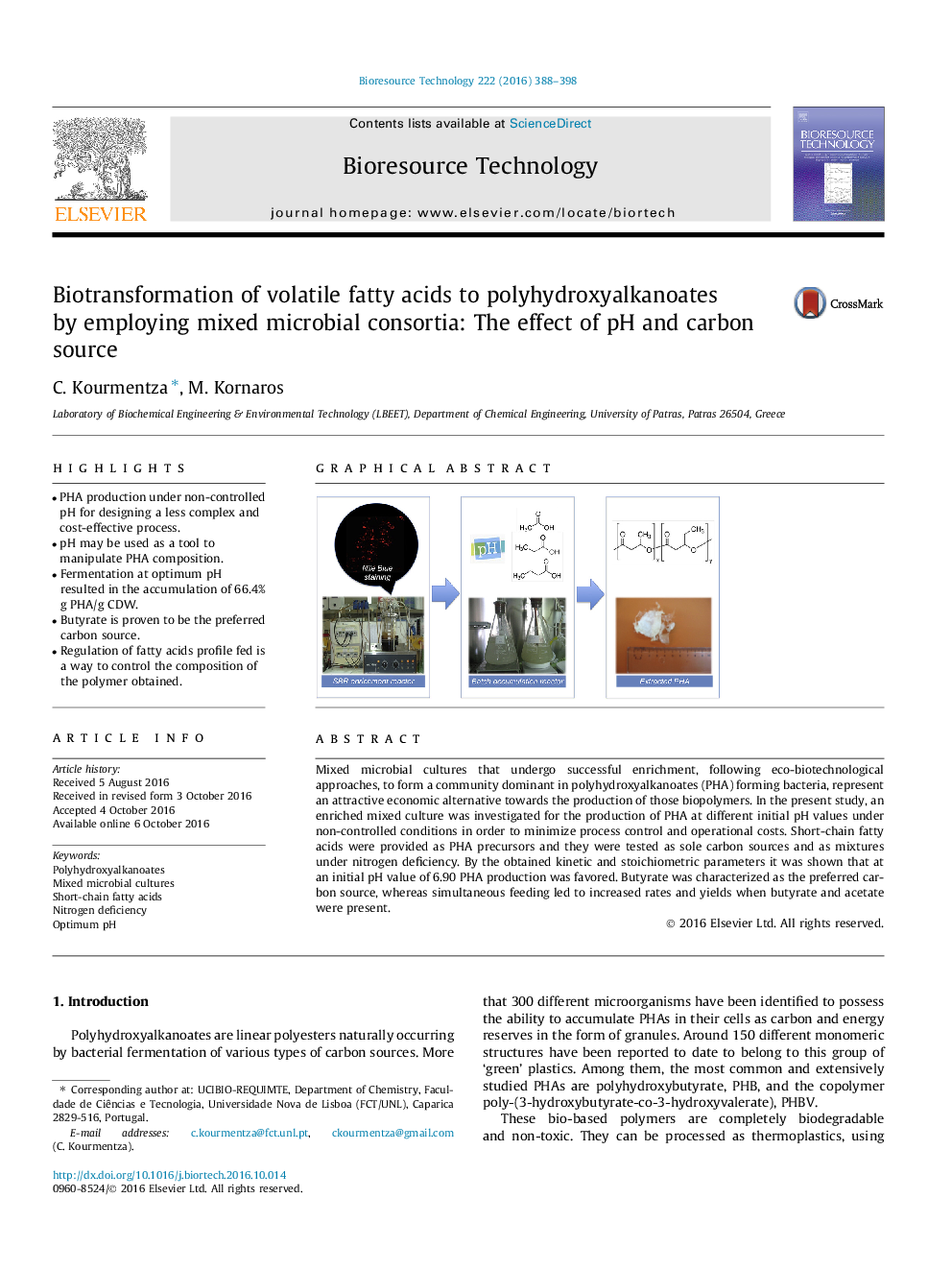
- PHA production under non-controlled pH for designing a less complex and cost-effective process.
- pH may be used as a tool to manipulate PHA composition.
- Fermentation at optimum pH resulted in the accumulation of 66.4% g PHA/g CDW.
- Butyrate is proven to be the preferred carbon source.
- Regulation of fatty acids profile fed is a way to control the composition of the polymer obtained.
Mixed microbial cultures that undergo successful enrichment, following eco-biotechnological approaches, to form a community dominant in polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) forming bacteria, represent an attractive economic alternative towards the production of those biopolymers. In the present study, an enriched mixed culture was investigated for the production of PHA at different initial pH values under non-controlled conditions in order to minimize process control and operational costs. Short-chain fatty acids were provided as PHA precursors and they were tested as sole carbon sources and as mixtures under nitrogen deficiency. By the obtained kinetic and stoichiometric parameters it was shown that at an initial pH value of 6.90 PHA production was favored. Butyrate was characterized as the preferred carbon source, whereas simultaneous feeding led to increased rates and yields when butyrate and acetate were present.
182
Journal: Bioresource Technology - Volume 222, December 2016, Pages 388-398