| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5750277 | 1619696 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- Ambient VOCs concentration can barely represent real exposure level occupationally.
- Real-time exposure concentration fluctuates with different activity patterns.
- Actual exposure level merely depends on the paint type that was consumed.
- Higher potential inhalation does imply probability of increasing inhalation dose.
Epidemiologic studies regarding solvent-based paints (SBPs) containing VOCs have demonstrated a strong correlation between chronic and acute adverse health effects and the SBPs. Therefore, new environmentally friendly paints as substitutes containing less or none VOCs have been rapidly developed in research for future sustainable use. However, a few studies focusing on penetration and exposure condition of the substitute have been reported duo to the complexity and inaccessibility of painting industry. Surveys specifically looking at the present status of exposure condition were conducted to ascertain the popularization of water-based paints (WBPs) which concluded that markers of SBPs were detected in all 134 samples indicating bad industrial penetration. VOCs exposure concentrations of painters ranged from 3.8 to 18.2Â mg/m3 for WBPs, 3.5Â ÃÂ 103 to 14.8Â ÃÂ 103Â mg/m3 for SBPs, respectively. The negative correlation between ambient concentration and breathing zone concentration suggested the former was incapable of representing the actual exposure concentration. The real-time concentration was proved to be closely associated with the activity patterns while the mean concentration level was found mostly dependent on the paint types. Authentic inhalation dose ranged from 7.68 to 15.84Â mg (WBPs) and 3.84 to 15.59Â g (SBPs), respectively, for occupational painters (work 8Â h per day) and the total inhalation dose was estimated through a new conception. The findings suggested that WBPs could significantly reduce VOCs emission and occupational exposure.
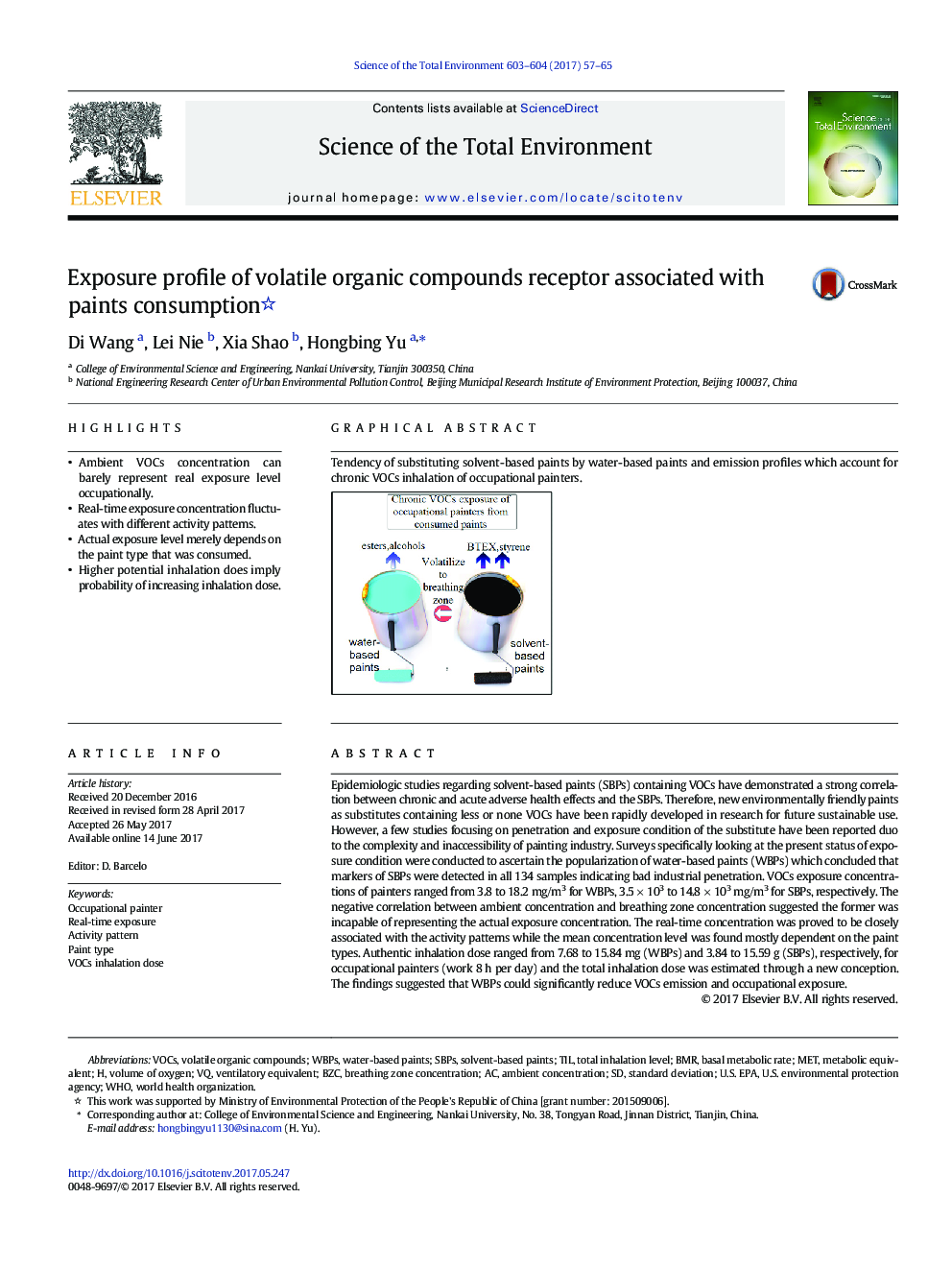
Tendency of substituting solvent-based paints by water-based paints and emission profiles which account for chronic VOCs inhalation of occupational painters.152
Journal: Science of The Total Environment - Volumes 603â604, 15 December 2017, Pages 57-65