| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5750829 | 1619702 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
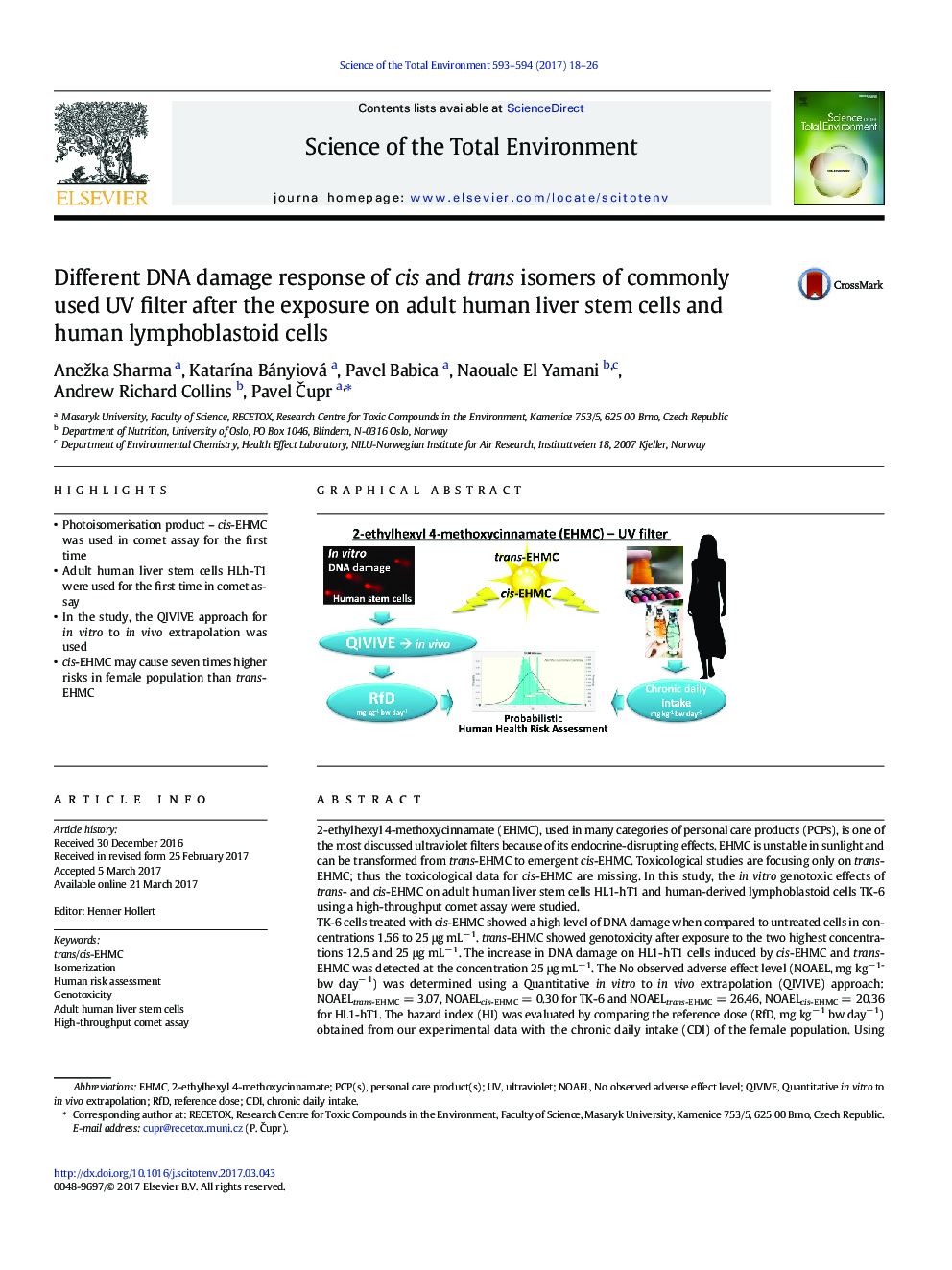
- Photoisomerisation product - cis-EHMC was used in comet assay for the first time
- Adult human liver stem cells HLh-T1 were used for the first time in comet assay
- In the study, the QIVIVE approach for in vitro to in vivo extrapolation was used
- cis-EHMC may cause seven times higher risks in female population than trans-EHMC
2-ethylhexyl 4-methoxycinnamate (EHMC), used in many categories of personal care products (PCPs), is one of the most discussed ultraviolet filters because of its endocrine-disrupting effects. EHMC is unstable in sunlight and can be transformed from trans-EHMC to emergent cis-EHMC. Toxicological studies are focusing only on trans-EHMC; thus the toxicological data for cis-EHMC are missing. In this study, the in vitro genotoxic effects of trans- and cis-EHMC on adult human liver stem cells HL1-hT1 and human-derived lymphoblastoid cells TK-6 using a high-throughput comet assay were studied.TK-6 cells treated with cis-EHMC showed a high level of DNA damage when compared to untreated cells in concentrations 1.56 to 25 μg mLâ 1. trans-EHMC showed genotoxicity after exposure to the two highest concentrations 12.5 and 25 μg mLâ 1. The increase in DNA damage on HL1-hT1 cells induced by cis-EHMC and trans-EHMC was detected at the concentration 25 μg mLâ 1. The No observed adverse effect level (NOAEL, mg kgâ 1 bw dayâ 1) was determined using a Quantitative in vitro to in vivo extrapolation (QIVIVE) approach: NOAELtrans-EHMC = 3.07, NOAELcis-EHMC = 0.30 for TK-6 and NOAELtrans-EHMC = 26.46, NOAELcis-EHMC = 20.36 for HL1-hT1. The hazard index (HI) was evaluated by comparing the reference dose (RfD, mg kgâ 1 bw dayâ 1) obtained from our experimental data with the chronic daily intake (CDI) of the female population. Using comet assay experimental data with the more sensitive TK-6 cells, HIcis-EHMC was 7 times higher than HItrans-EHMC. In terms of CDI, relative contributions were; dermal exposure route > oral > inhalation. According to our results we recommend the RfDtrans-EHMC = 0.20 and RfDcis-EHMC = 0.02 for trans-EHMC and cis-EHMC, respectively, to use for human health risk assessment.The significant difference in trans-EHMC and cis-EHMC response points to the need for toxicological reevaluation and application reassessment of both isomers in PCPs.
271
Journal: Science of The Total Environment - Volumes 593â594, 1 September 2017, Pages 18-26