| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 599244 | 1454269 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
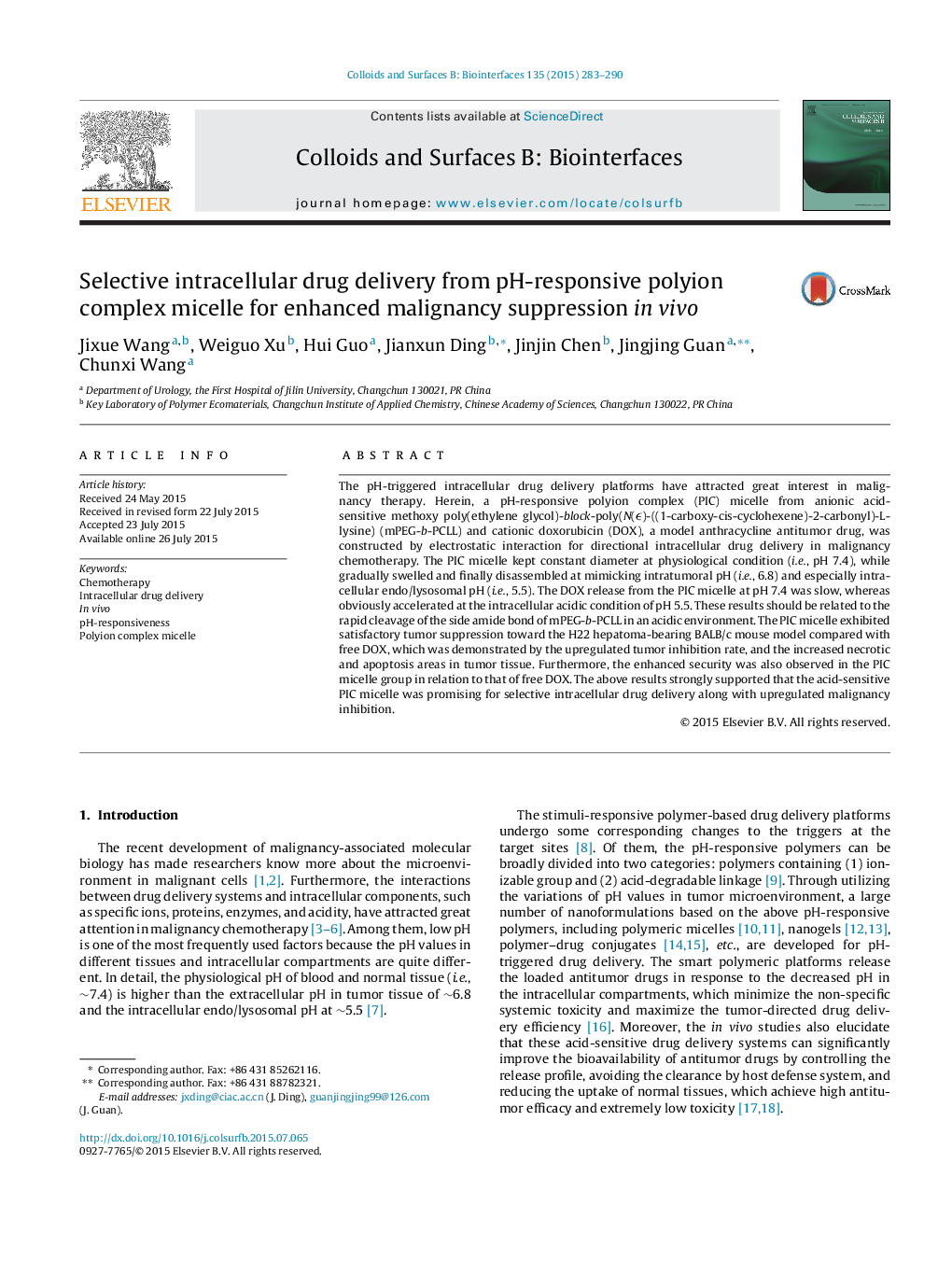
• A pH-responsive polyion complex (PIC) micelle is prepared from anionic acid-sensitive block copolymer and cationic doxorubicin (DOX).
• The PIC micelle exhibits acid-induced swelling and even disintegration.
• The DOX release can be accelerated by the intracellular acidic condition.
• The PIC micelle demonstrates exceptional tumor inhibition and security.
The pH-triggered intracellular drug delivery platforms have attracted great interest in malignancy therapy. Herein, a pH-responsive polyion complex (PIC) micelle from anionic acid-sensitive methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(N(ϵ)-((1-carboxy-cis-cyclohexene)-2-carbonyl)-L-lysine) (mPEG-b-PCLL) and cationic doxorubicin (DOX), a model anthracycline antitumor drug, was constructed by electrostatic interaction for directional intracellular drug delivery in malignancy chemotherapy. The PIC micelle kept constant diameter at physiological condition (i.e., pH 7.4), while gradually swelled and finally disassembled at mimicking intratumoral pH (i.e., 6.8) and especially intracellular endo/lysosomal pH (i.e., 5.5). The DOX release from the PIC micelle at pH 7.4 was slow, whereas obviously accelerated at the intracellular acidic condition of pH 5.5. These results should be related to the rapid cleavage of the side amide bond of mPEG-b-PCLL in an acidic environment. The PIC micelle exhibited satisfactory tumor suppression toward the H22 hepatoma-bearing BALB/c mouse model compared with free DOX, which was demonstrated by the upregulated tumor inhibition rate, and the increased necrotic and apoptosis areas in tumor tissue. Furthermore, the enhanced security was also observed in the PIC micelle group in relation to that of free DOX. The above results strongly supported that the acid-sensitive PIC micelle was promising for selective intracellular drug delivery along with upregulated malignancy inhibition.
A pH-responsive polyion complex micelle is exploited for targeting intracellular drug delivery with upregulated antitumor efficacy in vivo.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces - Volume 135, 1 November 2015, Pages 283–290