| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 624071 | 1455382 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
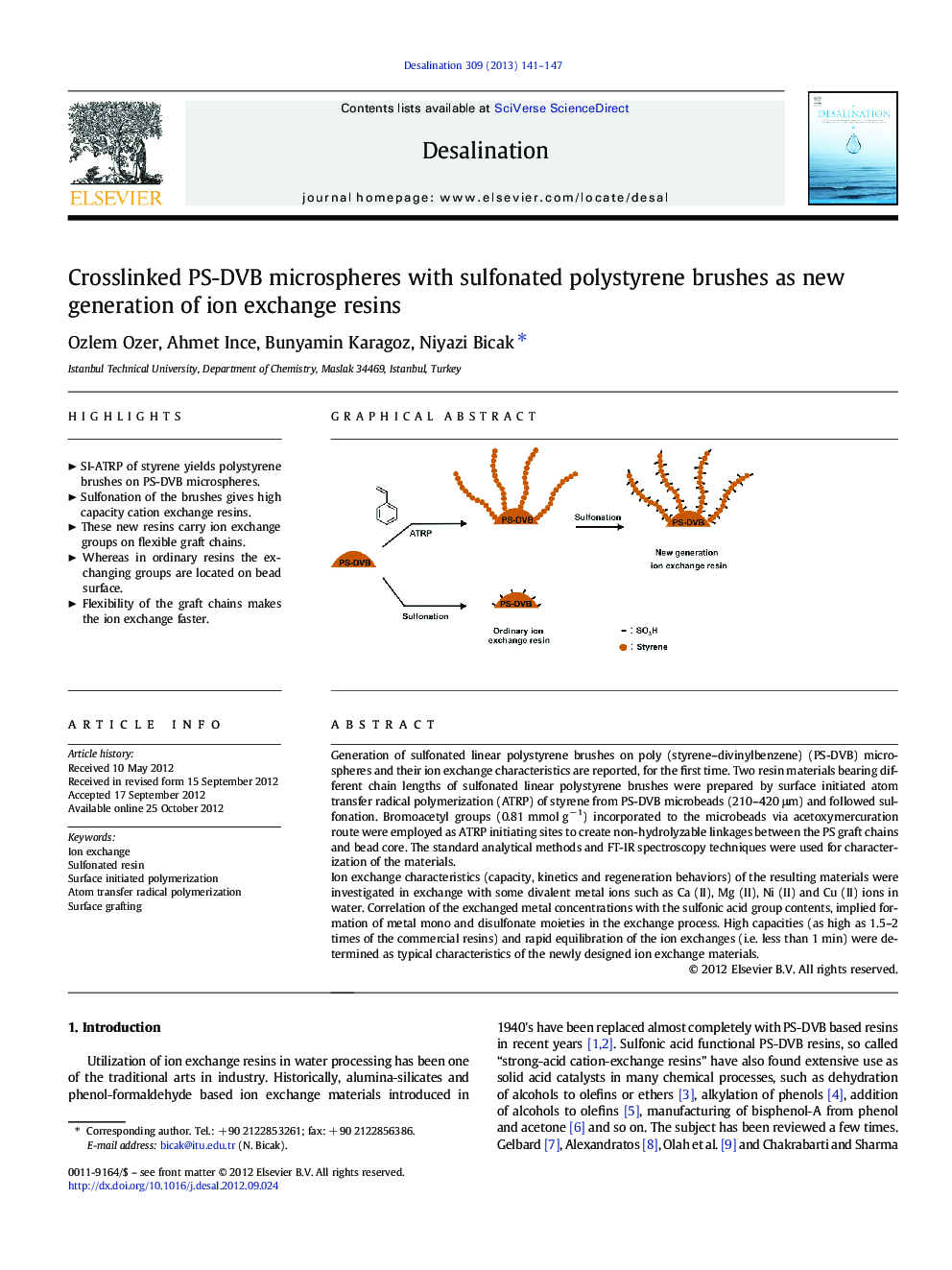
Generation of sulfonated linear polystyrene brushes on poly (styrene–divinylbenzene) (PS-DVB) microspheres and their ion exchange characteristics are reported, for the first time. Two resin materials bearing different chain lengths of sulfonated linear polystyrene brushes were prepared by surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of styrene from PS-DVB microbeads (210–420 μm) and followed sulfonation. Bromoacetyl groups (0.81 mmol g− 1) incorporated to the microbeads via acetoxymercuration route were employed as ATRP initiating sites to create non-hydrolyzable linkages between the PS graft chains and bead core. The standard analytical methods and FT-IR spectroscopy techniques were used for characterization of the materials.Ion exchange characteristics (capacity, kinetics and regeneration behaviors) of the resulting materials were investigated in exchange with some divalent metal ions such as Ca (II), Mg (II), Ni (II) and Cu (II) ions in water. Correlation of the exchanged metal concentrations with the sulfonic acid group contents, implied formation of metal mono and disulfonate moieties in the exchange process. High capacities (as high as 1.5–2 times of the commercial resins) and rapid equilibration of the ion exchanges (i.e. less than 1 min) were determined as typical characteristics of the newly designed ion exchange materials.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► SI-ATRP of styrene yields polystyrene brushes on PS-DVB microspheres.
► Sulfonation of the brushes gives high capacity cation exchange resins.
► These new resins carry ion exchange groups on flexible graft chains.
► Whereas in ordinary resins the exchanging groups are located on bead surface.
► Flexibility of the graft chains makes the ion exchange faster.
Journal: Desalination - Volume 309, 15 January 2013, Pages 141–147