| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6327834 | 1619768 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
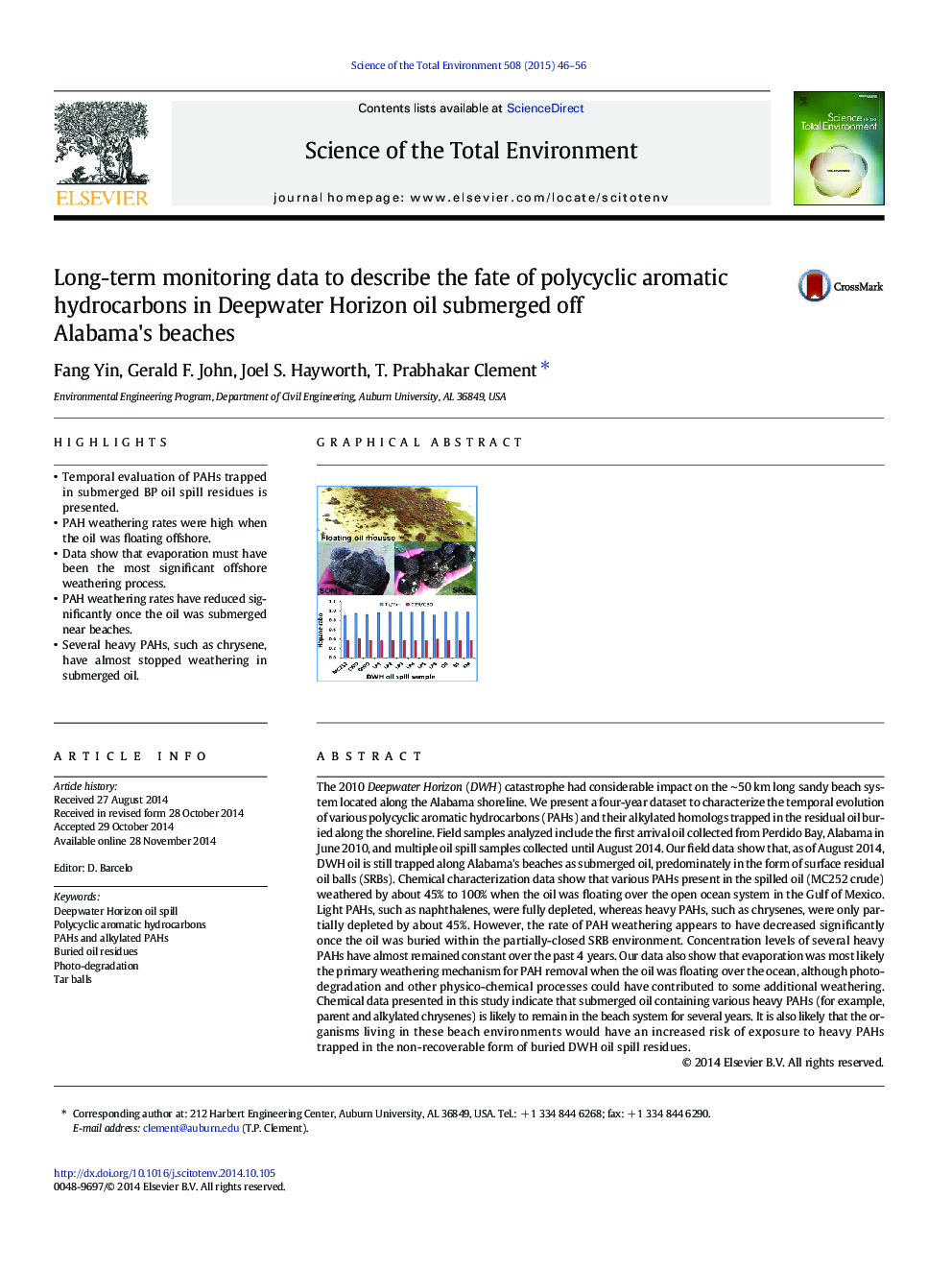
- Temporal evaluation of PAHs trapped in submerged BP oil spill residues is presented.
- PAH weathering rates were high when the oil was floating offshore.
- Data show that evaporation must have been the most significant offshore weathering process.
- PAH weathering rates have reduced significantly once the oil was submerged near beaches.
- Several heavy PAHs, such as chrysene, have almost stopped weathering in submerged oil.
The 2010 Deepwater Horizon (DWH) catastrophe had considerable impact on the â¼50Â km long sandy beach system located along the Alabama shoreline. We present a four-year dataset to characterize the temporal evolution of various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their alkylated homologs trapped in the residual oil buried along the shoreline. Field samples analyzed include the first arrival oil collected from Perdido Bay, Alabama in June 2010, and multiple oil spill samples collected until August 2014. Our field data show that, as of August 2014, DWH oil is still trapped along Alabama's beaches as submerged oil, predominately in the form of surface residual oil balls (SRBs). Chemical characterization data show that various PAHs present in the spilled oil (MC252 crude) weathered by about 45% to 100% when the oil was floating over the open ocean system in the Gulf of Mexico. Light PAHs, such as naphthalenes, were fully depleted, whereas heavy PAHs, such as chrysenes, were only partially depleted by about 45%. However, the rate of PAH weathering appears to have decreased significantly once the oil was buried within the partially-closed SRB environment. Concentration levels of several heavy PAHs have almost remained constant over the past 4Â years. Our data also show that evaporation was most likely the primary weathering mechanism for PAH removal when the oil was floating over the ocean, although photo-degradation and other physico-chemical processes could have contributed to some additional weathering. Chemical data presented in this study indicate that submerged oil containing various heavy PAHs (for example, parent and alkylated chrysenes) is likely to remain in the beach system for several years. It is also likely that the organisms living in these beach environments would have an increased risk of exposure to heavy PAHs trapped in the non-recoverable form of buried DWH oil spill residues.
231
Journal: Science of The Total Environment - Volume 508, 1 March 2015, Pages 46-56