| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465503 | 1422952 | 2017 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
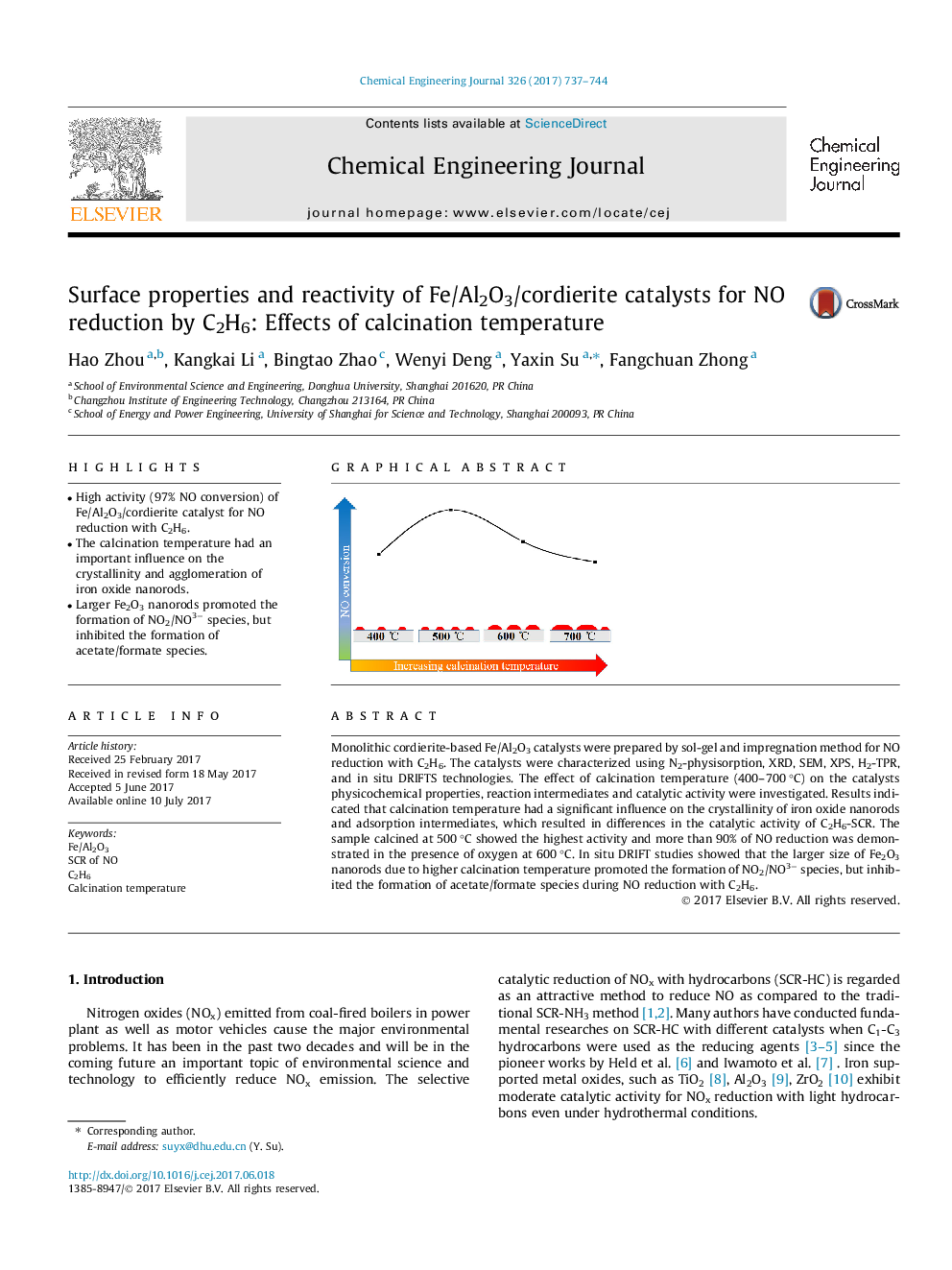
- High activity (97% NO conversion) of Fe/Al2O3/cordierite catalyst for NO reduction with C2H6.
- The calcination temperature had an important influence on the crystallinity and agglomeration of iron oxide nanorods.
- Larger Fe2O3 nanorods promoted the formation of NO2/NO3â species, but inhibited the formation of acetate/formate species.
Monolithic cordierite-based Fe/Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by sol-gel and impregnation method for NO reduction with C2H6. The catalysts were characterized using N2-physisorption, XRD, SEM, XPS, H2-TPR, and in situ DRIFTS technologies. The effect of calcination temperature (400-700 °C) on the catalysts physicochemical properties, reaction intermediates and catalytic activity were investigated. Results indicated that calcination temperature had a significant influence on the crystallinity of iron oxide nanorods and adsorption intermediates, which resulted in differences in the catalytic activity of C2H6-SCR. The sample calcined at 500 °C showed the highest activity and more than 90% of NO reduction was demonstrated in the presence of oxygen at 600 °C. In situ DRIFT studies showed that the larger size of Fe2O3 nanorods due to higher calcination temperature promoted the formation of NO2/NO3â species, but inhibited the formation of acetate/formate species during NO reduction with C2H6.
51
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 326, 15 October 2017, Pages 737-744