| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466085 | 1422953 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- Mesoporous black Ti3+/N-TiO2 spheres are fabricated.
- The narrowed bandgap of 2.11Â eV extends the photoresponse to near-infrared region.
- It possesses high surface area of 100Â m2Â gâ1 and large pore size of 6.5Â nm.
- It exhibits excellent visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance.
- It ascribes to the synergy of N, Ti3+ codoping and mesoporous frameworks.
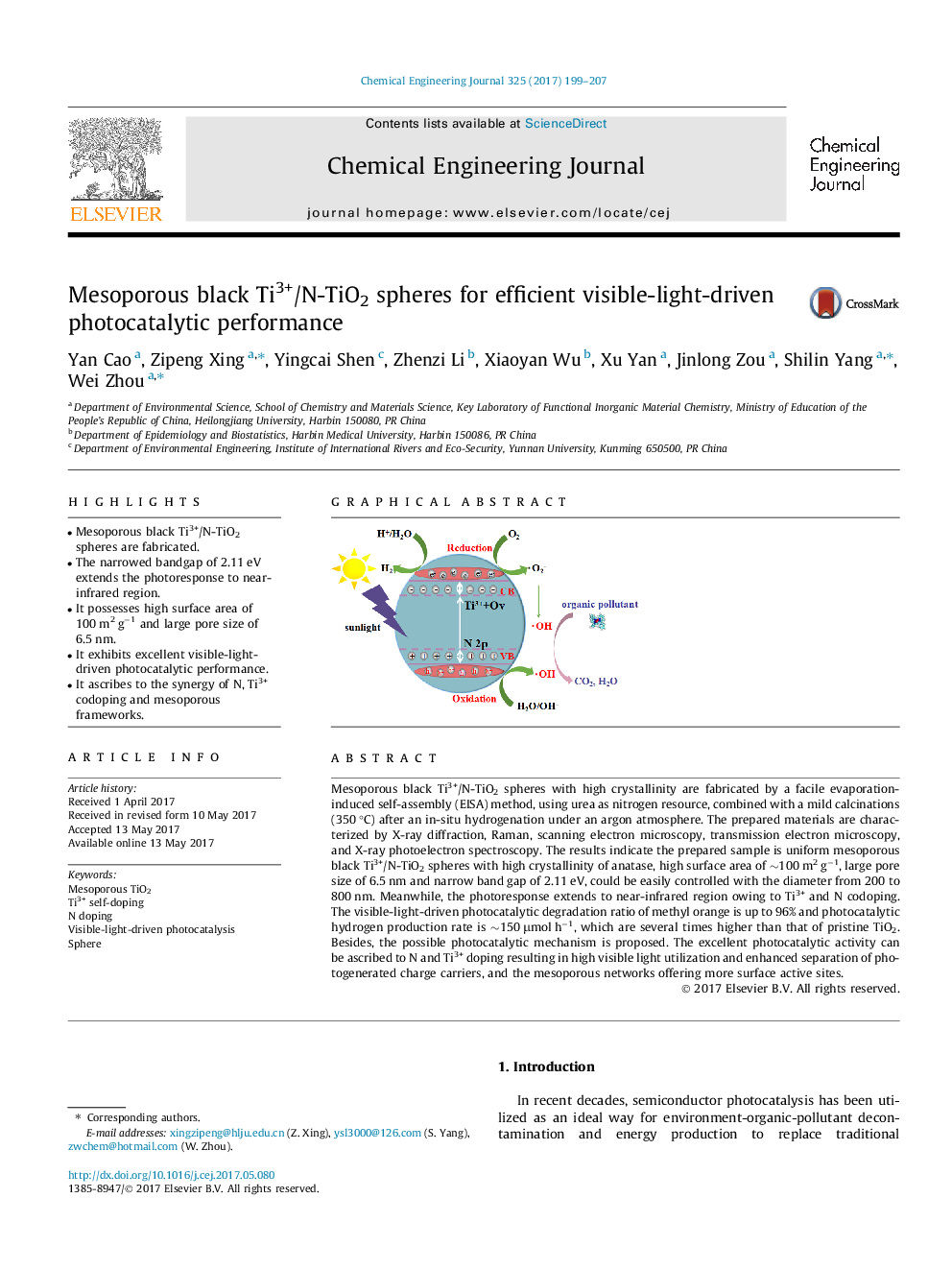
Mesoporous black Ti3+/N-TiO2 spheres with high crystallinity are fabricated by a facile evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) method, using urea as nitrogen resource, combined with a mild calcinations (350 °C) after an in-situ hydrogenation under an argon atmosphere. The prepared materials are characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results indicate the prepared sample is uniform mesoporous black Ti3+/N-TiO2 spheres with high crystallinity of anatase, high surface area of â¼100 m2 gâ1, large pore size of 6.5 nm and narrow band gap of 2.11 eV, could be easily controlled with the diameter from 200 to 800 nm. Meanwhile, the photoresponse extends to near-infrared region owing to Ti3+ and N codoping. The visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation ratio of methyl orange is up to 96% and photocatalytic hydrogen production rate is â¼150 μmol hâ1, which are several times higher than that of pristine TiO2. Besides, the possible photocatalytic mechanism is proposed. The excellent photocatalytic activity can be ascribed to N and Ti3+ doping resulting in high visible light utilization and enhanced separation of photogenerated charge carriers, and the mesoporous networks offering more surface active sites.
72
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 325, 1 October 2017, Pages 199-207