| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466619 | 1422965 | 2017 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- Combined use of peroxymonosulfate and KMnO4 (CUPP) showed powerful oxidizing ability.
- Colloidal/amorphous MnO2 from KMnO4 reduction can activate peroxymonosulfate.
- Amorphous MnO2-activated PMS showed adsorption-dependent oxidizing capability.
- Chloride, bicarbonate and phosphate showed different effects on the oxidizing ability.
- CUPP is simple but very applicable for in-situ remediation of contaminated groundwater.
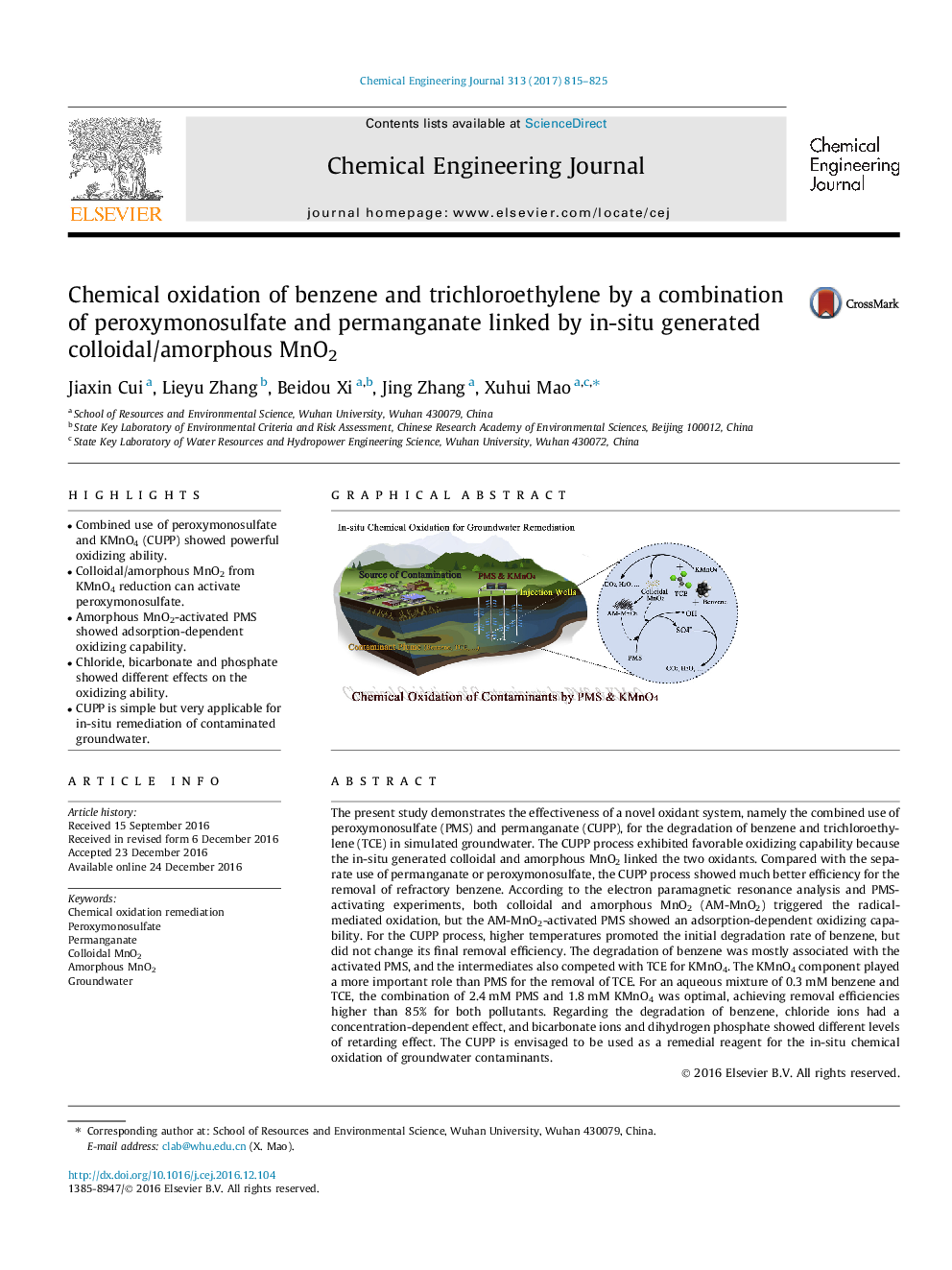
The present study demonstrates the effectiveness of a novel oxidant system, namely the combined use of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and permanganate (CUPP), for the degradation of benzene and trichloroethylene (TCE) in simulated groundwater. The CUPP process exhibited favorable oxidizing capability because the in-situ generated colloidal and amorphous MnO2 linked the two oxidants. Compared with the separate use of permanganate or peroxymonosulfate, the CUPP process showed much better efficiency for the removal of refractory benzene. According to the electron paramagnetic resonance analysis and PMS-activating experiments, both colloidal and amorphous MnO2 (AM-MnO2) triggered the radical-mediated oxidation, but the AM-MnO2-activated PMS showed an adsorption-dependent oxidizing capability. For the CUPP process, higher temperatures promoted the initial degradation rate of benzene, but did not change its final removal efficiency. The degradation of benzene was mostly associated with the activated PMS, and the intermediates also competed with TCE for KMnO4. The KMnO4 component played a more important role than PMS for the removal of TCE. For an aqueous mixture of 0.3Â mM benzene and TCE, the combination of 2.4Â mM PMS and 1.8Â mM KMnO4 was optimal, achieving removal efficiencies higher than 85% for both pollutants. Regarding the degradation of benzene, chloride ions had a concentration-dependent effect, and bicarbonate ions and dihydrogen phosphate showed different levels of retarding effect. The CUPP is envisaged to be used as a remedial reagent for the in-situ chemical oxidation of groundwater contaminants.
239
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 313, 1 April 2017, Pages 815-825