| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466700 | 1422965 | 2017 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
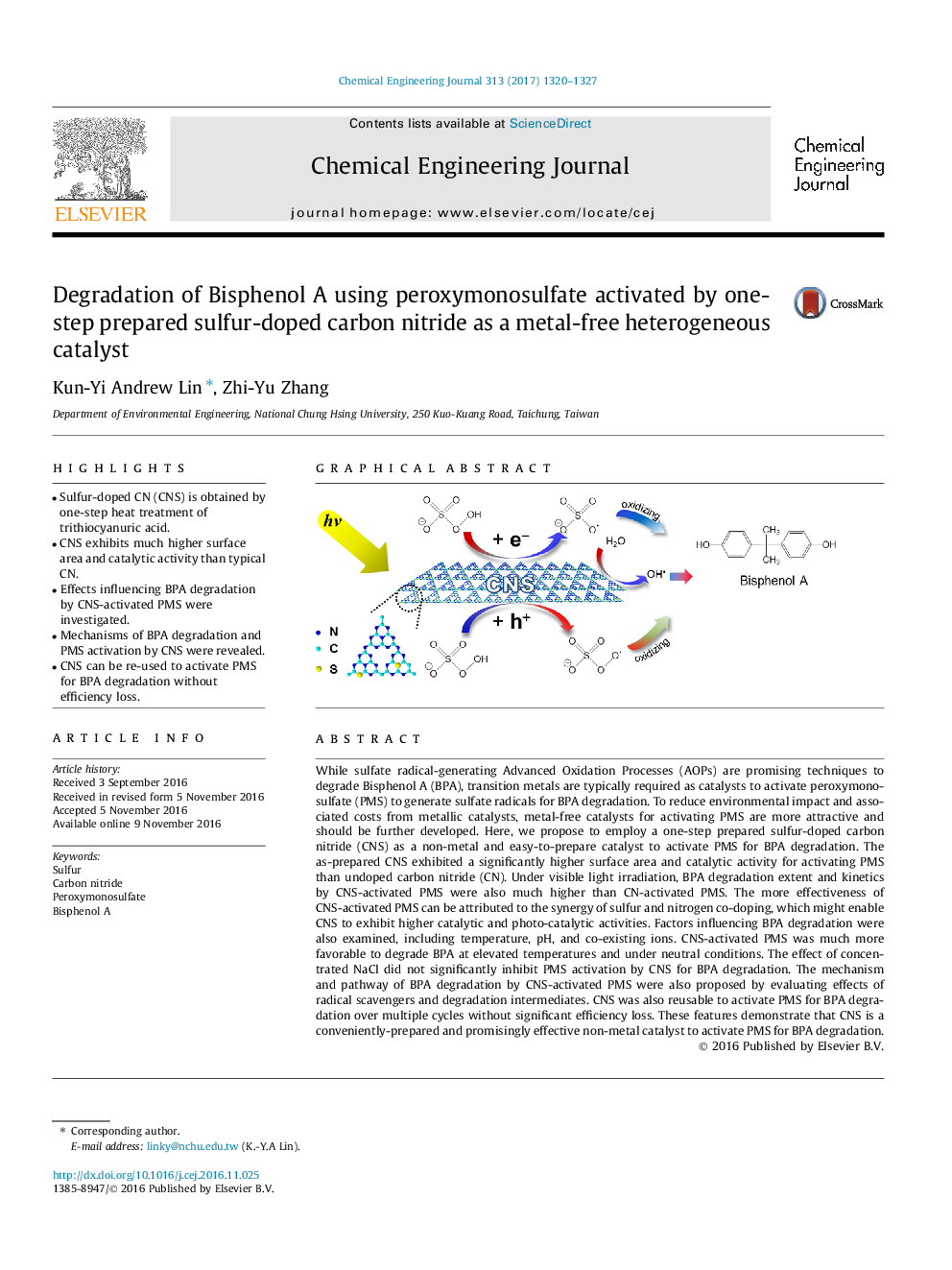
- Sulfur-doped CN (CNS) is obtained by one-step heat treatment of trithiocyanuric acid.
- CNS exhibits much higher surface area and catalytic activity than typical CN.
- Effects influencing BPA degradation by CNS-activated PMS were investigated.
- Mechanisms of BPA degradation and PMS activation by CNS were revealed.
- CNS can be re-used to activate PMS for BPA degradation without efficiency loss.
While sulfate radical-generating Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) are promising techniques to degrade Bisphenol A (BPA), transition metals are typically required as catalysts to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to generate sulfate radicals for BPA degradation. To reduce environmental impact and associated costs from metallic catalysts, metal-free catalysts for activating PMS are more attractive and should be further developed. Here, we propose to employ a one-step prepared sulfur-doped carbon nitride (CNS) as a non-metal and easy-to-prepare catalyst to activate PMS for BPA degradation. The as-prepared CNS exhibited a significantly higher surface area and catalytic activity for activating PMS than undoped carbon nitride (CN). Under visible light irradiation, BPA degradation extent and kinetics by CNS-activated PMS were also much higher than CN-activated PMS. The more effectiveness of CNS-activated PMS can be attributed to the synergy of sulfur and nitrogen co-doping, which might enable CNS to exhibit higher catalytic and photo-catalytic activities. Factors influencing BPA degradation were also examined, including temperature, pH, and co-existing ions. CNS-activated PMS was much more favorable to degrade BPA at elevated temperatures and under neutral conditions. The effect of concentrated NaCl did not significantly inhibit PMS activation by CNS for BPA degradation. The mechanism and pathway of BPA degradation by CNS-activated PMS were also proposed by evaluating effects of radical scavengers and degradation intermediates. CNS was also reusable to activate PMS for BPA degradation over multiple cycles without significant efficiency loss. These features demonstrate that CNS is a conveniently-prepared and promisingly effective non-metal catalyst to activate PMS for BPA degradation.
93
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 313, 1 April 2017, Pages 1320-1327