| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1162850 | 1490899 | 2016 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
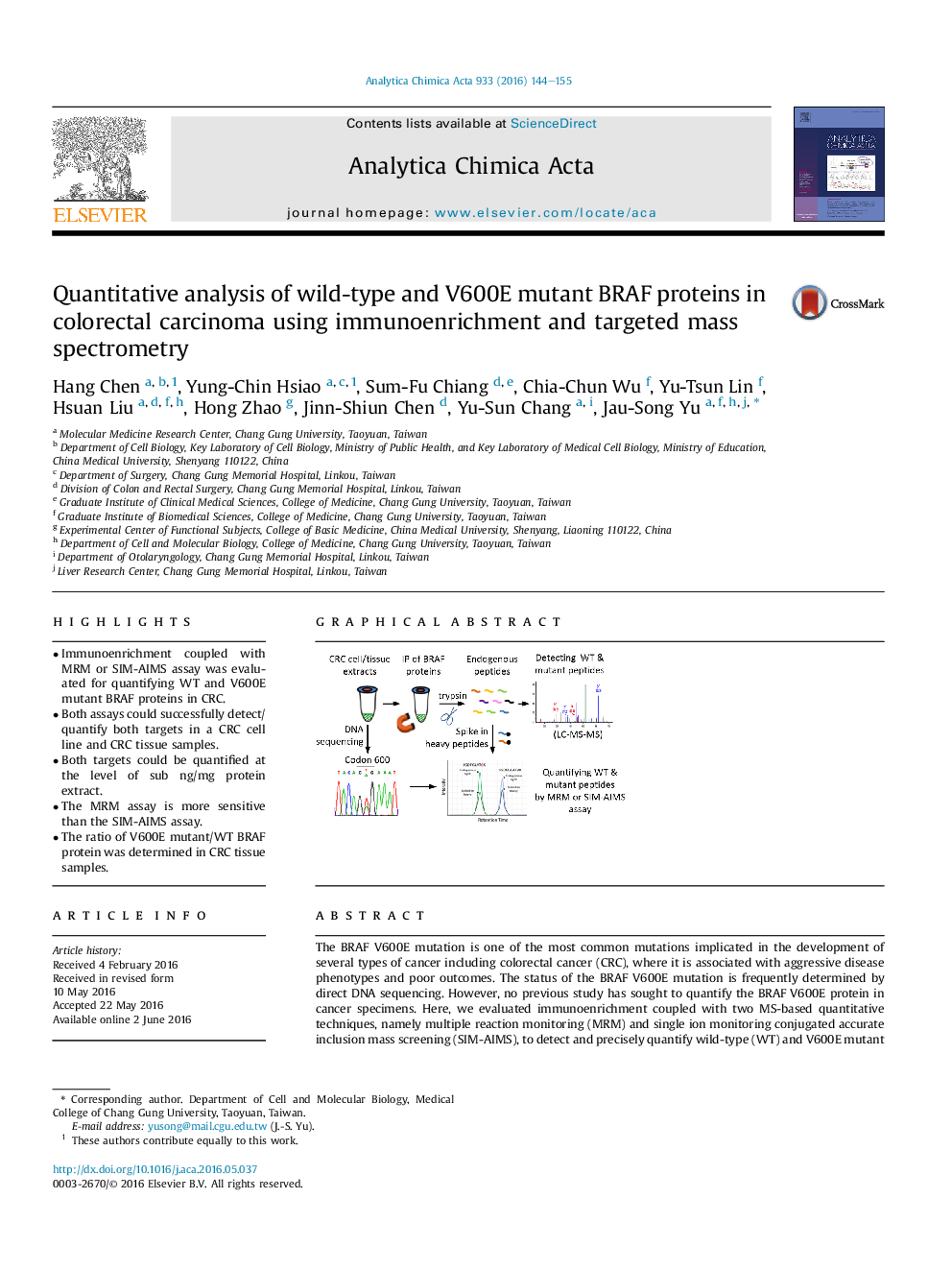
• Immunoenrichment coupled with MRM or SIM-AIMS assay was evaluated for quantifying WT and V600E mutant BRAF proteins in CRC.
• Both assays could successfully detect/quantify both targets in a CRC cell line and CRC tissue samples.
• Both targets could be quantified at the level of sub ng/mg protein extract.
• The MRM assay is more sensitive than the SIM-AIMS assay.
• The ratio of V600E mutant/WT BRAF protein was determined in CRC tissue samples.
The BRAF V600E mutation is one of the most common mutations implicated in the development of several types of cancer including colorectal cancer (CRC), where it is associated with aggressive disease phenotypes and poor outcomes. The status of the BRAF V600E mutation is frequently determined by direct DNA sequencing. However, no previous study has sought to quantify the BRAF V600E protein in cancer specimens. Here, we evaluated immunoenrichment coupled with two MS-based quantitative techniques, namely multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) and single ion monitoring conjugated accurate inclusion mass screening (SIM-AIMS), to detect and precisely quantify wild-type (WT) and V600E mutant BRAF proteins in DNA sequence-confirmed CRC tissue specimens. WT and V600E BRAF proteins were immunoprecipitated from a CRC cell line (HT-29), and their representative peptides (592IGDFGLATVK601 and 592IGDFGLATEK601, respectively) were confirmed by LC-MS/MS analysis and then quantified by MRM or SIM-AIMS with spiked stable isotope-labeled peptide standards. Both assays worked well for measuring WT BRAF from different amounts of HT-29 cell lysates, but the MRM assay was more sensitive than SIM-AIMS assay for quantifying lower levels of V600E BRAF. In protein extracts (2 mg) from 11 CRC tissue specimens, the MRM assay could measure WT BRAF in all 11 cases (0.32–1.66 ng) and the V600E BRAF in two cases (0.1–0.13 ng; mutant-to-WT ratio, 0.16–0.17). The SIM-AIMS assay could also detect WT and V600E BRAF in CRC specimens, but the measured levels of both targets were lower than those determined by MRM assay. Collectively, this study provides an effective method to precisely quantify WT and V600E BRAF proteins in complex biological samples using immunoenrichment-coupled targeted MS. Since the V600E BRAF protein has emerged as an important therapeutic target for cancer, the developed assay should facilitate future BRAF-related basic and clinical studies.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 933, 24 August 2016, Pages 144–155