| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163094 | 1490923 | 2016 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
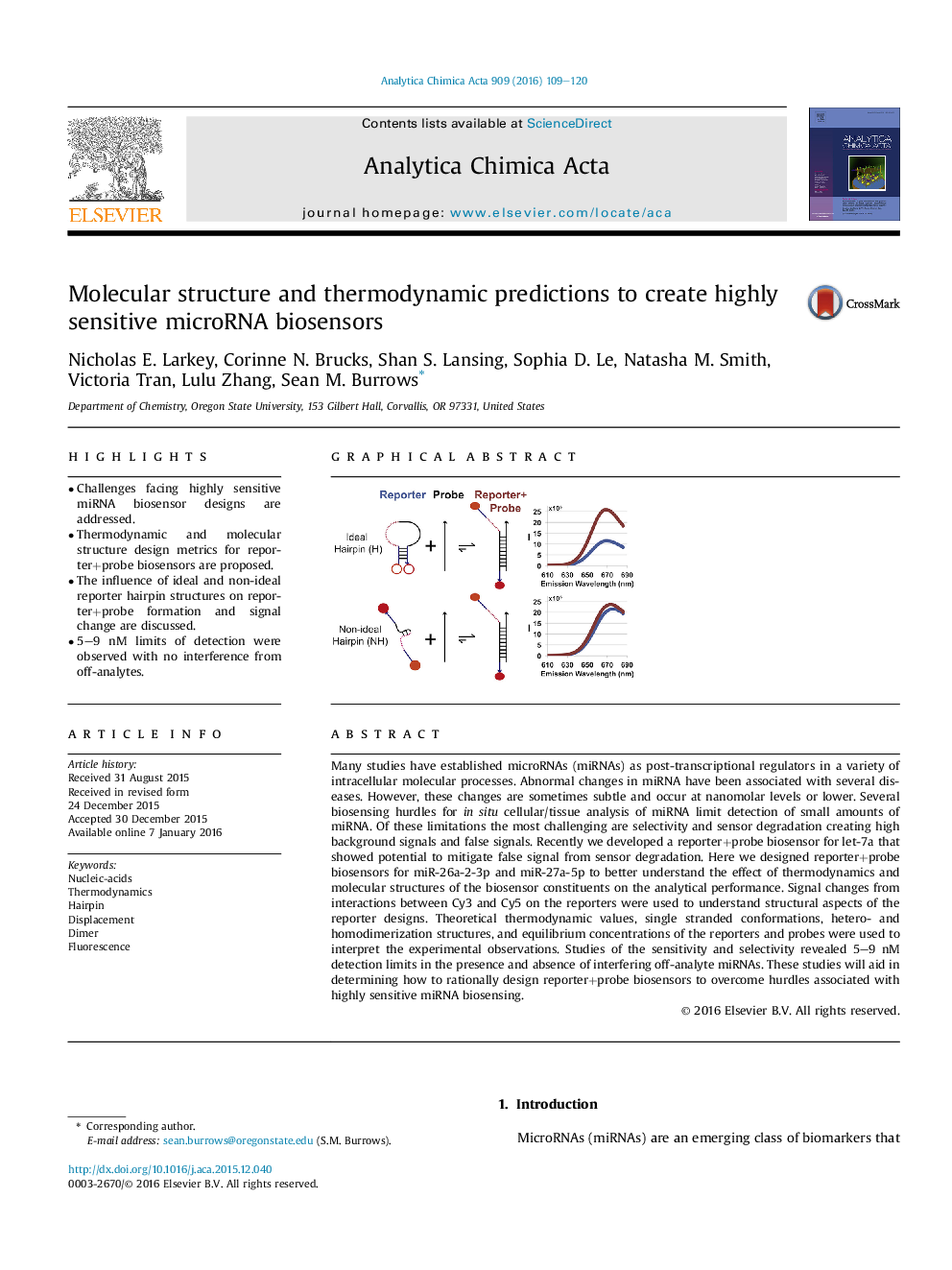
• Challenges facing highly sensitive miRNA biosensor designs are addressed.
• Thermodynamic and molecular structure design metrics for reporter+probe biosensors are proposed.
• The influence of ideal and non-ideal reporter hairpin structures on reporter+probe formation and signal change are discussed.
• 5–9 nM limits of detection were observed with no interference from off-analytes.
Many studies have established microRNAs (miRNAs) as post-transcriptional regulators in a variety of intracellular molecular processes. Abnormal changes in miRNA have been associated with several diseases. However, these changes are sometimes subtle and occur at nanomolar levels or lower. Several biosensing hurdles for in situ cellular/tissue analysis of miRNA limit detection of small amounts of miRNA. Of these limitations the most challenging are selectivity and sensor degradation creating high background signals and false signals. Recently we developed a reporter+probe biosensor for let-7a that showed potential to mitigate false signal from sensor degradation. Here we designed reporter+probe biosensors for miR-26a-2-3p and miR-27a-5p to better understand the effect of thermodynamics and molecular structures of the biosensor constituents on the analytical performance. Signal changes from interactions between Cy3 and Cy5 on the reporters were used to understand structural aspects of the reporter designs. Theoretical thermodynamic values, single stranded conformations, hetero- and homodimerization structures, and equilibrium concentrations of the reporters and probes were used to interpret the experimental observations. Studies of the sensitivity and selectivity revealed 5–9 nM detection limits in the presence and absence of interfering off-analyte miRNAs. These studies will aid in determining how to rationally design reporter+probe biosensors to overcome hurdles associated with highly sensitive miRNA biosensing.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 909, 25 February 2016, Pages 109–120