| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165526 | 1491069 | 2013 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
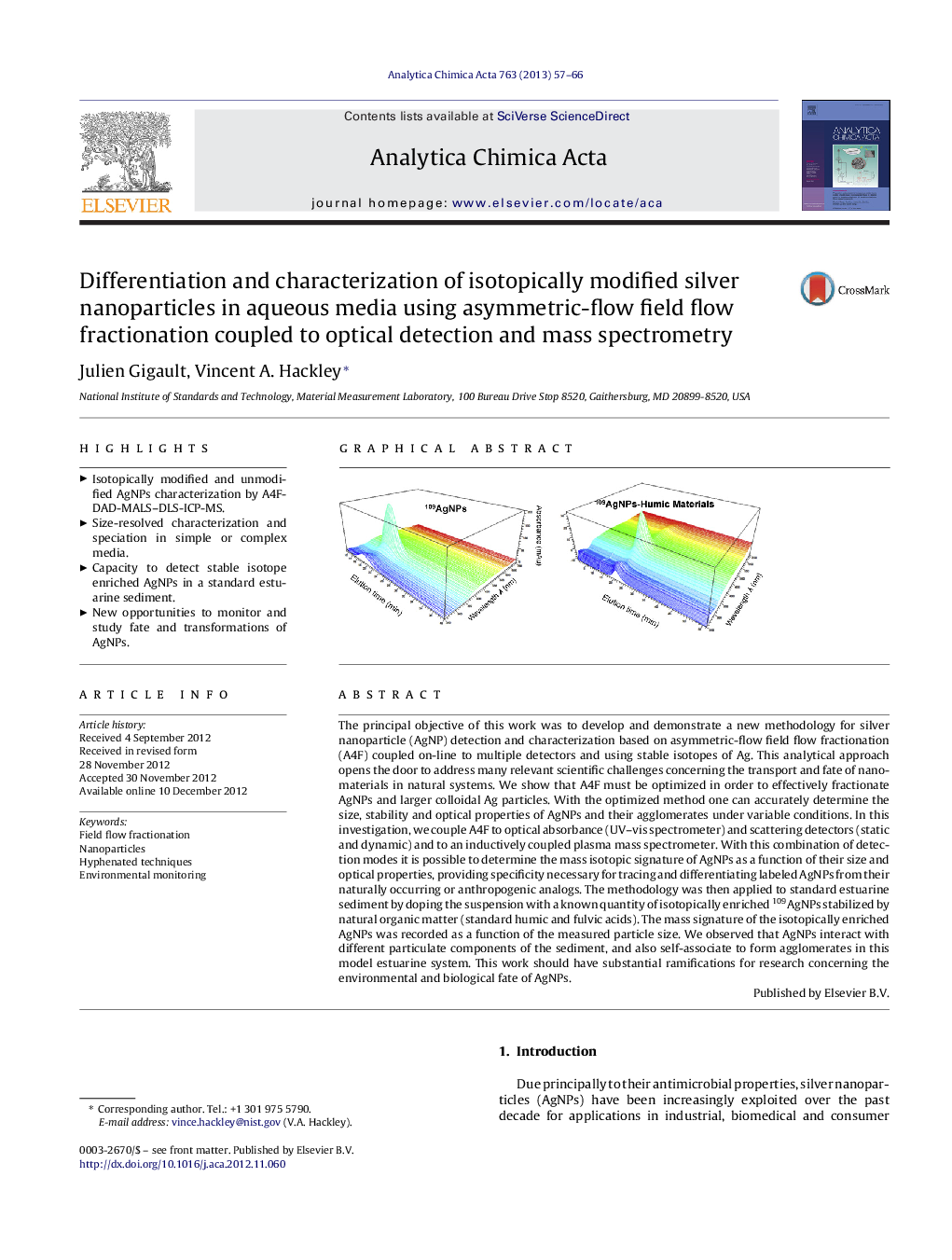
The principal objective of this work was to develop and demonstrate a new methodology for silver nanoparticle (AgNP) detection and characterization based on asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation (A4F) coupled on-line to multiple detectors and using stable isotopes of Ag. This analytical approach opens the door to address many relevant scientific challenges concerning the transport and fate of nanomaterials in natural systems. We show that A4F must be optimized in order to effectively fractionate AgNPs and larger colloidal Ag particles. With the optimized method one can accurately determine the size, stability and optical properties of AgNPs and their agglomerates under variable conditions. In this investigation, we couple A4F to optical absorbance (UV–vis spectrometer) and scattering detectors (static and dynamic) and to an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. With this combination of detection modes it is possible to determine the mass isotopic signature of AgNPs as a function of their size and optical properties, providing specificity necessary for tracing and differentiating labeled AgNPs from their naturally occurring or anthropogenic analogs. The methodology was then applied to standard estuarine sediment by doping the suspension with a known quantity of isotopically enriched 109AgNPs stabilized by natural organic matter (standard humic and fulvic acids). The mass signature of the isotopically enriched AgNPs was recorded as a function of the measured particle size. We observed that AgNPs interact with different particulate components of the sediment, and also self-associate to form agglomerates in this model estuarine system. This work should have substantial ramifications for research concerning the environmental and biological fate of AgNPs.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Isotopically modified and unmodified AgNPs characterization by A4F-DAD-MALS–DLS-ICP-MS.
► Size-resolved characterization and speciation in simple or complex media.
► Capacity to detect stable isotope enriched AgNPs in a standard estuarine sediment.
► New opportunities to monitor and study fate and transformations of AgNPs.
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 763, 6 February 2013, Pages 57–66