| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165785 | 1491054 | 2013 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Performance of calibration techniques using ‘a priori’ information is evaluated.
• Calibration models are built using NAP, IDC, SBC, ACLS and PLSR.
• Robustness of models is evaluated in presence of changing interferent structure.
• Among all techniques, ACLS is found to result in robust model with lowest RMSEP
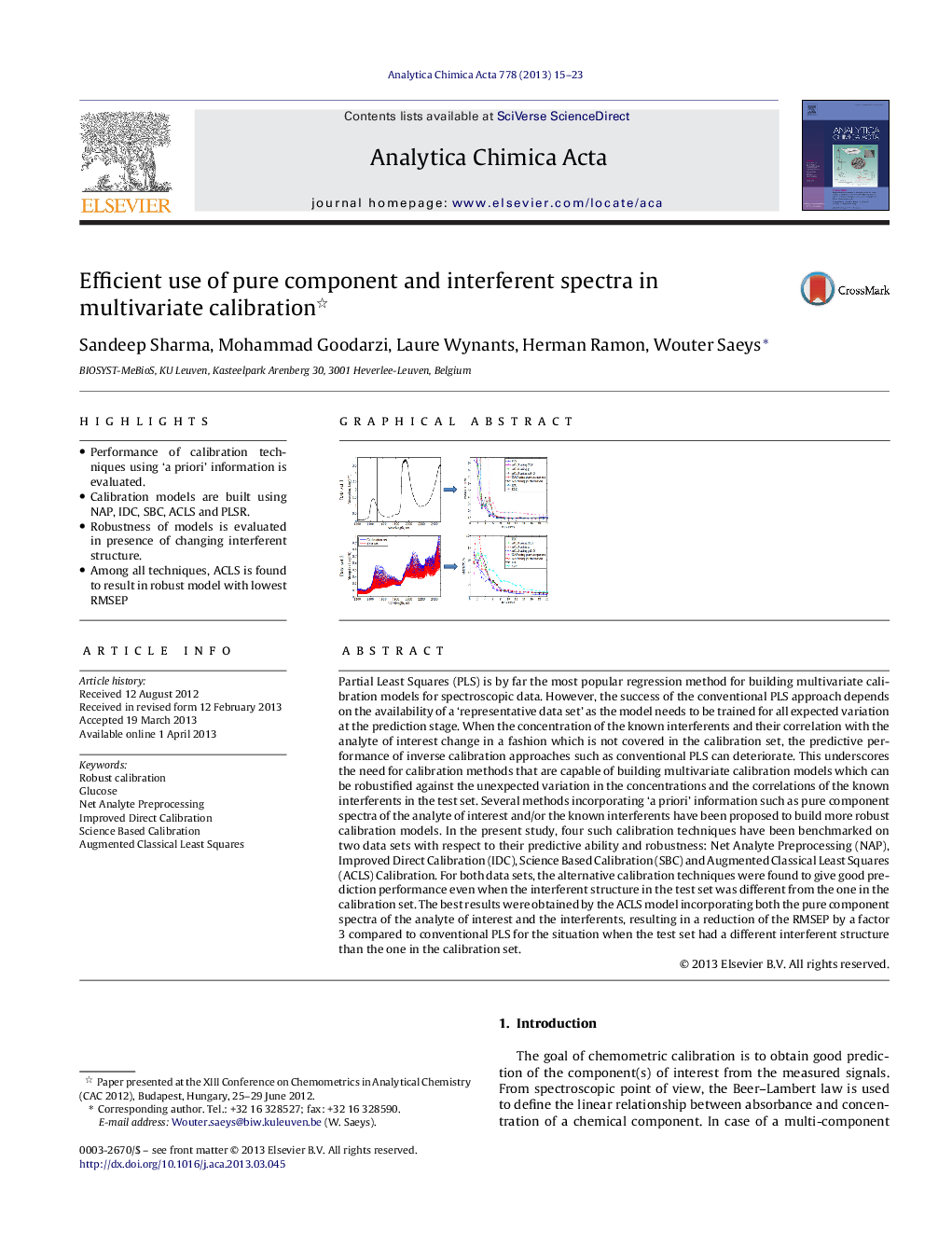
Partial Least Squares (PLS) is by far the most popular regression method for building multivariate calibration models for spectroscopic data. However, the success of the conventional PLS approach depends on the availability of a ‘representative data set’ as the model needs to be trained for all expected variation at the prediction stage. When the concentration of the known interferents and their correlation with the analyte of interest change in a fashion which is not covered in the calibration set, the predictive performance of inverse calibration approaches such as conventional PLS can deteriorate. This underscores the need for calibration methods that are capable of building multivariate calibration models which can be robustified against the unexpected variation in the concentrations and the correlations of the known interferents in the test set. Several methods incorporating ‘a priori’ information such as pure component spectra of the analyte of interest and/or the known interferents have been proposed to build more robust calibration models. In the present study, four such calibration techniques have been benchmarked on two data sets with respect to their predictive ability and robustness: Net Analyte Preprocessing (NAP), Improved Direct Calibration (IDC), Science Based Calibration (SBC) and Augmented Classical Least Squares (ACLS) Calibration. For both data sets, the alternative calibration techniques were found to give good prediction performance even when the interferent structure in the test set was different from the one in the calibration set. The best results were obtained by the ACLS model incorporating both the pure component spectra of the analyte of interest and the interferents, resulting in a reduction of the RMSEP by a factor 3 compared to conventional PLS for the situation when the test set had a different interferent structure than the one in the calibration set.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 778, 17 May 2013, Pages 15–23